A large corporation classifies its many divisions by their performance in the preceding year. Let P = {divisions that made a profit), L= {divisions that had an increase in labor costs), and T= {divisions whose total revenue increased). Describe the set using set-theoretic notation. {divisions with no increase in labor costs and divisions with no increase in total revenue) Choose the correct answer below. O L'nT' O LUT O L'UT'
A large corporation classifies its many divisions by their performance in the preceding year. Let P = {divisions that made a profit), L= {divisions that had an increase in labor costs), and T= {divisions whose total revenue increased). Describe the set using set-theoretic notation. {divisions with no increase in labor costs and divisions with no increase in total revenue) Choose the correct answer below. O L'nT' O LUT O L'UT'
Chapter9: Sequences, Probability And Counting Theory
Section9.5: Counting Principles
Problem 38SE: Suppose a set A has 2,048 subsets. How many distinct objects are contained in A?
Related questions
Question
100%
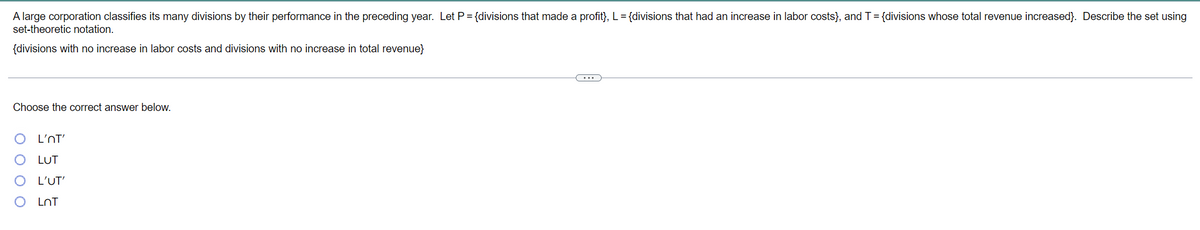
Transcribed Image Text:A large corporation classifies its many divisions by their performance in the preceding year. Let P= {divisions that made a profit}, L = {divisions that had an increase in labor costs}, and T= {divisions whose total revenue increased}. Describe the set using
set-theoretic notation.
{divisions with no increase in labor costs and divisions with no increase in total revenue}
Choose the correct answer below.
L'NT'
LUT
L'UT'
LnT
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you


Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning