a) Let y = 1*. Then 1x=0.5= dy dx dy |x=0.5 g'(0.5) = dx b) Let g(x) be the linear function so that the straight line y-g (x) passes through the points (0,1) and (1,1). Then approximating the derivative in Part a) with g'(0.5) yields 2 4 ) The absolute error in the approximation in Part b) is
a) Let y = 1*. Then 1x=0.5= dy dx dy |x=0.5 g'(0.5) = dx b) Let g(x) be the linear function so that the straight line y-g (x) passes through the points (0,1) and (1,1). Then approximating the derivative in Part a) with g'(0.5) yields 2 4 ) The absolute error in the approximation in Part b) is
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.6: The Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 93E
Related questions
Question
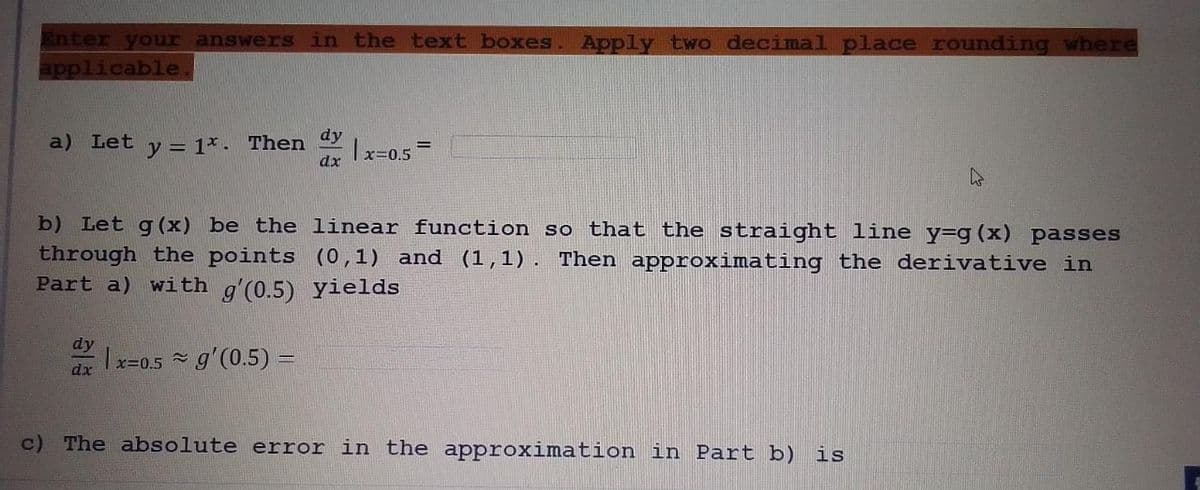
Transcribed Image Text:Enter your answers in the text boxes. Apply two decimal place rounding where
applicable.
a) Let
y = 1*. Then
dy
dx
x=0.5 g'(0.5) =
dy
dx
2
|x=0.5
b) Let g(x) be the linear function so that the straight line y=g (x) passes
through the points (0,1) and (1,1). Then approximating the derivative in
Part a) with g'(0.5) yields
=
c) The absolute error in the approximation in Part b)
4
is
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning