Below, we see a region bounded by two curves and the x-axis. 1.5 .5 -1.5 The region shaded in light blue is bounded on the left by the curve y = x (in dark blue), on the right by the curve y = -x + 2 (in dark red), and below by the r-axis. Part 1. Suppose that we wish to integrate with respect to a to find the value of the shaded area. This will require two integrals. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate values and functions that the integrals below describe the area of the shaded region.
Below, we see a region bounded by two curves and the x-axis. 1.5 .5 -1.5 The region shaded in light blue is bounded on the left by the curve y = x (in dark blue), on the right by the curve y = -x + 2 (in dark red), and below by the r-axis. Part 1. Suppose that we wish to integrate with respect to a to find the value of the shaded area. This will require two integrals. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate values and functions that the integrals below describe the area of the shaded region.
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
100%
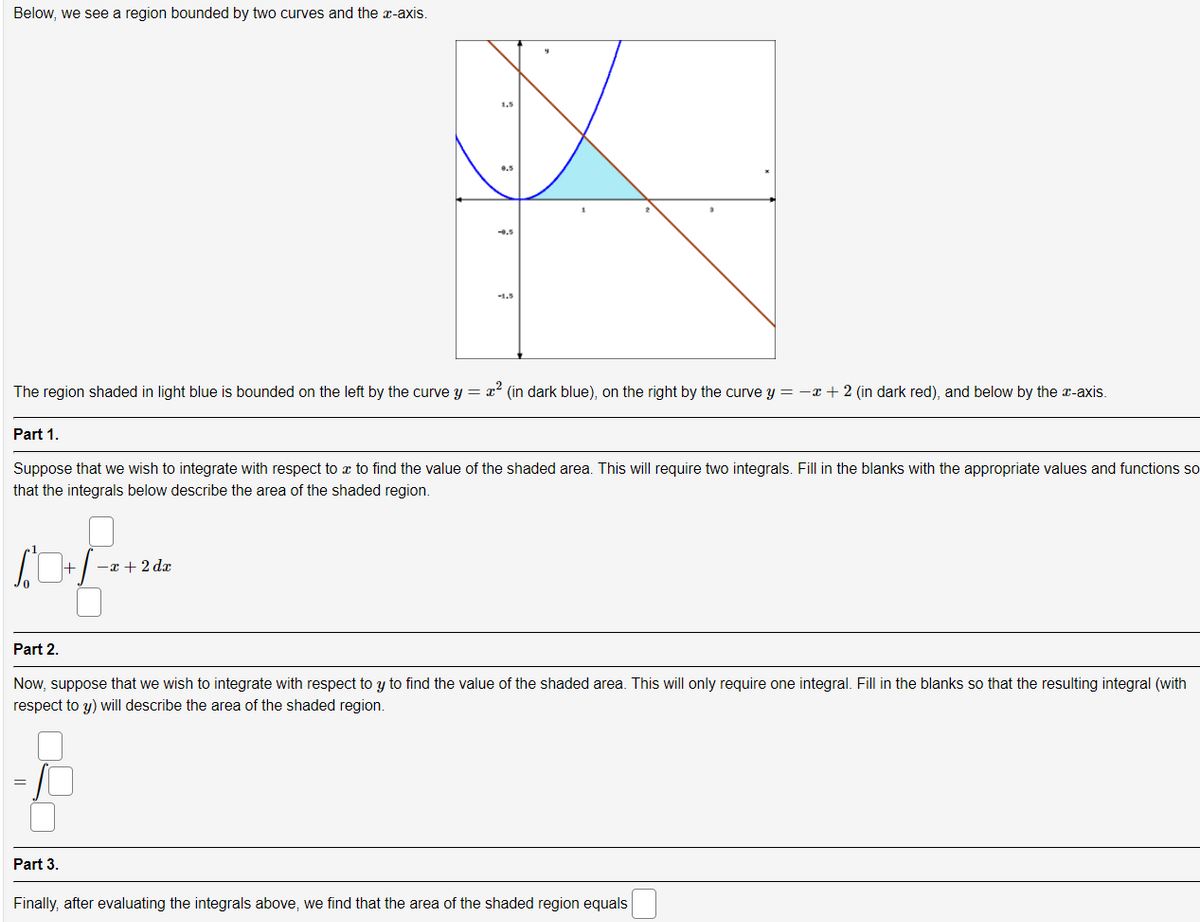
Transcribed Image Text:Below, we see a region bounded by two curves and the x-axis.
1,5
The region shaded in light blue is bounded on the left by the curve y = x? (in dark blue), on the right by the curve y = -x + 2 (in dark red), and below by the x-axis.
Part 1.
Suppose that we wish to integrate with respect to a to find the value of the shaded area. This will require two integrals. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate values and functions so
that the integrals below describe the area of the shaded region.
+
-x +2 dz
Part 2.
Now, suppose that we wish to integrate with respect to y to find the value of the shaded area. This will only require one integral. Fill in the blanks so that the resulting integral (with
respect to y) will describe the area of the shaded region.
Part 3.
Finally, after evaluating the integrals above, we find that the area of the shaded region equals
Transcribed Image Text:1.5
un
8.5
), ar
th
3
h the
ar
-8.5
-1.5
ate
i th
lank
Expert Solution
Step 1
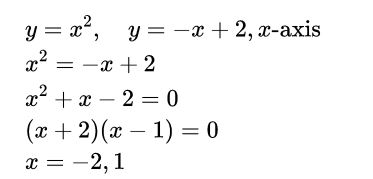
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning