below). The red arrow indicates the amino acid lysin (K) that binds to the oxygen of the retinol (indicated by the blue arrow). The purple arrow indicates the retinal bound to the rhodopsin. In healthy individuals, retinal is abundant and can binds to the rhodopsin, making it functional (light-sensitive). H3C CH3 CH3 cytoplasmic side 0000 000 CH3 Retinal extracellular side C-I OO CO LOOD CO00 000 0000 000 CH3 COO 000 0000 GUIA 000 000 000 0000 0030 0000 000 C-II 000 000 CO @o Rhodopsin (primary structure) FOO OCK NOWE OV00 OPO 000 0600 DOOO 0000 COO COO 0000 0000000 Gooo 9000 E-II COOH-terminal C-III OO 200 000 DOO 000 000 E-III Čoooo NH₂-terminal Rhodopsin + retinal (tertiary structure) 6. This lysine (K) is in a transmembrane domain of rhodopsin and can bind to retinal. Based on the chemical property of lysine, which of the following can you conclude? A. Lysine is a hydrophobic amino acid that binds to water molecules, hydrophobic tails of phospholipids and to retinal B. Lysine is a negatively charged amino acid that has a high affinity for the hydrophobic tails of phospholipids C. Lysine is a positively charged amino acid that has a high affinity for the hydrophobic tails of phospholipids D. Lysine is a hydrophilic amino acid oriented towards the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids and can bind to them E. Lysine is a positively charged amino acid that does not interact with hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids but instead is located inside the rhodopsin (in its tertiary structure) and binds to the electronegative oxygen of retinal
below). The red arrow indicates the amino acid lysin (K) that binds to the oxygen of the retinol (indicated by the blue arrow). The purple arrow indicates the retinal bound to the rhodopsin. In healthy individuals, retinal is abundant and can binds to the rhodopsin, making it functional (light-sensitive). H3C CH3 CH3 cytoplasmic side 0000 000 CH3 Retinal extracellular side C-I OO CO LOOD CO00 000 0000 000 CH3 COO 000 0000 GUIA 000 000 000 0000 0030 0000 000 C-II 000 000 CO @o Rhodopsin (primary structure) FOO OCK NOWE OV00 OPO 000 0600 DOOO 0000 COO COO 0000 0000000 Gooo 9000 E-II COOH-terminal C-III OO 200 000 DOO 000 000 E-III Čoooo NH₂-terminal Rhodopsin + retinal (tertiary structure) 6. This lysine (K) is in a transmembrane domain of rhodopsin and can bind to retinal. Based on the chemical property of lysine, which of the following can you conclude? A. Lysine is a hydrophobic amino acid that binds to water molecules, hydrophobic tails of phospholipids and to retinal B. Lysine is a negatively charged amino acid that has a high affinity for the hydrophobic tails of phospholipids C. Lysine is a positively charged amino acid that has a high affinity for the hydrophobic tails of phospholipids D. Lysine is a hydrophilic amino acid oriented towards the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids and can bind to them E. Lysine is a positively charged amino acid that does not interact with hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids but instead is located inside the rhodopsin (in its tertiary structure) and binds to the electronegative oxygen of retinal
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Chapter1: The Human Body: An Orientation
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,...
Related questions
Question
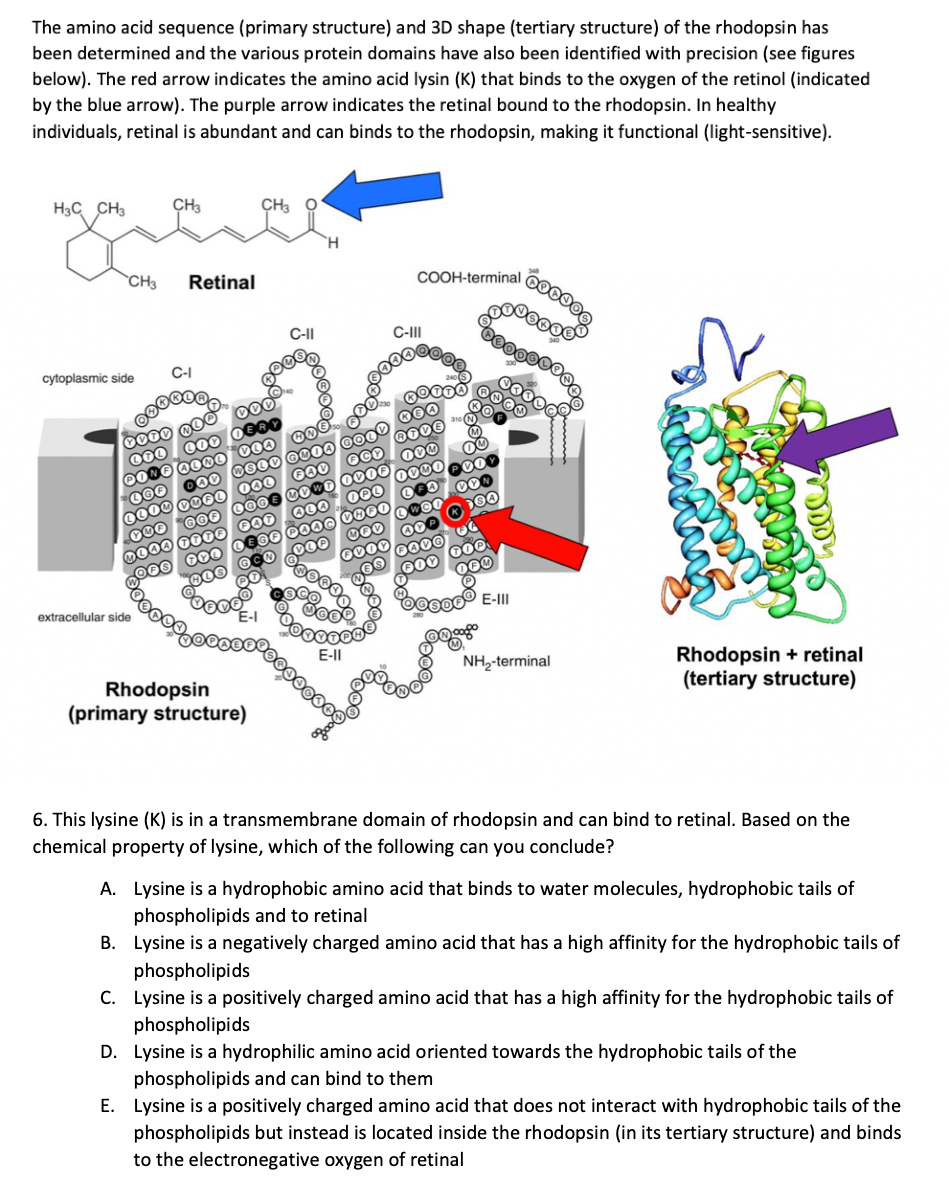
Transcribed Image Text:The amino acid sequence (primary structure) and 3D shape (tertiary structure) of the rhodopsin has
been determined and the various protein domains have also been identified with precision (see figures
below). The red arrow indicates the amino acid lysin (K) that binds to the oxygen of the retinol (indicated
by the blue arrow). The purple arrow indicates the retinal bound to the rhodopsin. In healthy
individuals, retinal is abundant and can binds to the rhodopsin, making it functional (light-sensitive).
H3C CH3 CH3
CH3
cytoplasmic side
Retinal
C-I
extracellular side
0000 MOO
OOO
400 DERY
000
PONE ALMO VOO
LGF
LLOD VUEL
CH3
HOO
AD SLV GO04
FAV
OCK
000
LOO
GOF
YO
DOAA TOTO ⓇAD
MOWE OV00
OPL
ALA
LEGE DOOD VOOO
COP
DES 000
600
GCO
OV
FOOD
Rhodopsin
(primary structure)
C-II
E-II
COOH-terminal
C-III
RIVE
OOM
DOWO
LWCO
40
DOVO
FOX
ON
DO
000
D04
boooooo
000
000
100,00
******
E-III
NH₂-terminal
Rhodopsin + retinal
(tertiary structure)
6. This lysine (K) is in a transmembrane domain of rhodopsin and can bind to retinal. Based on the
chemical property of lysine, which of the following can you conclude?
A. Lysine is a hydrophobic amino acid that binds to water molecules, hydrophobic tails of
phospholipids and to retinal
B. Lysine is a negatively charged amino acid that has a high affinity for the hydrophobic tails of
phospholipids
C. Lysine is a positively charged amino acid that has a high affinity for the hydrophobic tails of
phospholipids
D. Lysine is a hydrophilic amino acid oriented towards the hydrophobic tails of the
phospholipids and can bind to them
E. Lysine is a positively charged amino acid that does not interact with hydrophobic tails of the
phospholipids but instead is located inside the rhodopsin (in its tertiary structure) and binds
to the electronegative oxygen of retinal
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780134580999
Author:
Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:
PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:
9781947172517
Author:
Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:
OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781259398629
Author:
McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:
Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9780815344322
Author:
Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:
W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:
9781260159363
Author:
Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:
9781260231700
Author:
Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:
McGraw Hill Education