(a) If z = -1+i then determine | z| = r and Arg( z) = 0 and write z in polar form: z = r(cos 0 + i sin 0). (b) Apply De Moivre's Theorem to express z® = (-1 + i )³ in the form a + b i . (c) Find all cube roots of z = -1+i in polar form and then plot them in the complex plane.
(a) If z = -1+i then determine | z| = r and Arg( z) = 0 and write z in polar form: z = r(cos 0 + i sin 0). (b) Apply De Moivre's Theorem to express z® = (-1 + i )³ in the form a + b i . (c) Find all cube roots of z = -1+i in polar form and then plot them in the complex plane.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section11.5: Polar Coordinates
Problem 85E
Related questions
Question
This problem is related to De Moivre's Theorem
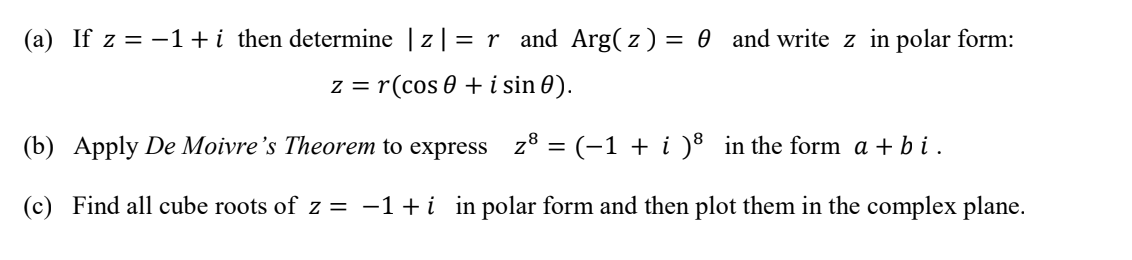
Transcribed Image Text:(a) If z = -1+i then determine | z| = r and Arg( z) = 0 and write z in polar form:
z = r(cos 0 + i sin 0).
(b) Apply De Moivre's Theorem to express z8 = (-1 + i )8 in the form a + b i.
(c) Find all cube roots of z = -1+i in polar form and then plot them in the complex plane.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage