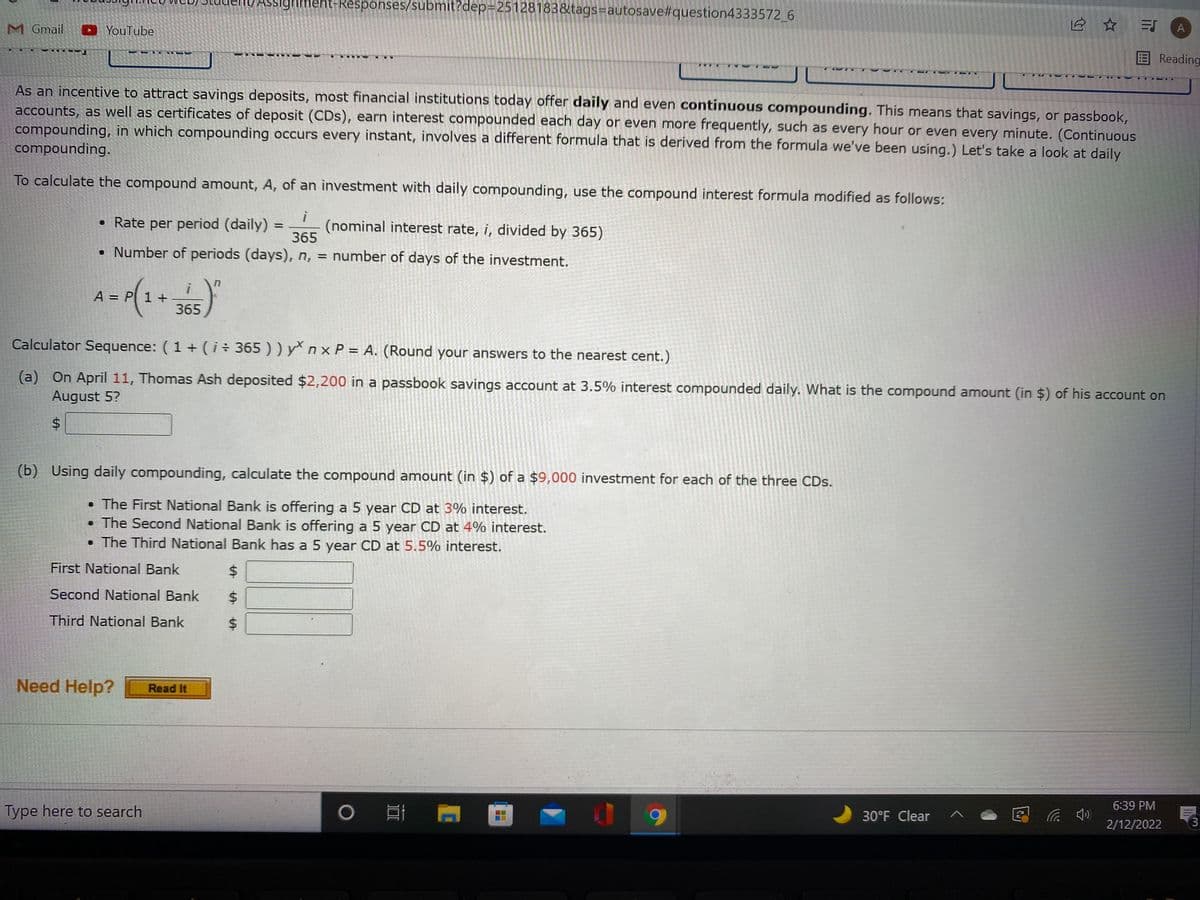
As an incentive to attract savings deposits, most financial institutions today offer daily and even continuous compounding. This means that savings, or passbook, accounts, as well as certificates of deposit (CDs), earn interest compounded each day or even more frequently, such as every hour or even every minute. (Continuous compounding, in which compounding occurs every instant, involves a different formula that is derived from the formula we've been using.) Let's take a look at daily compounding. To calculate the compound amount, A, of an investment with daily compounding, use the compound interest formula modified as follows: • Rate per period (daily) = (nominal interest rate, i, divided by 365) 365 • Number of periods (days), n, = number of days of the investment. A-(1 1 + 365 A%3D Calculator Sequence: (1 + (i 365 ) ) ynxP = A. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) (a) On April 11, Thomas Ash deposited $2,200 in a passbook savings account at 3.5% interest compounded daily. What is the compound amount (in $) of his account on August 5? %24 (b) Using daily compounding, calculate the compound amount (in $) of a $9,000 investment for each of the three CDs. • The First National Bank is offering a 5 year CD at 3% interest. The Second National Bank is offering a 5 year CD at 4% interest. • The Third National Bank has a 5 year CD at 5.5% interest. First National Bank %24 Second National Bank %24 Third National Bank %24
As an incentive to attract savings deposits, most financial institutions today offer daily and even continuous compounding. This means that savings, or passbook, accounts, as well as certificates of deposit (CDs), earn interest compounded each day or even more frequently, such as every hour or even every minute. (Continuous compounding, in which compounding occurs every instant, involves a different formula that is derived from the formula we've been using.) Let's take a look at daily compounding. To calculate the compound amount, A, of an investment with daily compounding, use the compound interest formula modified as follows: • Rate per period (daily) = (nominal interest rate, i, divided by 365) 365 • Number of periods (days), n, = number of days of the investment. A-(1 1 + 365 A%3D Calculator Sequence: (1 + (i 365 ) ) ynxP = A. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) (a) On April 11, Thomas Ash deposited $2,200 in a passbook savings account at 3.5% interest compounded daily. What is the compound amount (in $) of his account on August 5? %24 (b) Using daily compounding, calculate the compound amount (in $) of a $9,000 investment for each of the three CDs. • The First National Bank is offering a 5 year CD at 3% interest. The Second National Bank is offering a 5 year CD at 4% interest. • The Third National Bank has a 5 year CD at 5.5% interest. First National Bank %24 Second National Bank %24 Third National Bank %24
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Makers
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305654174
Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Chapter9: Current Liabilities, Contingencies, And The Time Value Of Money
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9.11MCP
Related questions
Question
100%
Transcribed Image Text:Sighment-Responses/submit?dep3D25128183&tags%3Dautosave#question4333572_6
M Gmail
YouTube
Reading
As an incentive to attract savings deposits, most financial institutions today offer daily and even continuous compounding. This means that savings, or passbook,
accounts, as well as certificates of deposit (CDs), earn interest compounded each day or even more frequently, such as every hour or even every minute. (Continuous
compounding, in which compounding occurs every instant, involves a different formula that is derived from the formula we've been using.) Let's take a look at daily
compounding.
To calculate the compound amount, A, of an investment with daily compounding, use the compound interest formula modified as follows:
• Rate per period (daily)
(nominal interest rate, i, divided by 365)
365
%3D
• Number of periods (days), n, = number of days of the investment.
A = P 1+
365
Calculator Sequence: ( 1 +(i÷ 365 ) ) y n x P = A. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.)
(a) On April 11, Thomas Ash deposited $2,200 in a passbook savings account at 3.5% interest compounded daily. What is the compound amount (in $) of his account on
August 5?
(b) Using daily compounding, calculate the compound amount (in $) of a $9,000 investment for each of the three CDs.
• The First National Bank is offering a 5 year CD at 3% interest.
• The Second National Bank is offering a 5 year CD at 4% interest.
• The Third National Bank has a 5 year CD at 5.5% interest.
First National Bank
Second National Bank
Third National Bank
Need Help?
Read It
6:39 PM
Type here to search
30°F Clear
2/12/2022
(3
%24
%24
%24
%24
Expert Solution
Step 1
The compounded amount is the value of the initial deposit along with compound interest. Compound interest is the process by which the accumulated interest is added back to the principal for computing the next interest. The higher the frequency of compounding, the higher is the amount.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make…
Accounting
ISBN:
9781305654174
Author:
Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. Norton
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning