A seasoned parachutist went for a skydiving trip where he performed freefall before deploying the parachute. According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, there are two forces acting on the body of the parachutist, the forces of gravity (F,) and drag force due to air resistance (Fa) as shown in Figure 1. TIM UTM Fa= -cv IM FUT EM UTM LIM Fe= -mg UTM TTM x(t) LTM FUIM M TM UTM TIM UTM TUT GROUND Figure 1: Force acting on body of free-fall where x(t) is the position of the parachutist from the ground at given time, t is the time of fall calculated from the start of jump, m is the parachutist’s mass, g is the gravitational acceleration, v is the velocity of the fall and c is the drag coefficient. The equation for the velocity and the position is given by the equations below: UTMUT v(t) = (e-ct/m – 1) %3D ITM FUIM UTM (Eq. 1.1) x() =D x(0) - Dt-프(0) Where x(0) = 3200 m, m = 79.8 kg, g = 9.81m/s² and c = 6.6 kg/s. It was established that the critical position to deploy the parachutes is at 762 m from the ground to avoid any incident. %3D (Eq. 1.2) (a) Use false position method to determine time at the critical position. Use initial guess of t = 0 s and ty = 50 s. Only show the 1ª and 2nd iterations in full calculation and use 4 decimal places for all your answers. Complete five iterations and summarize your answers in Table 1.
A seasoned parachutist went for a skydiving trip where he performed freefall before deploying the parachute. According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, there are two forces acting on the body of the parachutist, the forces of gravity (F,) and drag force due to air resistance (Fa) as shown in Figure 1. TIM UTM Fa= -cv IM FUT EM UTM LIM Fe= -mg UTM TTM x(t) LTM FUIM M TM UTM TIM UTM TUT GROUND Figure 1: Force acting on body of free-fall where x(t) is the position of the parachutist from the ground at given time, t is the time of fall calculated from the start of jump, m is the parachutist’s mass, g is the gravitational acceleration, v is the velocity of the fall and c is the drag coefficient. The equation for the velocity and the position is given by the equations below: UTMUT v(t) = (e-ct/m – 1) %3D ITM FUIM UTM (Eq. 1.1) x() =D x(0) - Dt-프(0) Where x(0) = 3200 m, m = 79.8 kg, g = 9.81m/s² and c = 6.6 kg/s. It was established that the critical position to deploy the parachutes is at 762 m from the ground to avoid any incident. %3D (Eq. 1.2) (a) Use false position method to determine time at the critical position. Use initial guess of t = 0 s and ty = 50 s. Only show the 1ª and 2nd iterations in full calculation and use 4 decimal places for all your answers. Complete five iterations and summarize your answers in Table 1.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter1: Vectors
Section1.4: Applications
Problem 8EQ
Related questions
Question
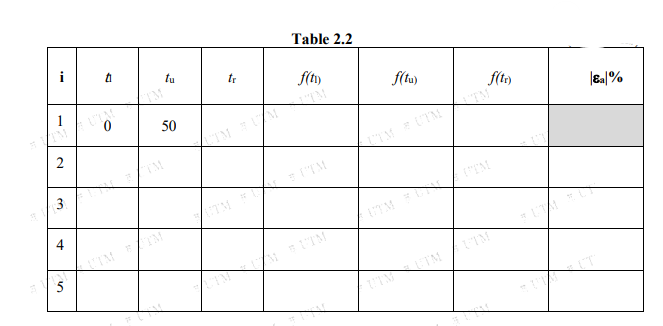
Transcribed Image Text:Table 2.2
i
tu
tr
f(t)
f(tu)
f(ta)
50
2
3.
ITM
UTM
TM
5
UIM TM / I
4.
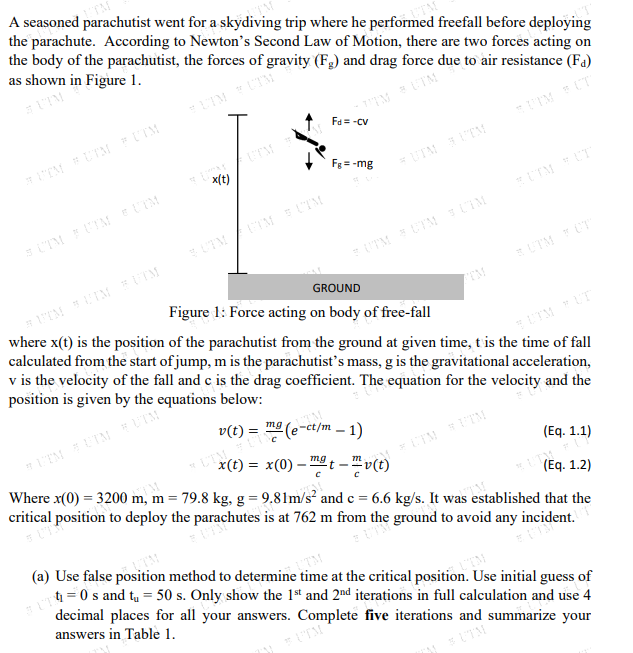
Transcribed Image Text:A seasoned parachutist went for a skydiving trip where he performed freefall before deploying
the parachute. According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, there are two forcës acting on
the body of the parachutist, the forces of gravity (F,) and drag force due to air resistance (Fa)
as shown in Figure 1.
Fa = -cv
ITM EUTM FUTM
* UTM TM
Fg= -mg
x(t)
UTM UT
UTM /IM LTM
UTM UTM TUIM
UTM F UT
GROUND
Figure 1: Force acting on body of free-fall
where x(t) is the position of the parachutist from the ground at given time, t is the time of fall
calculated from the start of jump, m is the parachutist's mass, g is the gravitational acceleration,
v is the velocity of the fall and c is the drag coefficient. The equation for the velocity and the
position is given by the equations below:
EUTM PUT
v(t) =
mg
-et/m – 1)
(Eq. 1.1)
x(t) = x(0) –
Where x(0) = 3200 m, m = 79.8 kg, g = 9.81m/s² and c = 6.6 kg/s. It was established that the
critical position to deploy the parachutes is at 762 m from the ground to avoid any incident.
?t -v(t)
mg
(Eq. 1.2)
(a) Use false position method to determine time at the critical position. Use initial guess of
t1 = 0 s and tųu = 50 s. Only show the 1st and 2md iterations in full calculation and use 4
decimal places for all your answers. Complete five iterations and summarize your
answers in Table 1.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning