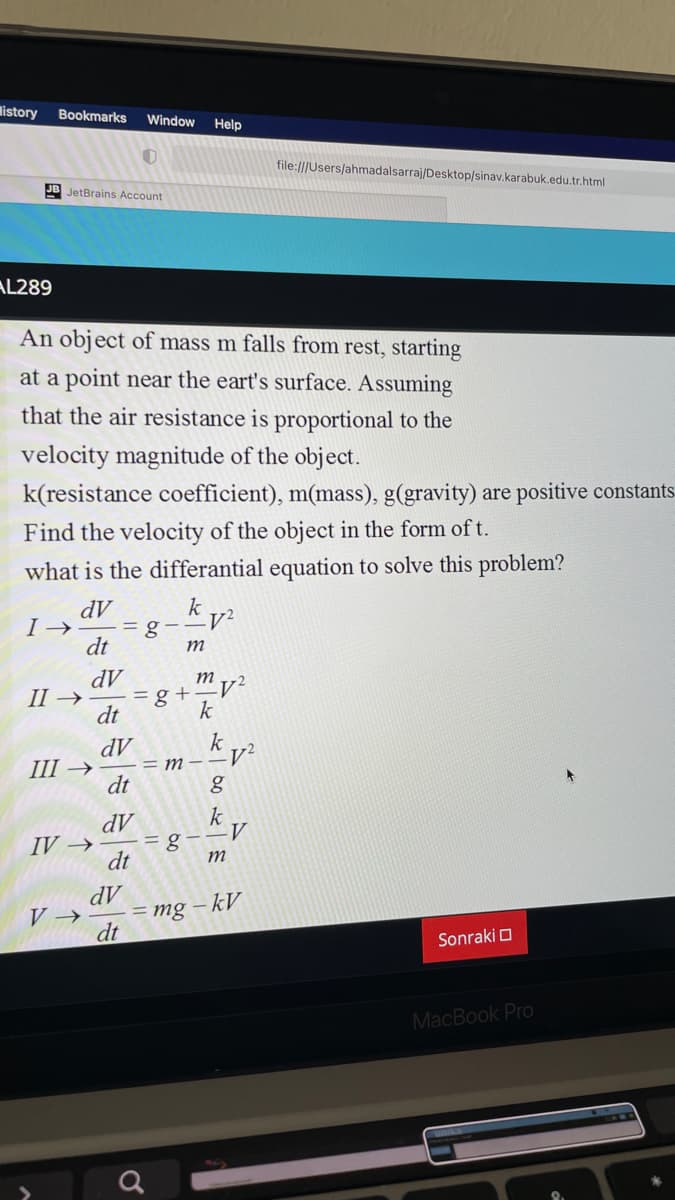
An object of mass m falls from rest, starting at a point near the eart's surface. Assuming that the air resistance is proportional to the velocity magnitude of the object. k(resistance coefficient), m(mass), g(gravity) are positive constants. Find the velocity of the object in the form of t. what is the differantial equation to solve this problem? dV =g- dt dV mv² =g+ k II → dt k dV = m – –V² dt III → - - dV k g--V dt IV → %3D m V → dV = mg – kV -
An object of mass m falls from rest, starting at a point near the eart's surface. Assuming that the air resistance is proportional to the velocity magnitude of the object. k(resistance coefficient), m(mass), g(gravity) are positive constants. Find the velocity of the object in the form of t. what is the differantial equation to solve this problem? dV =g- dt dV mv² =g+ k II → dt k dV = m – –V² dt III → - - dV k g--V dt IV → %3D m V → dV = mg – kV -
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter7: Analytic Trigonometry
Section7.6: The Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Problem 91E
Related questions
Question
differential equations
Transcribed Image Text:listory
Bookmarks
Window
Help
file:///Users/ahmadalsarraj/Desktop/sinav.karabuk.edu.tr.html
JB JetBrains Account
AL289
An object of mass m falls from rest, starting
at a point near the eart's surface. Assuming
that the air resistance is proportional to the
velocity magnitude of the object.
k(resistance coefficient), m(mass), g(gravity) are positive constants.
Find the velocity of the object in the form of t.
what is the differantial equation to solve this problem?
dV
I →
=g-
dt
k
m
dV
m
II →
= g +
k
dt
dV
Ш >
dt
k
M – –V²
k
dV
=g--V
dt
IV →
dV
= mg – kV
dt
V →
Sonraki O
MacBook Pro

Transcribed Image Text:ns - CAL289
dV
k
4-
dt
m
dV
m
-2
II
>
dt
dV
k
III
->
= M
dt
dV
IV →
dt
m
dV
= mg -kV
dt
A) II
B) II
C) I
D) IV
O EL V
Ma
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell