a. What effect would a $9.05 million operating expense have on this year's earnings? What effect would it have on next year's earnings? (Select all the choices that apply.) A. A $9.05 million operating expense would be immediately expensed, increasing operating expenses by $9.05 million. This would lead to a reduction in taxes of 25% x $9.05 million = $2.26 million. B. A $9.05 million operating expense would be immediately expensed, increasing operating expenses by $9.05 million. This would lead to an increase in taxes of 25% x $9.05 million = $2.26 million. C. Earnings would decline by $9.05 million - $2.26 million = $6.79 million. The same effect would be seen on next year's earnings. D. Earnings would decline by $9.05 million - $2.26 million = $6.79 million. There would be no effect on next year's earnings.
a. What effect would a $9.05 million operating expense have on this year's earnings? What effect would it have on next year's earnings? (Select all the choices that apply.) A. A $9.05 million operating expense would be immediately expensed, increasing operating expenses by $9.05 million. This would lead to a reduction in taxes of 25% x $9.05 million = $2.26 million. B. A $9.05 million operating expense would be immediately expensed, increasing operating expenses by $9.05 million. This would lead to an increase in taxes of 25% x $9.05 million = $2.26 million. C. Earnings would decline by $9.05 million - $2.26 million = $6.79 million. The same effect would be seen on next year's earnings. D. Earnings would decline by $9.05 million - $2.26 million = $6.79 million. There would be no effect on next year's earnings.
Chapter9: Capital Budgeting And Cash Flow Analysis
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 20P
Related questions
Question
100%

Transcribed Image Text:Suppose a firm's tax rate is 25%.
a. What effect would a $9.05 million operating expense have on this year's earnings? What effect would it have on
next year's earnings?
b. What effect would a $10.2 million capital expense have on this year's earnings if the capital expenditure is
depreciated at a rate of $2.04 million per year for five years? What effect would it have on next year's earnings?
a. What effect would a $9.05 million operating expense have on this year's earnings? What effect would it have on
next year's earnings? (Select all the choices that apply.)
A. A $9.05 million operating expense would be immediately expensed, increasing operating expenses by $9.05
million. This would lead to a reduction in taxes of 25% x $9.05 million = $2.26 million.
B. A $9.05 million operating expense would be immediately expensed, increasing operating expenses by $9.05
million. This would lead to an increase in taxes of 25% × $9.05 million = $2.26 million.
C. Earnings would decline by $9.05 million - $2.26 million = $6.79 million. The same effect would be seen on
next year's earnings.
D. Earnings would decline by $9.05 million - $2.26 million = $6.79 million. There would be no effect on next
year's earnings.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
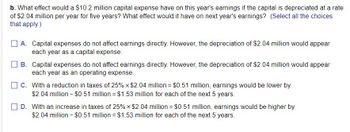
Transcribed Image Text:b. What effect would a $10.2 million capital expense have on this year's earnings if the capital is depreciated at a rate
of $2.04 million per year for five years? What effect would it have on next year's earnings? (Select all the choices
that apply.)
A. Capital expenses do not affect earnings directly. However, the depreciation of $2.04 million would appear
each year as a capital expense.
B. Capital expenses do not affect earnings directly. However, the depreciation of $2.04 million would appear
each year as an operating expense.
C. With a reduction in taxes of 25% × $2.04 million = $0.51 million, earnings would be lower by
$2.04 million - $0.51 million = $1.53 million for each of the next 5 years.
D. With an increase in taxes of 25% × $2.04 million = $0.51 million, earnings would be higher by
$2.04 million - $0.51 million = $1.53 million for each of the next 5 years.
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
Finance
ISBN:
9781337514835
Author:
MOYER
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course…
Finance
ISBN:
9781337395083
Author:
Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:
Cengage Learning




Financial Reporting, Financial Statement Analysis…
Finance
ISBN:
9781285190907
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Stephen P. Baginski, Mark Bradshaw
Publisher:
Cengage Learning