Based on the following data, make a comparison between the use of the flow of inventory costs assumptions with the FIFO and LIFO methods and provide an overview of why in the end LIFO should not be used. (on the image below) Create Schedules of COGS using the following format: (replace XXX with the correct number from your calculation)
Based on the following data, make a comparison between the use of the flow of inventory costs assumptions with the FIFO and LIFO methods and provide an overview of why in the end LIFO should not be used. (on the image below) Create Schedules of COGS using the following format: (replace XXX with the correct number from your calculation)
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter7: Inventories: Cost Measurement And Flow Assumptions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 16E: Dollar-Value LIFO A company adopted the LIFO method when its inventory was 1,800. One year later its...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
Based on the following data, make a comparison between the use of the flow of inventory costs assumptions with the FIFO and LIFO methods and provide an overview of why in the end LIFO should not be used. (on the image below)
Create Schedules of COGS using the following format:
(replace XXX with the correct number from your calculation)
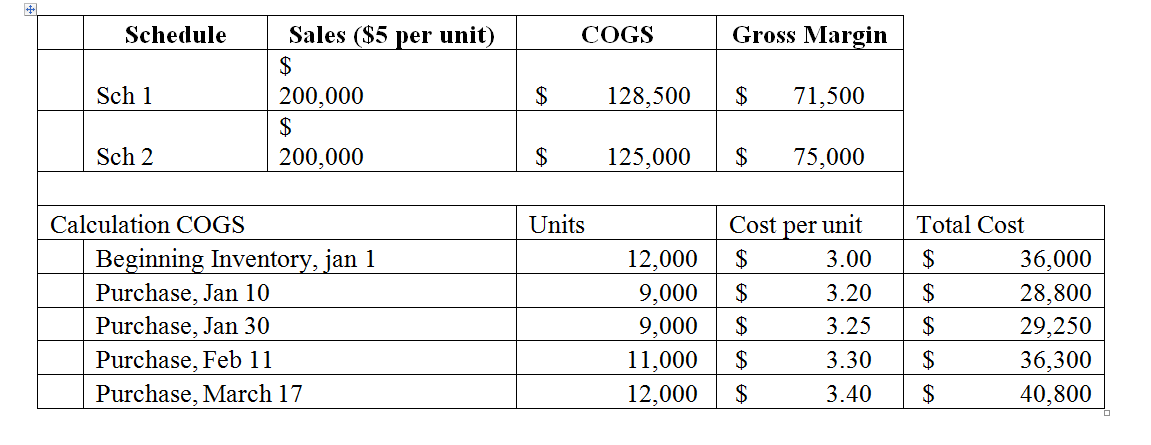
Transcribed Image Text:Schedule
Sales ($5 per unit)
СOGS
Gross Margin
$
Sch 1
$
$
200,000
$
128,500
71,500
Sch 2
200,000
$
125,000
$
75,000
Calculation COGS
Units
Cost per unit
Total Cost
Beginning Inventory, jan 1
Purchase, Jan 10
Purchase, Jan 30
12,000
$
3.00
$
36,000
9,000
$
3.20
$
28,800
9,000
$
3.25
$
29,250
Purchase, Feb 11
11,000
$
3.30
$
36,300
Purchase, March 17
12,000
$
3.40
$
40,800
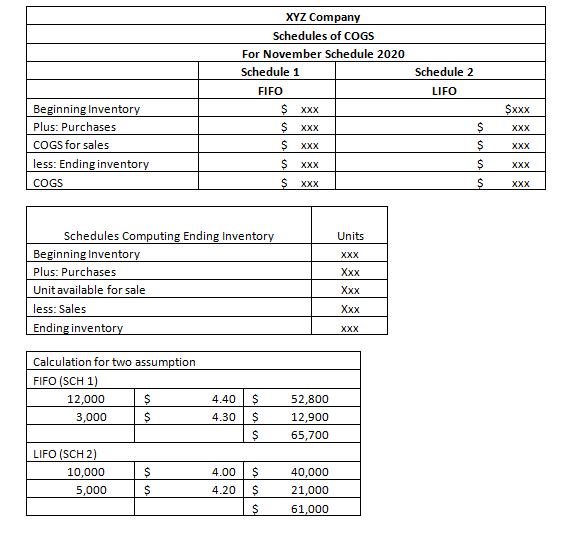
Transcribed Image Text:XYZ Company
Schedules of COGS
For November Schedule 2020
Schedule 1
Schedule 2
FIFO
LIFO
Beginning Inventory
$ XXX
Sxx
Plus: Purchases
XXX
XXX
COGS for sales
less: Ending inventory
XXX
XXX
XXX
XXX
COGS
XXX
XXX
Schedules Computing Ending Inventory
Beginning Inventory
Plus: Purchases
Unit available for sale
less: Sales
Ending inventory
Units
XXX
Ххх
Xxx
Ххх
XXX
Calculation for two assumption
FIFO (SCH 1)
12,000
4.40
52,800
3,000
4.30
12,900
65,700
LIFO (SCH 2)
10,000
4.00
40,000
5,000
4.20
21,000
61,000
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning