(a) Y1, Y2, ..., Yn form a random sample from a probability distribution with cumu- lative distribution function Fy(y) and probability density function fy(y). Let Y(1) = min{Y1, Y2,..., Yn}. Write the cumulative distribution function for Y(1) in terms of Fy(y) and hence show that the probability density function for Y(1) is fy, (y) = n{1– Fy(y)}"-'fy(y).
(a) Y1, Y2, ..., Yn form a random sample from a probability distribution with cumu- lative distribution function Fy(y) and probability density function fy(y). Let Y(1) = min{Y1, Y2,..., Yn}. Write the cumulative distribution function for Y(1) in terms of Fy(y) and hence show that the probability density function for Y(1) is fy, (y) = n{1– Fy(y)}"-'fy(y).
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:Sheldon Ross
Chapter1: Combinatorial Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.1P: a. How many different 7-place license plates are possible if the first 2 places are for letters and...
Related questions
Question
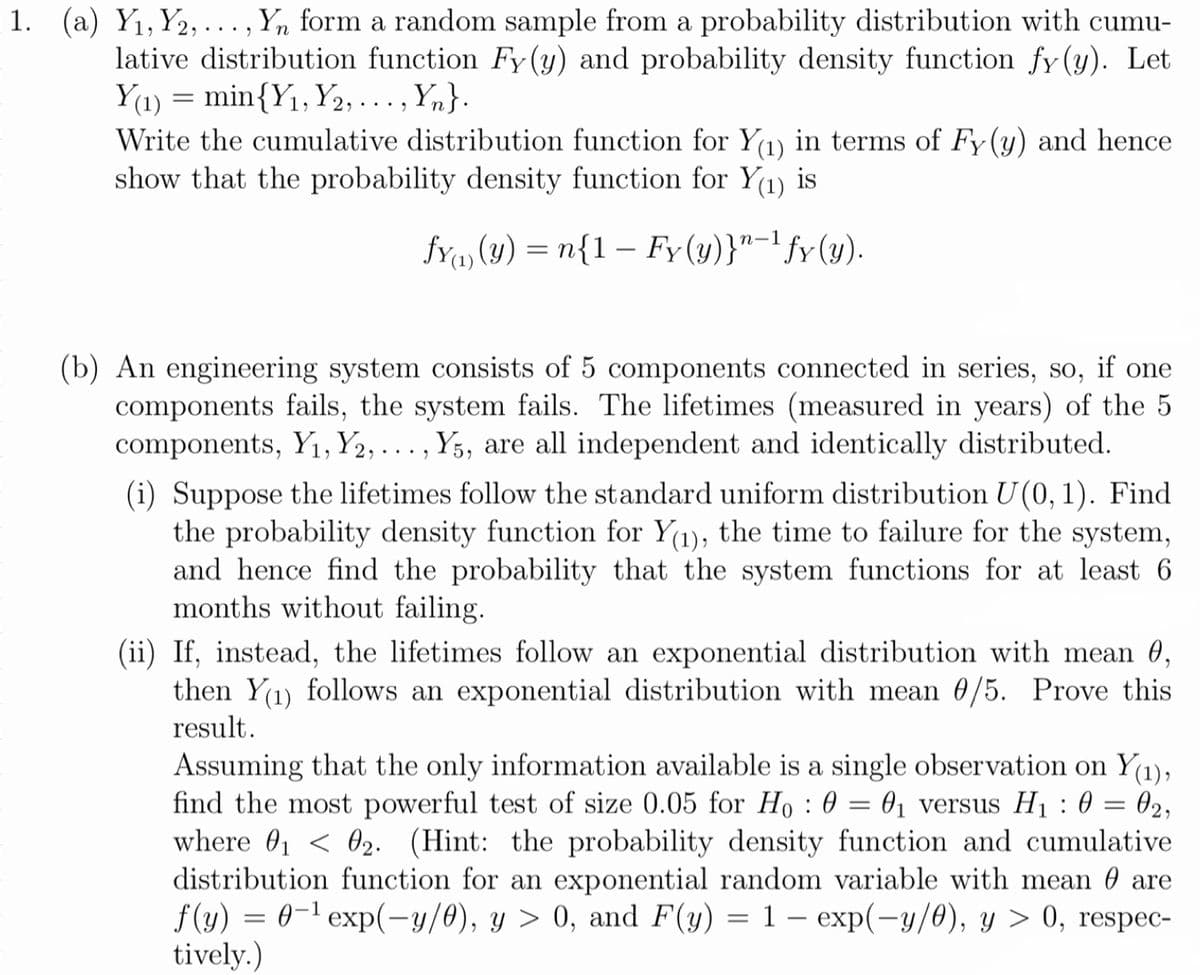
Transcribed Image Text:1. (a) Y1,Y2, ... , Yn form a random sample from a probability distribution with cumu-
lative distribution function Fy (y) and probability density function fy (y). Let
Y(1) = min{Y1, Y2,..., Yn}.
Write the cumulative distribution function for Y(1) in terms of Fy(y) and hence
show that the probability density function for Y(1) is
fY, (y) = n{1 – Fy(y)}"-' fy(y).
(b) An engineering system consists of 5 components connected in series, so, if one
components fails, the system fails. The lifetimes (measured in years) of the 5
components, Yı, Y2, . . . , Y5, are all independent and identically distributed.
(i) Suppose the lifetimes follow the standard uniform distribution U (0, 1). Find
the probability density function for Y(1), the time to failure for the system,
and hence find the probability that the system functions for at least 6
months without failing.
(ii) If, instead, the lifetimes follow an exponential distribution with mean 0,
then Y(1) follows an exponential distribution with mean 0/5. Prove this
result.
Assuming that the only information available is a single observation on Y(1),
find the most powerful test of size 0.05 for Ho : 0 = 01 versus H1 : 0
where 01 < 02. (Hint: the probability density function and cumulative
distribution function for an exponential random variable with mean 0 are
f (y) = 0-1 exp(-y/0), y > 0, and F(y) = 1 – exp(-y/0), y > 0, respec-
tively.)
02,
||
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, probability and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON


A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:
9780134753119
Author:
Sheldon Ross
Publisher:
PEARSON
