An object of mass m falling near the surface of the earth is retarded by air resistance proportional to its velocity so that, according to Newton's Second Law of Motion, dv m- dt mg – kv, where v=v (t) is the velocity of the object at time t, andg is the acceleration of gravity near the surface of the earth. Assume that the object falls from rest at time t=0, that is v (0) =0. The velocity of the object at time t=m/k is v (m/k) = (1 – e-1) O A. mg k O B. None of these
An object of mass m falling near the surface of the earth is retarded by air resistance proportional to its velocity so that, according to Newton's Second Law of Motion, dv m- dt mg – kv, where v=v (t) is the velocity of the object at time t, andg is the acceleration of gravity near the surface of the earth. Assume that the object falls from rest at time t=0, that is v (0) =0. The velocity of the object at time t=m/k is v (m/k) = (1 – e-1) O A. mg k O B. None of these
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.7: Applications
Problem 18EQ
Related questions
Question
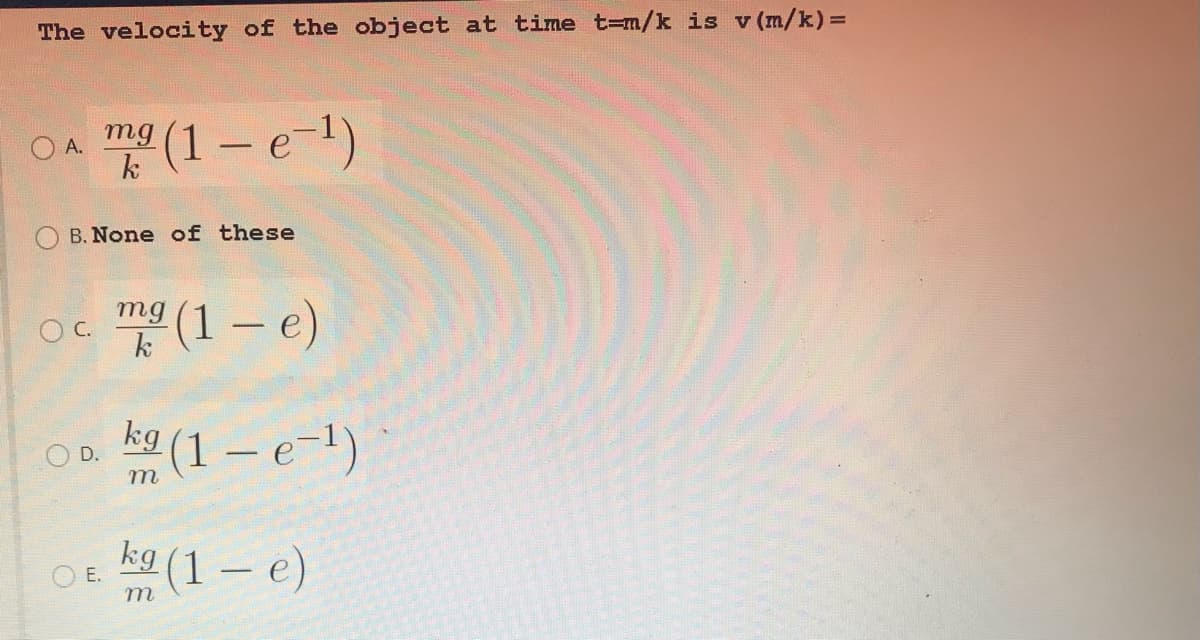
Transcribed Image Text:The velocity of the object at time t=m/k is v (m/k)=
(1 – e-1)
O A.
mg
k
O B. None of these
Oc (1 – e)
mg
k
-
kg
m (1 – e-1)
D.
kg (1 – e)
O E.
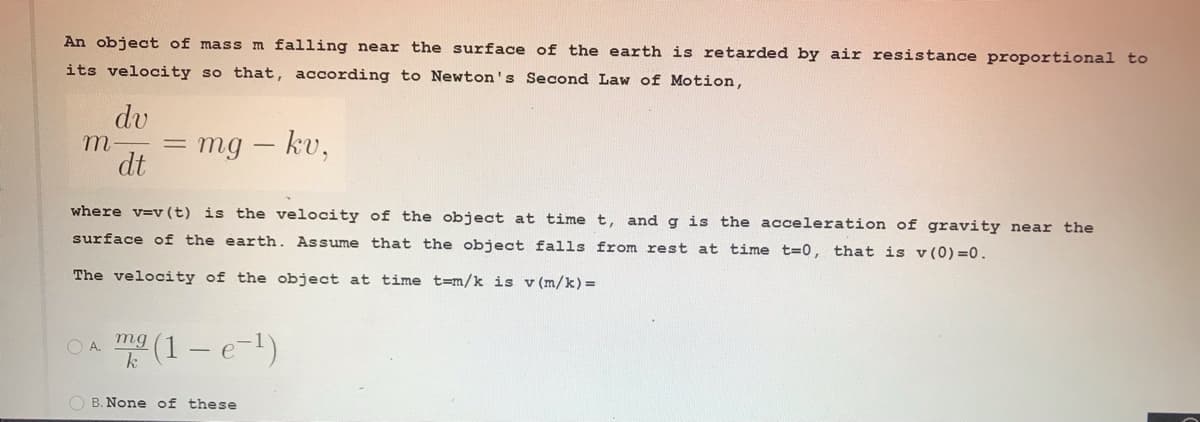
Transcribed Image Text:An object of mass m falling near the surface of the earth is retarded by air resistance proportional to
its velocity so that, according to Newton's Second Law of Motion,
dv
m-
mg – kv,
dt
where v=v (t) is the velocity of the object at time t, andg is the acceleration of gravity near the
surface of the earth. Assume that the object falls from rest at time t=0, that is v (0) =0.
The velocity of the object at time t=m/k is v (m/k)=
(1 – e-1)
OA.
mg
k
O B. None of these
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning