At the end of each year, $6500 is invested in an IRA earning 3% interest compounded annually. Answer parts (A) and (B) below. (A) How much will be in the account at the end of 40 years? Use the following annuity formula, where P= periodic payment, = rate per period, n= number of payments (periods), and F = FV = future value. (1 + i)" - 1 F(P.i,n) = P- There will be $ in the account at the end of 40 years. (Simplify your answer. Do not round until the final answer. Then round to two decimal places as needed.) (B) Use graphical approximation methods to determine the rate of interest that would produce $910,000 in the account at the end of 40 years. An interest rate of approximately % will produce $910,000 in the account at the end of 40 years. (Type an integer or decimal rounded to the nearest tenth as needed.)
At the end of each year, $6500 is invested in an IRA earning 3% interest compounded annually. Answer parts (A) and (B) below. (A) How much will be in the account at the end of 40 years? Use the following annuity formula, where P= periodic payment, = rate per period, n= number of payments (periods), and F = FV = future value. (1 + i)" - 1 F(P.i,n) = P- There will be $ in the account at the end of 40 years. (Simplify your answer. Do not round until the final answer. Then round to two decimal places as needed.) (B) Use graphical approximation methods to determine the rate of interest that would produce $910,000 in the account at the end of 40 years. An interest rate of approximately % will produce $910,000 in the account at the end of 40 years. (Type an integer or decimal rounded to the nearest tenth as needed.)
Chapter9: Sequences, Probability And Counting Theory
Section9.4: Series And Their Notations
Problem 56SE: To get the best loan rates available, the Riches want to save enough money to place 20% down on a...
Related questions
Question
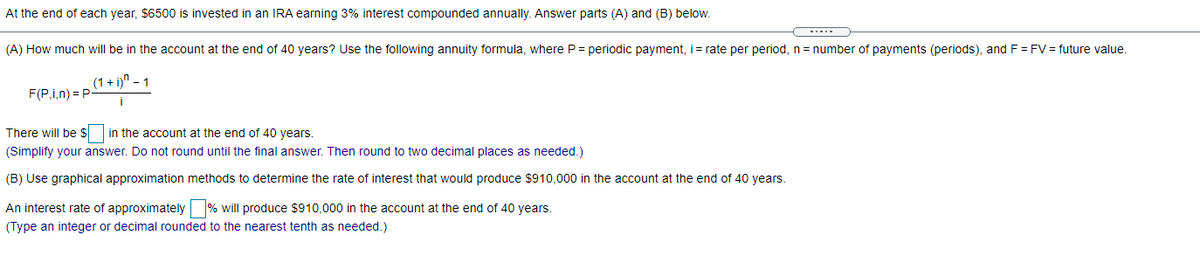
Transcribed Image Text:At the end of each year, $6500 is invested in an IRA earning 3% interest compounded annually. Answer parts (A) and (B) below.
(A) How much will be in the account at the end of 40 years? Use the following annuity formula, where P = periodic payment, i= rate per period, n = number of payments (periods), andF = FV = future value.
(1 + i)" – 1
F(P,i,n) = P
i
There will be $ in the account at the end of 40 years.
(Simplify your answer. Do not round until the final answer. Then round to two decimal places as needed.)
(B) Use graphical approximation methods to determine the rate of interest that would produce $910,000 in the account at the end of 40 years.
An interest rate of approximately % will produce $910,000 in the account at the end of 40 years.
(Type an integer or decimal rounded to the nearest tenth as needed.)
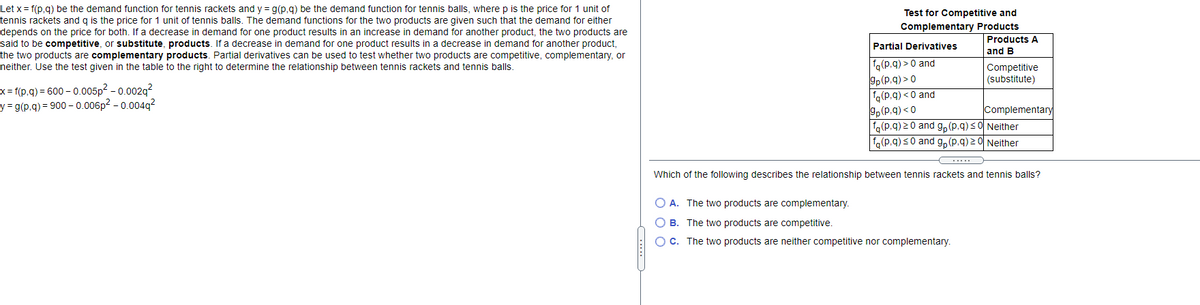
Transcribed Image Text:Let x = f(p,g) be the demand function for tennis rackets and y = g(p,g) be the demand function for tennis balls, where p is the price for 1 unit of
tennis rackets and g is the price for 1 unit of tennis balls. The demand functions for the two products are given such that the demand for either
depends on the price for both. If a decrease in demand for one product results in an increase in demand for another product, the two products are
said to be competitive, or substitute, products. If a decrease in demand for one product results in a decrease in demand for another product,
Test for Competitive and
Complementary Products
Products A
Partial Derivatives
and B
the two products are complementary products. Partial derivatives can be used to test whether two products are competitive, complementary, or
fq(p.q) > 0 and
gp(p.q) > 0
fo(p.q) <0 and
9p(P.q) < 0
fg(p.q) 20 and g, (p.q)<0 Neither
fo(p.q) s0 and g, (p,q) 2 0 Neither
Competitive
(substitute)
neither. Use the test given in the table to the right to determine the relationship between tennis rackets and tennis balls.
x = f(p.q) = 600 – 0.005p2 - 0.002g?
y = g(p.q) = 900 – 0.006p² – 0.004q²
Complementary
.....
Which of the following describes the relationship between tennis rackets and tennis balls?
O A. The two products are complementary.
O B. The two products are competitive.
OC. The two products are neither competitive nor complementary.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, algebra and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you



College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning



College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning