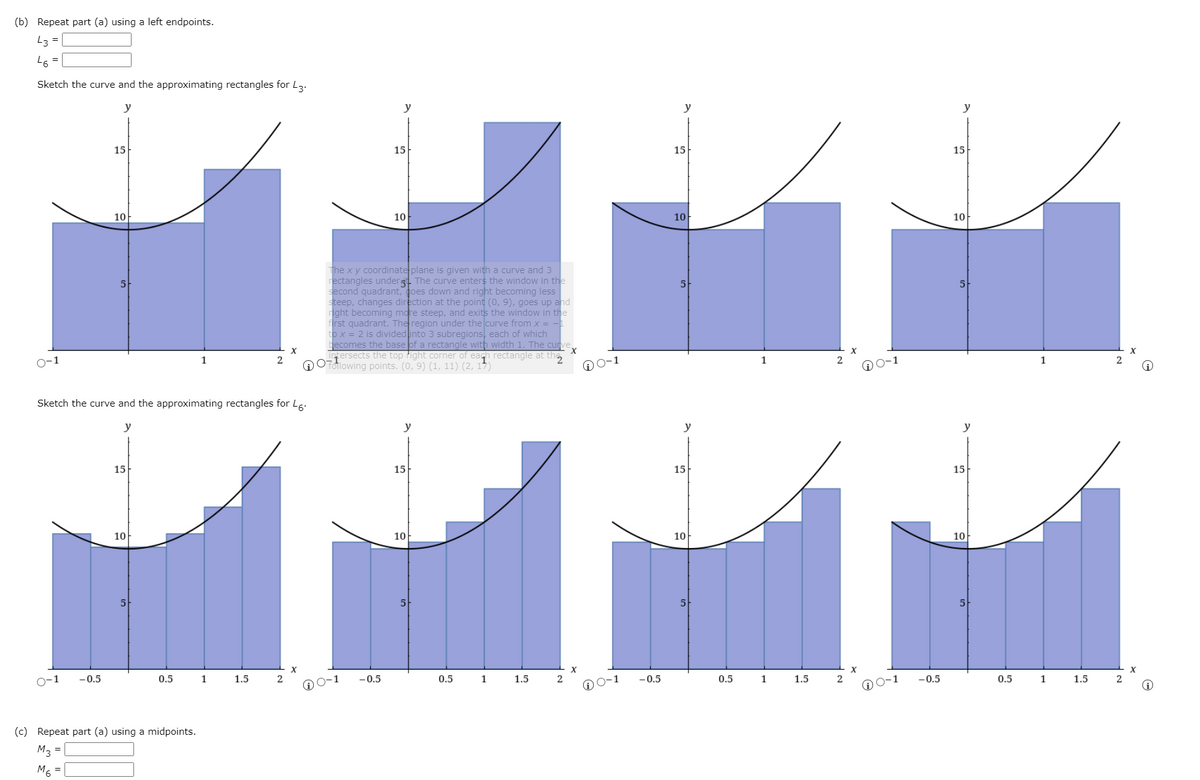
(b) Repeat part (a) using a left endpoints. L3= Sketch the curve and the approximating rectangles for La . y y y 15 15 15 15 10 10 10 10 he x y coordinate plane is given with a curve and 3 ectangles underg The curve enters the window in the econd quadrant, oes down and right becoming less teep, changes direction at the point (0, 9), goes up and ght becoming more steep, and exits the window in the rst quadrant. The region under the curve from x ox= 2 is dividednto 3 subregions, each of which ecomes the base of a rectangle with width 1. The curve esects the top ight corner of eagh rectangle at the Q0Tdiowing points. (0, 9) (1, 11) (2, 15) 0-1 D0-1 D0-1 Sketch the curve and the approximating rectangles for Le y 15 15 15 15 10 10 10 10 o-1 -0.5 0.5 1 1.5 -0.5 D0-1 0.5 1.5 -0.5 00-1 0.5 1 1.5 2 -0.5 0.5 1 D0-1 1.5 (c) Repeat part (a) using a midpoints. M3 -
(b) Repeat part (a) using a left endpoints. L3= Sketch the curve and the approximating rectangles for La . y y y 15 15 15 15 10 10 10 10 he x y coordinate plane is given with a curve and 3 ectangles underg The curve enters the window in the econd quadrant, oes down and right becoming less teep, changes direction at the point (0, 9), goes up and ght becoming more steep, and exits the window in the rst quadrant. The region under the curve from x ox= 2 is dividednto 3 subregions, each of which ecomes the base of a rectangle with width 1. The curve esects the top ight corner of eagh rectangle at the Q0Tdiowing points. (0, 9) (1, 11) (2, 15) 0-1 D0-1 D0-1 Sketch the curve and the approximating rectangles for Le y 15 15 15 15 10 10 10 10 o-1 -0.5 0.5 1 1.5 -0.5 D0-1 0.5 1.5 -0.5 00-1 0.5 1 1.5 2 -0.5 0.5 1 D0-1 1.5 (c) Repeat part (a) using a midpoints. M3 -
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Student Edition 2015
1st Edition
ISBN:9781680331141
Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Chapter10: Radical Functions And Equations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 9CR
Related questions
Question
Transcribed Image Text:QOowing he top fight corner of each rectangle at the
(b) Repeat part (a) using a left endpoints.
L3 =
L6 =
Sketch the curve and the approximating rectangles for L3.
y
y
y
15
15
15
15
10
10
10
10
The x y coordinate plane is given with a curve and 3
rectangles underg The curve enters the window in the
second quadrant, goes down and right becoming less
steep, changes direction at the point (0, 9), goes up and
right becoming more steep, and exits the window in the
first quadrant. The region under the curve from x = -
to x = 2 is divided into 3 subregions, each of which
becomes the base of a rectangle with width 1. The curve
5
5
5
2
2.
O0-1
O-1
1
points. (0, 9) (1, 11) (2, 17)
1
O0-1
1
Sketch the curve and the approximating rectangles for L6:
y
y
y
15
15
15
15
10
10
10
10
5
5
5
5
X
2
O0-1
o-1
-0.5
0.5
1
1.5
-0.5
0.5
1
1.5
O0-1
-0.5
0.5
1
1.5
2
G0-1
-0.5
0.5
1
1.5
2
(c) Repeat part (a) using a midpoints.
M3 =
M6 =
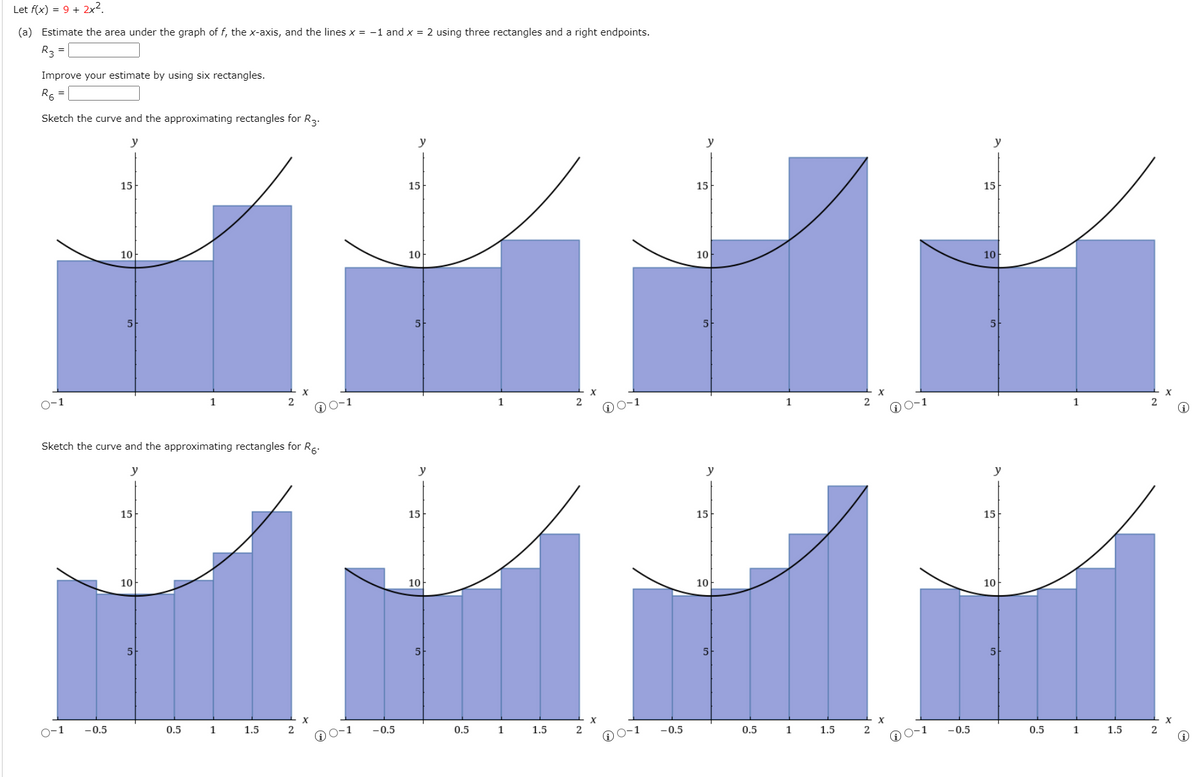
Transcribed Image Text:Let f(x) = 9 + 2x².
(a) Estimate the area under the graph of f, the x-axis, and the lines x = -1 and x = 2 using three rectangles and a right endpoints.
R3 =
Improve your estimate by using six rectangles.
R6 =
Sketch the curve and the approximating rectangles for R2.
y
y
y
y
15
15
15
15
10
10-
10
10
5
5
5
X
0-1
1
1
O-1
1
2
D-1
1
2
Sketch the curve and the approximating rectangles for Rg.
y
y
y
15
15
15
15
10
10
10
10
5
5
5
2
O0-1
-0.5
0.5
1
1.5
-0.5
0.5
1
1.5
2
@O-1
-0.5
O-1
0.5
1.5
2
-1
-0.5
0.5
1
1.5
2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781680331141
Author:
HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT
Publisher:
Houghton Mifflin Harcourt

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning