A smooth curve is normal to a surface f(x,y,z) = c at a point of intersection if the curve's velocity vector is a nonzero scalar multiple of Vf at the point. Show that the 7 curve r(t) = /ti+ vtj-7(t+3)k is normal to the surface x + y - 7z = 51 when t= 1.
A smooth curve is normal to a surface f(x,y,z) = c at a point of intersection if the curve's velocity vector is a nonzero scalar multiple of Vf at the point. Show that the 7 curve r(t) = /ti+ vtj-7(t+3)k is normal to the surface x + y - 7z = 51 when t= 1.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18T
Related questions
Question
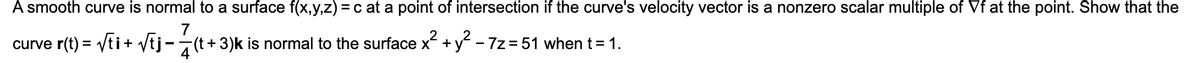
Transcribed Image Text:A smooth curve is normal to a surface f(x,y,z) = c at a point of intersection if the curve's velocity vector is a nonzero scalar multiple of Vf at the point. Show that the
curve r(t) = Vti+ Vtj-
7
7(t + 3)k is normal to the surface x +y - 7z = 51 when t= 1.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given:
To Find:
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage