A wind turbine with a 30-m rotor diameter is mounted with its hub at 50 m above a ground surface that is characterized by shrubs and hedges illustrated in Figure 2. Estimate the ratio of specific power in the wind at the lowest point that a rotor blade tip reaches to the highest point it rises to. Pes 65 m 50 m P35 35 m Crops, hedges, shrubs Figure 2 Wind turbine Table 2 Friction coefficient for various terrain characteristics Friction Coefficient Terrain Characteristics Smooth hard ground, calm water Tall grass on level ground High crops, hedges and shrubs Wooded countryside, many trees Small town with trees and shrubs 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.40 Large city with tall buildings
A wind turbine with a 30-m rotor diameter is mounted with its hub at 50 m above a ground surface that is characterized by shrubs and hedges illustrated in Figure 2. Estimate the ratio of specific power in the wind at the lowest point that a rotor blade tip reaches to the highest point it rises to. Pes 65 m 50 m P35 35 m Crops, hedges, shrubs Figure 2 Wind turbine Table 2 Friction coefficient for various terrain characteristics Friction Coefficient Terrain Characteristics Smooth hard ground, calm water Tall grass on level ground High crops, hedges and shrubs Wooded countryside, many trees Small town with trees and shrubs 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.40 Large city with tall buildings
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning with these NEW titles from Engineering!)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305387102
Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Chapter5: Analysis Of Convection Heat Transfer
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 5.32P
Related questions
Question
100%
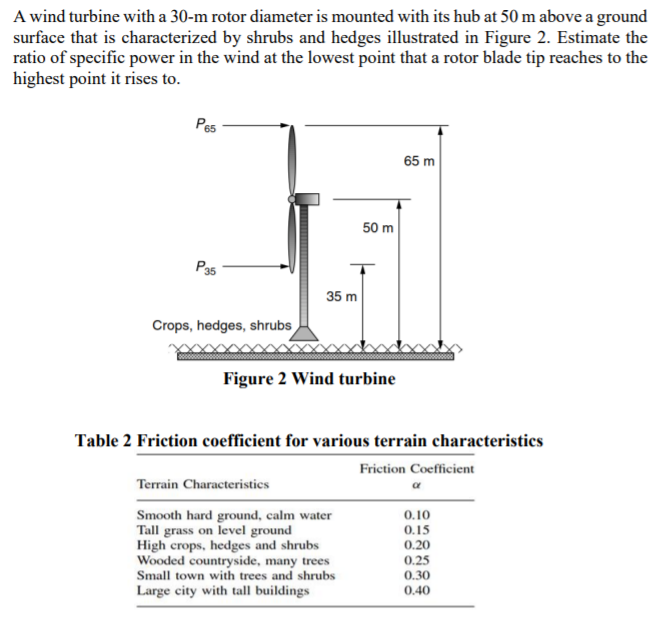
Transcribed Image Text:A wind turbine with a 30-m rotor diameter is mounted with its hub at 50 m above a ground
surface that is characterized by shrubs and hedges illustrated in Figure 2. Estimate the
ratio of specific power in the wind at the lowest point that a rotor blade tip reaches to the
highest point it rises to.
Pe5
65 m
50 m
35 m
Crops, hedges, shrubs
Figure 2 Wind turbine
Table 2 Friction coefficient for various terrain characteristics
Friction Coefficient
Terrain Characteristics
Smooth hard ground, calm water
Tall grass on level ground
High crops, hedges and shrubs
Wooded countryside, many trees
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
Small town with trees and shrubs
Large city with tall buildings
0.40
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305387102
Author:
Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning