(a,b,c) • (d,e, f)= ad + be+cf Finding the magnitude of 3D vectors is also essentially the same as it is for 2D vectors: Ka.b.c) = Va² +b² +c? %3D Now find the angle 0 between your two vectors using this formula: V• W 0 = cos MML Show your work in the space below. Be sure to find 0 in radians, not in degrees: (a,b,c) x (d,e,f) (.05266, -.85998, .50760)x(.05272,-.85096, .50594)=(.05266 x .05272)+(-.85988 x -.85096)+(.50760 x .50594)
(a,b,c) • (d,e, f)= ad + be+cf Finding the magnitude of 3D vectors is also essentially the same as it is for 2D vectors: Ka.b.c) = Va² +b² +c? %3D Now find the angle 0 between your two vectors using this formula: V• W 0 = cos MML Show your work in the space below. Be sure to find 0 in radians, not in degrees: (a,b,c) x (d,e,f) (.05266, -.85998, .50760)x(.05272,-.85096, .50594)=(.05266 x .05272)+(-.85988 x -.85096)+(.50760 x .50594)
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
I need help with
the steps on page two
Transcribed Image Text:O WI
De
y! cal
Sy (.0 P Pre
y! ho 3 Fin
O Fin y In
ƏN O
1njrQguo0dB.d216dXSWQmALv25Y70AgqKsnCpycyyMOtNSlpHevoJw/27861604,220,0,0,4,3D6/Assets/676645-8122016-
n Connexus
%00L
| +
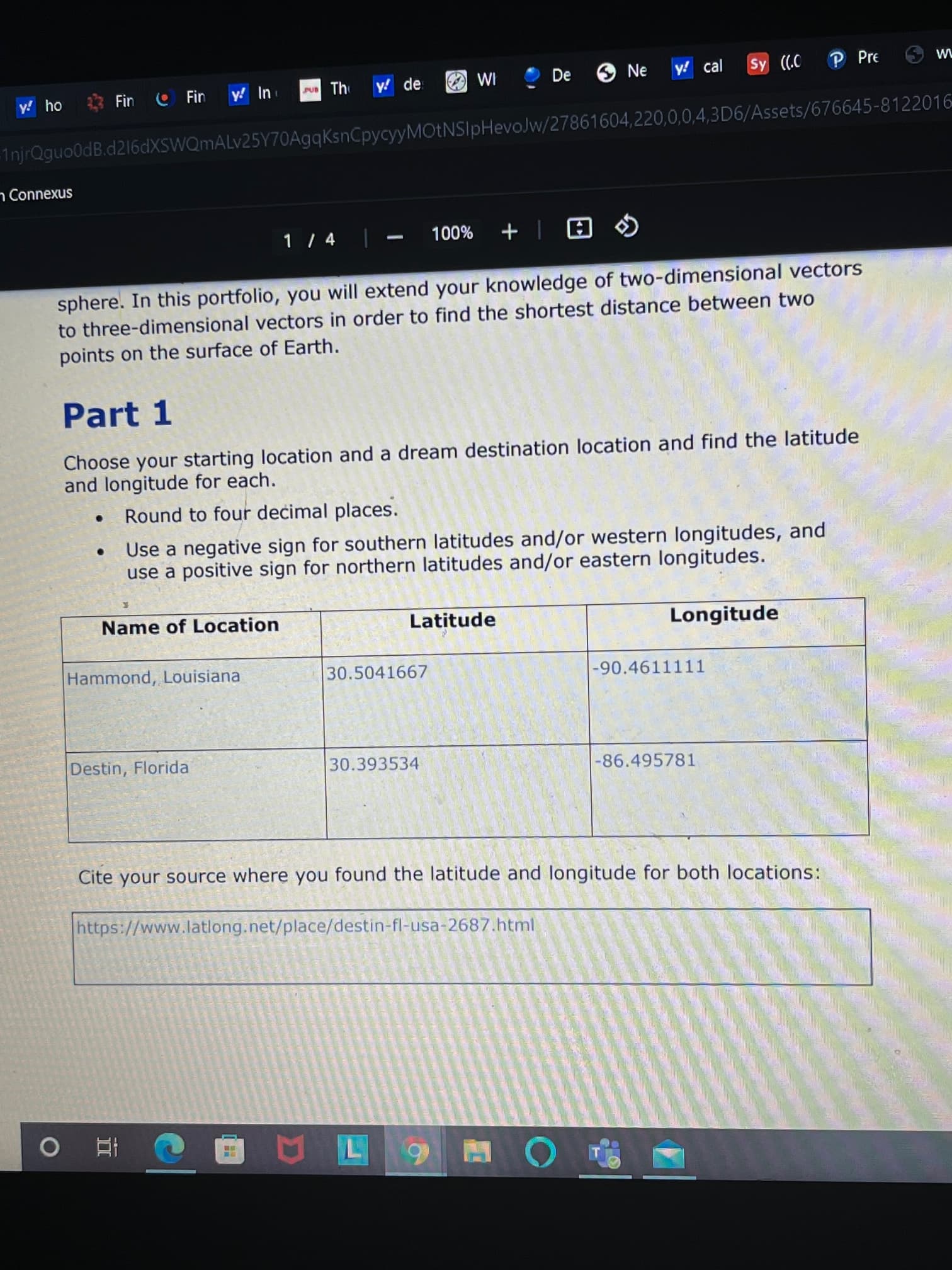
sphere. In this portfolio, you will extend your knowledge of two-dimensional vectors
to three-dimensional vectors in order to find the shortest distance between two
points on the surface of Earth.
Part 1
Choose your starting location and a dream destination location and find the latitude
and longitude for each.
Round to four decimal places.
Use a negative sign for southern latitudes and/or western longitudes, and
use a positive sign for northern latitudes and/or eastern longitudes.
Name of Location
Latitude
Longitude
Hammond, Louisiana
30.5041667
|-90.4611111
Destin, Florida
30.393534
-86.495781
Cite your source where you found the latitude and longitude for both locations:
https://www.latlong.net/place/destin-fl-usa-2687.html
立 。
Transcribed Image Text:y! 3d
Ne
P Pre
O') AS
y! cal
The
y! de
O WI
S Ho
2Fin
OFin
y! In
sz-04epbSinjiQguoOdB d216dXSWQmALv25Y70AggKsnCpycyyMOtNSlpHevoJw/27861604,220,0,0,4,3D6/Assets/676645-8122016-74626-AM-684044
P Pearson Connexus
3/4
%00L
日| +
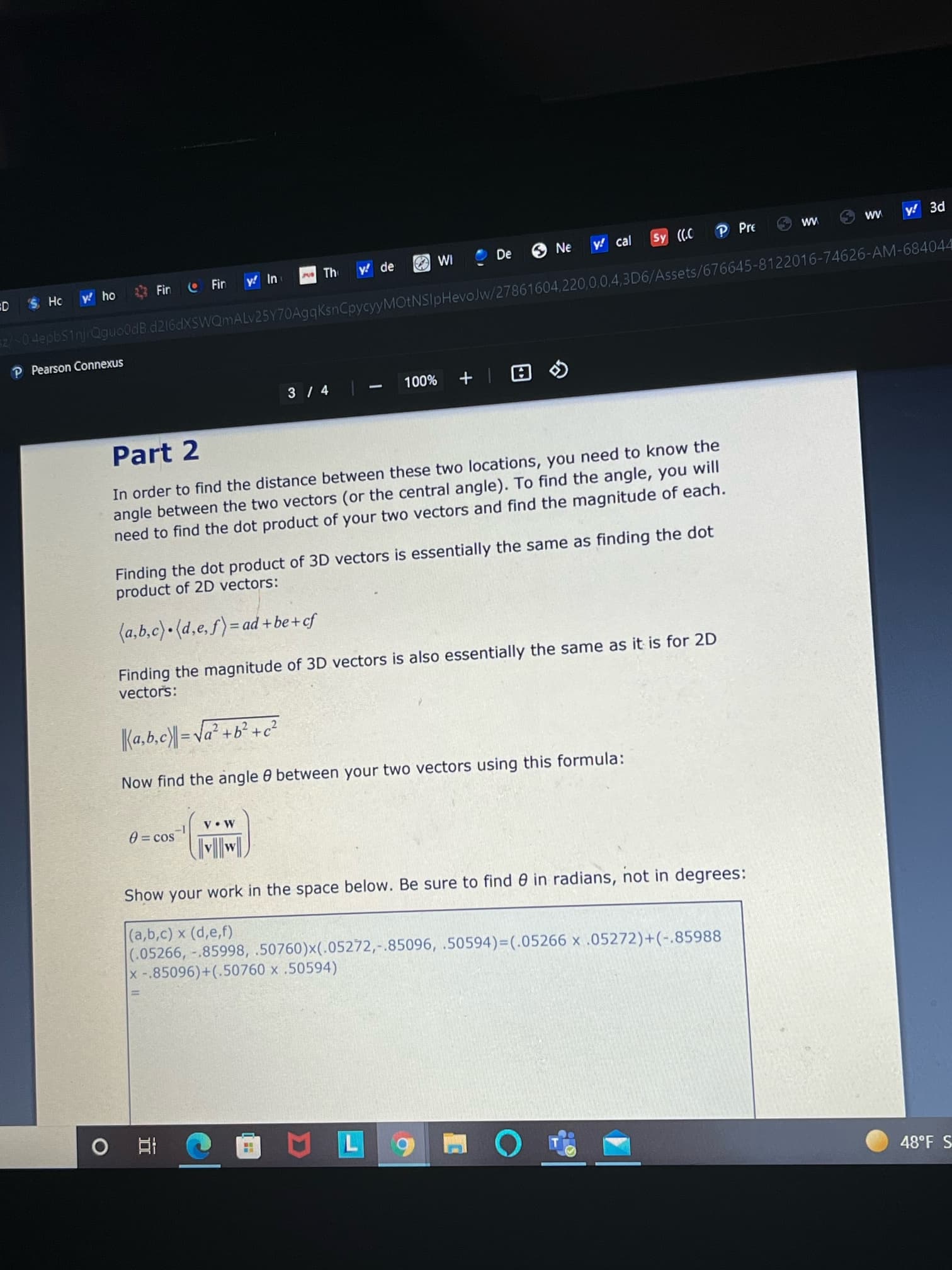
Part 2
In order to find the distance between these two locations, you need to know the
angle between the two vectors (or the central angle). To find the angle, you will
need to find the dot product of your two vectors and find the magnitude of each.
Finding the dot product of 3D vectors is essentially the same as finding the dot
product of 2D vectors:
(a,b,c) (d,e, f)= ad +be+cf
Finding the magnitude of 3D vectors is also essentially the same as it is for 2D
vectors:
Ka,b.c)| = Va² +b² +c²
Now find the angle 0 between your two vectors using this formula:
V•W
0 = cos
Show your work in the space below. Be sure to find 6 in radians, not in degrees:
(a,b,c) x (d,e,f)
(.05266, -.85998, .50760)x(.05272,-.85096, .50594)=(.05266 x .05272)+(-.85988
x -.85096)+(.50760 x .50594)
立 0
48°F S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning