By considering different paths of approach, show that the function below has no limit as (x,y)→(0,0). x4 f(x.y) = Examine the values of f along curves that end at (0,0). Along which set of curves is fa constant value? O A. y= kx, x# 0 O B. y = kx°, x+0 Oc. y= kx2, x+0 O D. y= kx + kx², x#0 If (x,y) approaches (0,0) along the curve when k=1 used in the set of curves found above, what is the limit? (Simplify your answer.) If (x,y) approaches (0,0) along the curve when k= 0 used in the set of curves found above, what is the limit? (Simplify your answer.) What can you conclude? A. Since f has two different limits along two different paths to (0,0), in cannot be determined whether or not f has a limit as (x,y) approaches (0,0) O B. Since f has the same limit along two different paths to (0,0), by the two-path test, f has no limit as (x,y) approaches (0,0). O c. Since f has two different limits along two different paths to (0,0), by the two-path test, f has no limit as (x.y) approaches (0,0). O D. Since f has the same limit along two different paths to (0,0), in cannot be determined whether or not f has a limit as (x,y) approaches (0,0).
By considering different paths of approach, show that the function below has no limit as (x,y)→(0,0). x4 f(x.y) = Examine the values of f along curves that end at (0,0). Along which set of curves is fa constant value? O A. y= kx, x# 0 O B. y = kx°, x+0 Oc. y= kx2, x+0 O D. y= kx + kx², x#0 If (x,y) approaches (0,0) along the curve when k=1 used in the set of curves found above, what is the limit? (Simplify your answer.) If (x,y) approaches (0,0) along the curve when k= 0 used in the set of curves found above, what is the limit? (Simplify your answer.) What can you conclude? A. Since f has two different limits along two different paths to (0,0), in cannot be determined whether or not f has a limit as (x,y) approaches (0,0) O B. Since f has the same limit along two different paths to (0,0), by the two-path test, f has no limit as (x,y) approaches (0,0). O c. Since f has two different limits along two different paths to (0,0), by the two-path test, f has no limit as (x.y) approaches (0,0). O D. Since f has the same limit along two different paths to (0,0), in cannot be determined whether or not f has a limit as (x,y) approaches (0,0).
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
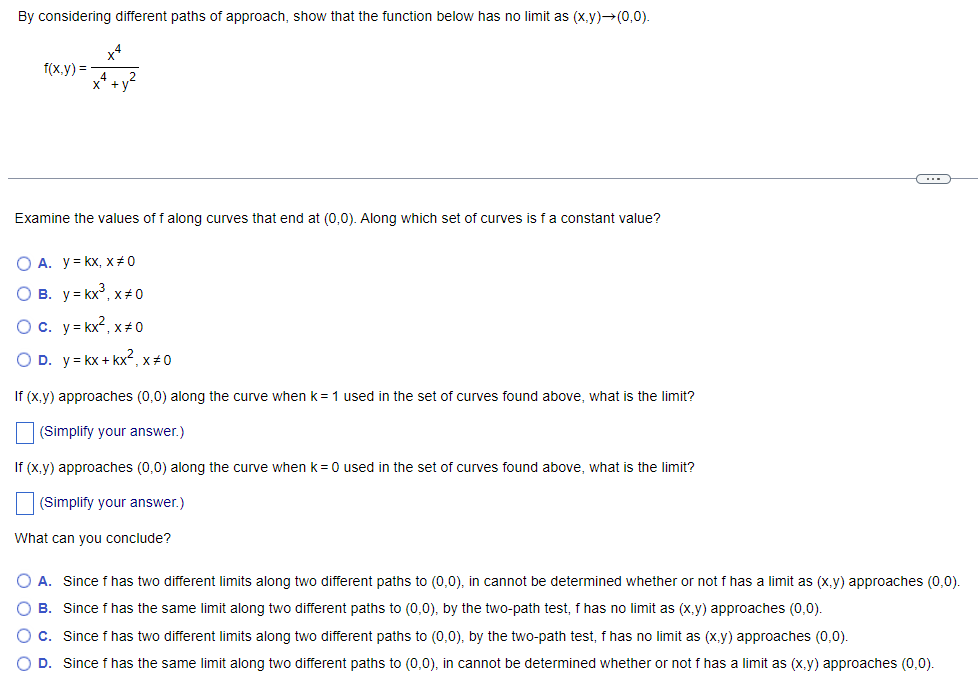
Transcribed Image Text:By considering different paths of approach, show that the function below has no limit as (x,y)→(0,0).
x4
f(x.y) =
Examine the values of f along curves that end at (0,0). Along which set of curves is fa constant value?
O A. y= kx, x# 0
O B. y = kx°, x+0
Oc. y= kx2, x+0
O D. y= kx + kx², x#0
If (x,y) approaches (0,0) along the curve when k=1 used in the set of curves found above, what is the limit?
(Simplify your answer.)
If (x,y) approaches (0,0) along the curve when k= 0 used in the set of curves found above, what is the limit?
(Simplify your answer.)
What can you conclude?
A. Since f has two different limits along two different paths to (0,0), in cannot be determined whether or not f has a limit as (x,y) approaches (0,0)
O B. Since f has the same limit along two different paths to (0,0), by the two-path test, f has no limit as (x,y) approaches (0,0).
O c. Since f has two different limits along two different paths to (0,0), by the two-path test, f has no limit as (x.y) approaches (0,0).
O D. Since f has the same limit along two different paths to (0,0), in cannot be determined whether or not f has a limit as (x,y) approaches (0,0).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning