(b) Suppose that for a particular disease c = 0.6/day, and b = 10/day. What value must k remain below to prevent the disease from becoming endemic? k<
(b) Suppose that for a particular disease c = 0.6/day, and b = 10/day. What value must k remain below to prevent the disease from becoming endemic? k<
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter5: Inverse, Exponential, And Logarithmic Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 15T
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
8.1-20) part b please
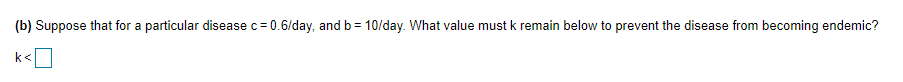
Transcribed Image Text:(b) Suppose that for a particular disease c= 0.6/day, and b = 10/day. What value must k remain below to prevent the disease from becoming endemic?
k<

Transcribed Image Text:One way to control the spread of a disease is to run public health programs that educate people on how to limit their exposure to the disease. For example, frequent
handwashing can prevent people from picking up a virus after touching surfaces that may live on. Complete parts (a) and (b).
ds
= cI -
dt
kb
N SI
where S(t) represents the number of susceptible people at time t, I(t) represents the number of infected people at
(a) The epidemic model used is
dI
kb
dt NSI - cI
that time, coefficient k is a constant of proportionality, coefficient c is the recovery rate, and coefficient b is the number of other people an individual contacts in one
unit of time. Explain why in our model such efforts to control the disease would affect the value of the parameter k, but would not affect b or c. Choose the correct
answer below.
'A. Efforts to control the disease will cause the number of infected individuals to decrease. If the total population does not change, then the proportion of
infected individuals contacted in unit time, k, must also decrease. The variables b and c should not be affected.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning