Between your evening meal and breakfast, your blood glucose drops and your liver becomes a net producer rather than a consumer of glucose. Which statements describe the hormone-stimulated process that triggers glucose production by the liver? The increase in (CAMP] causes protein kinase A to phosphorylate pyruvate kinase, thus inhibiting glycolysis in muscle tissue to promote gluconeogenesis in the liver. O The decrease in [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate] stimulates FBPase-1, the key enzyme in gluconeogenesis. Epinephrine stimulates an enzyme cascade involving hepatic protein kinase A (PKA) and phosphorylase b kinase, which eventually leads to glycogen breakdown in the liver. The rapid decrease in blood glucose levels triggers glucagon release by the pancreas. O Glucagon stimulates CAMP-dependent phosphorylation of PFK-2/FBPase-2, which decreases [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate). The decrease in [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate] stimulates PFK-1, the key enzyme in gluconeogenesis.
Between your evening meal and breakfast, your blood glucose drops and your liver becomes a net producer rather than a consumer of glucose. Which statements describe the hormone-stimulated process that triggers glucose production by the liver? The increase in (CAMP] causes protein kinase A to phosphorylate pyruvate kinase, thus inhibiting glycolysis in muscle tissue to promote gluconeogenesis in the liver. O The decrease in [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate] stimulates FBPase-1, the key enzyme in gluconeogenesis. Epinephrine stimulates an enzyme cascade involving hepatic protein kinase A (PKA) and phosphorylase b kinase, which eventually leads to glycogen breakdown in the liver. The rapid decrease in blood glucose levels triggers glucagon release by the pancreas. O Glucagon stimulates CAMP-dependent phosphorylation of PFK-2/FBPase-2, which decreases [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate). The decrease in [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate] stimulates PFK-1, the key enzyme in gluconeogenesis.
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781285866932
Author:Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:Lauralee Sherwood
Chapter19: The Peripheral Endocrine Glands
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 13UC
Related questions
Question
![Between your evening meal and breakfast, your blood glucose drops and your liver becomes a net producer rather than a
consumer of glucose.
Which statements describe the hormone-stimulated process that triggers glucose production by the liver?
The increase in (CAMP] causes protein kinase A to phosphorylate pyruvate kinase, thus inhibiting glycolysis in muscle
tissue to promote gluconeogenesis in the liver.
The decrease in [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate] stimulates FBPase-1, the key enzyme in gluconeogenesis.
Epinephrine stimulates an enzyme cascade involving hepatic protein kinase A (PKA) and phosphorylase b kinase,
which eventually leads to glycogen breakdown in the liver.
O The rapid decrease in blood glucose levels triggers glucagon release by the pancreas.
Glucagon stimulates CAMP-dependent phosphorylation of PFK-2/FBPase-2, which decreases
[fructose 2,6-bisphosphate].
The decrease in [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate] stimulates PFK-1, the key enzyme in gluconeogenesis.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Fedd7c55f-5862-4ccb-842d-ed25b8dd3140%2F73cead3f-27bb-4873-9cd0-fba599b723f8%2F5kp053lm_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Between your evening meal and breakfast, your blood glucose drops and your liver becomes a net producer rather than a
consumer of glucose.
Which statements describe the hormone-stimulated process that triggers glucose production by the liver?
The increase in (CAMP] causes protein kinase A to phosphorylate pyruvate kinase, thus inhibiting glycolysis in muscle
tissue to promote gluconeogenesis in the liver.
The decrease in [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate] stimulates FBPase-1, the key enzyme in gluconeogenesis.
Epinephrine stimulates an enzyme cascade involving hepatic protein kinase A (PKA) and phosphorylase b kinase,
which eventually leads to glycogen breakdown in the liver.
O The rapid decrease in blood glucose levels triggers glucagon release by the pancreas.
Glucagon stimulates CAMP-dependent phosphorylation of PFK-2/FBPase-2, which decreases
[fructose 2,6-bisphosphate].
The decrease in [fructose 2,6-bisphosphate] stimulates PFK-1, the key enzyme in gluconeogenesis.
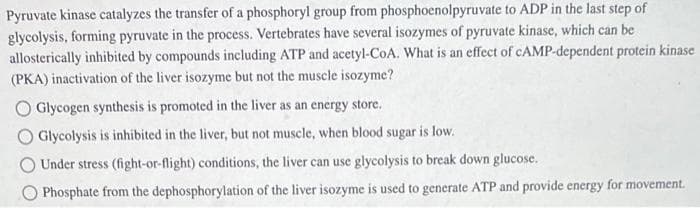
Transcribed Image Text:Pyruvate kinase catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP in the last step of
glycolysis, forming pyruvate in the process. Vertebrates have several isozymes of pyruvate kinase, which can be
allosterically inhibited by compounds including ATP and acetyl-CoA. What is an effect of CAMP-dependent protein kinase
(PKA) inactivation of the liver isozyme but not the muscle isozyme?
Glycogen synthesis is promoted in the liver as an energy store.
O Glycolysis is inhibited in the liver, but not muscle, when blood sugar is low.
Under stress (fight-or-flight) conditions, the liver can use glycolysis to break down glucose.
Phosphate from the dephosphorylation of the liver isozyme is used to generate ATP and provide energy for movement.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap …
Biology
ISBN:
9781285866932
Author:
Lauralee Sherwood
Publisher:
Cengage Learning