a. Find the most general real-valued solution of the linear system (*) -( æ(t) + c. y(t) b. Choose the best option below that describes the behavior of the solutions. Note that you should be able to do this based on your answer in Part a. without plotting a phase plane. The solutions diverge away from without spiral rotation (source / unstable node) The solutions converge towards u without spiral rotation (sink / stable node) The solutions race towards zero and then veer away towards infinity (saddle point) O The solutions are all circles or ellipses around a central point (center point / ellipses) The solutions spiral away from v (spiral source / unstable node) The solutions spiral towards (spiral sink / stable node)
a. Find the most general real-valued solution of the linear system (*) -( æ(t) + c. y(t) b. Choose the best option below that describes the behavior of the solutions. Note that you should be able to do this based on your answer in Part a. without plotting a phase plane. The solutions diverge away from without spiral rotation (source / unstable node) The solutions converge towards u without spiral rotation (sink / stable node) The solutions race towards zero and then veer away towards infinity (saddle point) O The solutions are all circles or ellipses around a central point (center point / ellipses) The solutions spiral away from v (spiral source / unstable node) The solutions spiral towards (spiral sink / stable node)
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.4: Applications
Problem 17EQ
Related questions
Question
solving systems of ODE
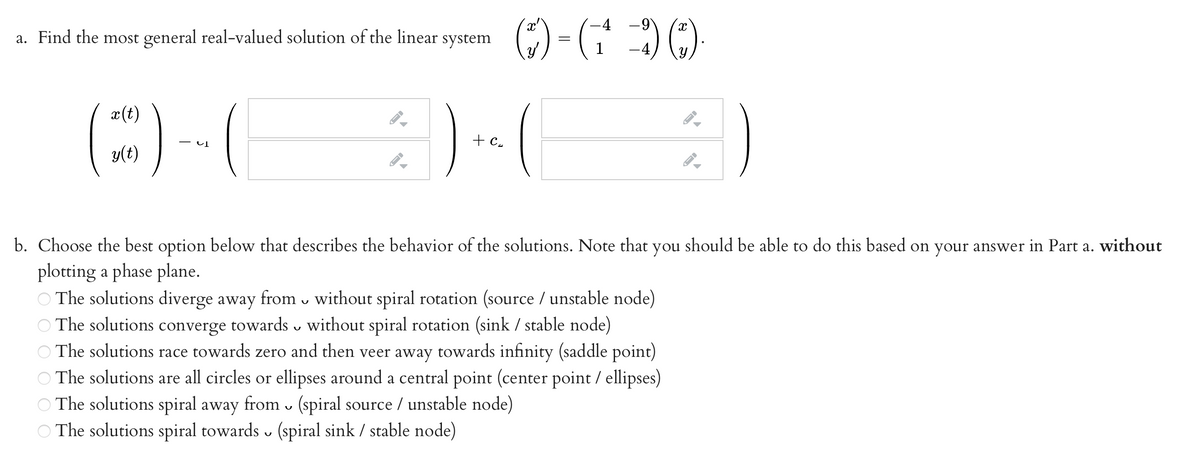
Transcribed Image Text:-4
a. Find the most general real-valued solution of the linear system
(E) -(
) . (
x(t)
+ c.
y(t)
b. Choose the best option below that describes the behavior of the solutions. Note that you should be able to do this based on your answer in Part a. without
plotting a phase plane.
The solutions diverge away from v without spiral rotation (source / unstable node)
The solutions converge towards v without spiral rotation (sink / stable node)
The solutions race towards zero and then veer away towards infinity (saddle point)
O The solutions are all circles or ellipses around a central point (center point / ellipses)
O The solutions spiral away from v (spiral source / unstable node)
The solutions spiral towards (spiral sink / stable node)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, advanced-math and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning