A load of lumber of weight W is raised as shown by a mobile crane. At this instant, the wheel at His locked and the wheel at K is free to rotate. The external load W is attached via a hook to a cable that is supported by frictionless pulleys A and E, attached to boom ABC, and the cable is secured to a motorized winch under the hood. Boom ABC is supported by both boom BF and rod CD via hinge joints at B and C, respectively. The piston rod CD is also hinged at D and is used to change the angle of boom ABC by pivoting the boom about hinge B; at this instant, AB is horizontal and CD is vertical, as shown. The weight of the boom ABC and the weight of the vehicle body are 3kN (acting at 2.0 m from A, as shown) and 50kN (acting 2.0 m from H, as shown), respectively. All dimensions are in meters. 0.6 m 0.4 m -2.0 m- 0.3 m C A B FD 3 kN W 50 kN H 2.0 m -2.0 m - 0.5 m im 0.9 m
A load of lumber of weight W is raised as shown by a mobile crane. At this instant, the wheel at His locked and the wheel at K is free to rotate. The external load W is attached via a hook to a cable that is supported by frictionless pulleys A and E, attached to boom ABC, and the cable is secured to a motorized winch under the hood. Boom ABC is supported by both boom BF and rod CD via hinge joints at B and C, respectively. The piston rod CD is also hinged at D and is used to change the angle of boom ABC by pivoting the boom about hinge B; at this instant, AB is horizontal and CD is vertical, as shown. The weight of the boom ABC and the weight of the vehicle body are 3kN (acting at 2.0 m from A, as shown) and 50kN (acting 2.0 m from H, as shown), respectively. All dimensions are in meters. 0.6 m 0.4 m -2.0 m- 0.3 m C A B FD 3 kN W 50 kN H 2.0 m -2.0 m - 0.5 m im 0.9 m
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter4: Coplanar Equilibrium Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 4.117P: The device shown is an overload prevention mechanism. When the force acting on the smooth peg at D...
Related questions
Question
show all steps
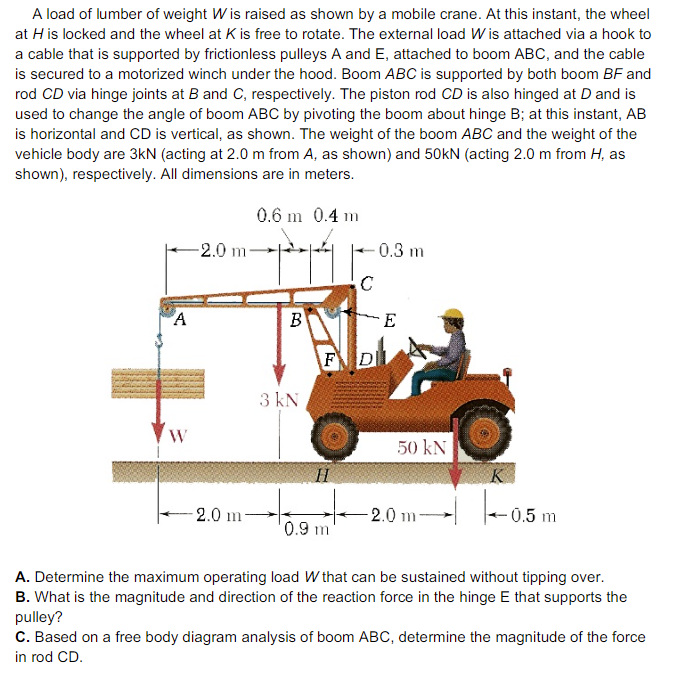
Transcribed Image Text:A load of lumber of weight W is raised as shown by a mobile crane. At this instant, the wheel
at H is locked and the wheel at K is free to rotate. The external load W is attached via a hook to
a cable that is supported by frictionless pulleys A and E, attached to boom ABC, and the cable
is secured to a motorized winch under the hood. Boom ABC is supported by both boom BFand
rod CD via hinge joints at B and C, respectively. The piston rod CD is also hinged at D and is
used to change the angle of boom ABC by pivoting the boom about hinge B; at this instant, AB
is horizontal and CD is vertical, as shown. The weight of the boom ABC and the weight of the
vehicle body are 3kN (acting at 2.0 m from A, as shown) and 50kN (acting 2.0 m from H, as
shown), respectively. All dimensions are in meters.
0.6 m 0.4 m
-2.0 m-
0.3 m
A
B
E
FD
3 kN
W
50 kN
H
2.0 m
2.0 m
- 0.5 m
'0.9 m
A. Determine the maximum operating load W that can be sustained without tipping over.
B. What is the magnitude and direction of the reaction force in the hinge E that supports the
pulley?
C. Based on a free body diagram analysis of boom ABC, determine the magnitude of the force
in rod CD.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L