Calculate all the primitive roots of 41 and 26.
Elements Of Modern Algebra
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Chapter2: The Integers
Section2.8: Introduction To Cryptography (optional)
Problem 23E
Related questions
Question
#13
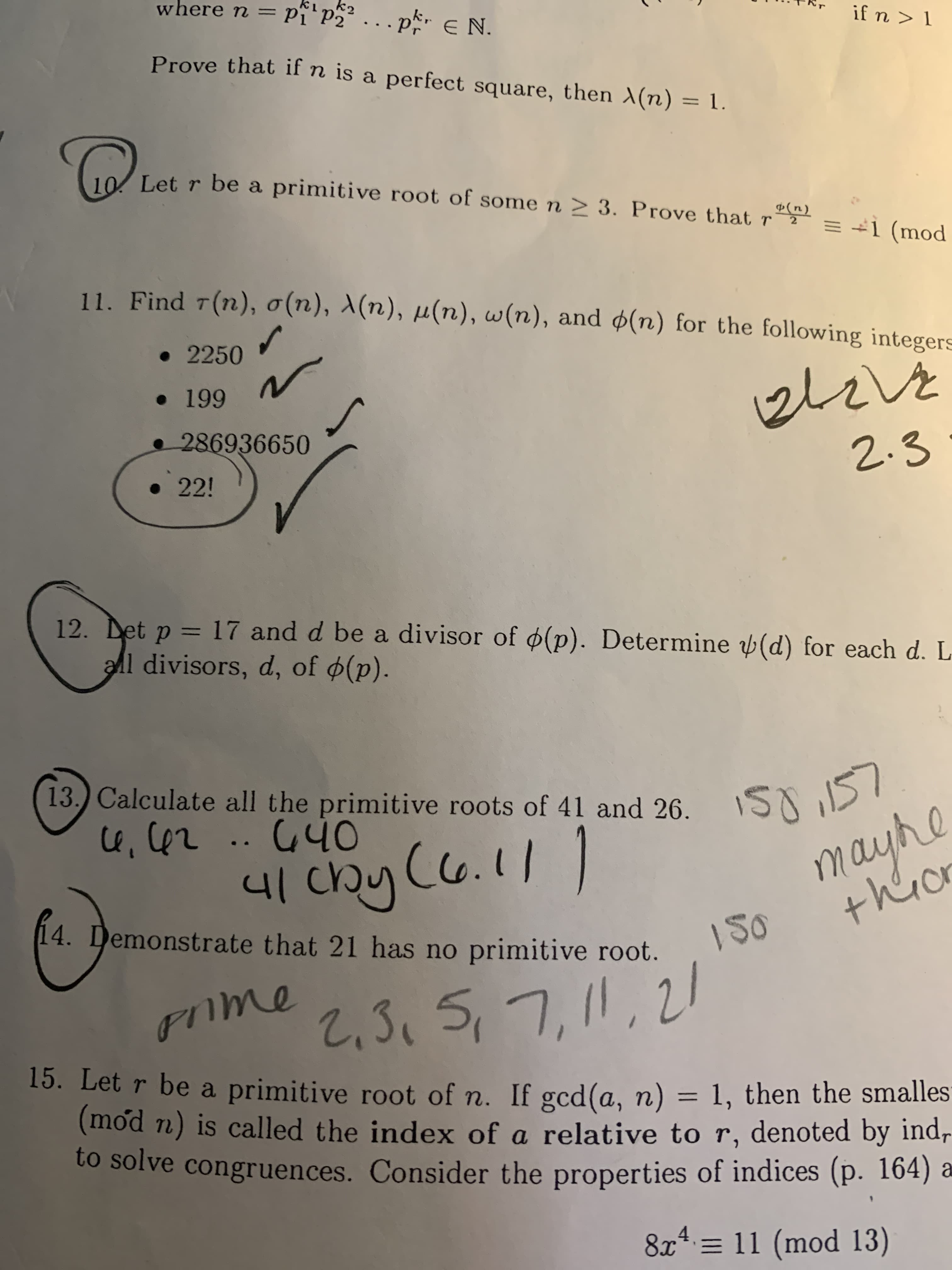
Transcribed Image Text:where n =
. p e N.
I<u J!
Prove that if n is a perfect square, then X(n) = 1.
$ (n)
10/ Let r be a primitive root of some n > 3. Prove that r
= +1 (mod
11. Find 7(n), o(n), X(n), µ(n), w(n), and ø(n) for the following integers
•2250
286936650
2.3
•22!
12. Det p = 17 and d be a divisor of ø(p). Determine (d) for each d. L
all divisors, d, of ø(p).
13.) Calculate all the primitive roots of 41 and 26. S0
Oわり… て切'の
|1の)
4. Demonstrate that 21 has no primitive root.
sime
2,3,5,7,11,21
15. Let r be a primitive root of n. If gcd(a, n) = 1, then the smalles
(mod n) is called the index of a relative to r, denoted by ind-
to solve congruences. Consider the properties of indices (p. 164) a
||
8x* = 11 (mod 13)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463230
Author:
Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:
Cengage Learning,

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage