OB. f(x) is increasing on no interval (part B) Find where f(x) is decreasing. O A. f(x) is decreasing on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is decreasing on no interval (part C) Find where g has a local minimum. O A. f(x) has a local minimum at the following x-value(s): x = O B. f(x) has no local minimum (part d) Find where f(x) has a local maximum. O A. f(x) has a local maximum at the following x-value(s): x = O B. f(x) has no local maximum (part E) Find where f(x) is concave up. O A. f(x) is concave up on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is concave up on no interval (part F) Find where f(x) is concave down. O A. f(x) is concave down on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is concave down on no interval (part G) Find where f(x) has an inflection point. O A. f(x) has an inflection point at the following x-value(s): x = O B. f(x) has no inflection point Consider the function f(x), whose first and second derivatives are given below: 26 8x27 208x(x-54) = (x), (x-52)2 %3D %3D x-52 Note: Do not attempt to calculate f(x). Also, assume that f(x) has the same domain as f'(x). (part A) Find where f(x) is increasing. O A. f(x) is increasing on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is increasing on no interval (part B) Find where f(x) is decreasing. O A. f(x) is decreasing on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is decreasing on no interval (part C) Find where g has a local minimum. O A. f(x) has a local minimum at the following x-value(s): x= O B. f(x) has no local minimum (part d) Find where f(x) has a local maximum. O A. f(x) has a local maximum at the following x-value(s): x = O B. f(x) has no local maximum (part E) Find where f(x) is concave up. O A. f(x) is concave up on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is concave up on no interval
OB. f(x) is increasing on no interval (part B) Find where f(x) is decreasing. O A. f(x) is decreasing on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is decreasing on no interval (part C) Find where g has a local minimum. O A. f(x) has a local minimum at the following x-value(s): x = O B. f(x) has no local minimum (part d) Find where f(x) has a local maximum. O A. f(x) has a local maximum at the following x-value(s): x = O B. f(x) has no local maximum (part E) Find where f(x) is concave up. O A. f(x) is concave up on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is concave up on no interval (part F) Find where f(x) is concave down. O A. f(x) is concave down on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is concave down on no interval (part G) Find where f(x) has an inflection point. O A. f(x) has an inflection point at the following x-value(s): x = O B. f(x) has no inflection point Consider the function f(x), whose first and second derivatives are given below: 26 8x27 208x(x-54) = (x), (x-52)2 %3D %3D x-52 Note: Do not attempt to calculate f(x). Also, assume that f(x) has the same domain as f'(x). (part A) Find where f(x) is increasing. O A. f(x) is increasing on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is increasing on no interval (part B) Find where f(x) is decreasing. O A. f(x) is decreasing on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is decreasing on no interval (part C) Find where g has a local minimum. O A. f(x) has a local minimum at the following x-value(s): x= O B. f(x) has no local minimum (part d) Find where f(x) has a local maximum. O A. f(x) has a local maximum at the following x-value(s): x = O B. f(x) has no local maximum (part E) Find where f(x) is concave up. O A. f(x) is concave up on the following interval(s): O B. f(x) is concave up on no interval
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
ChapterP: Prerequisites
SectionP.6: Analyzing Graphs Of Functions
Problem 6ECP: Find the average rates of change of f(x)=x2+2x (a) from x1=3 to x2=2 and (b) from x1=2 to x2=0.
Related questions
Question
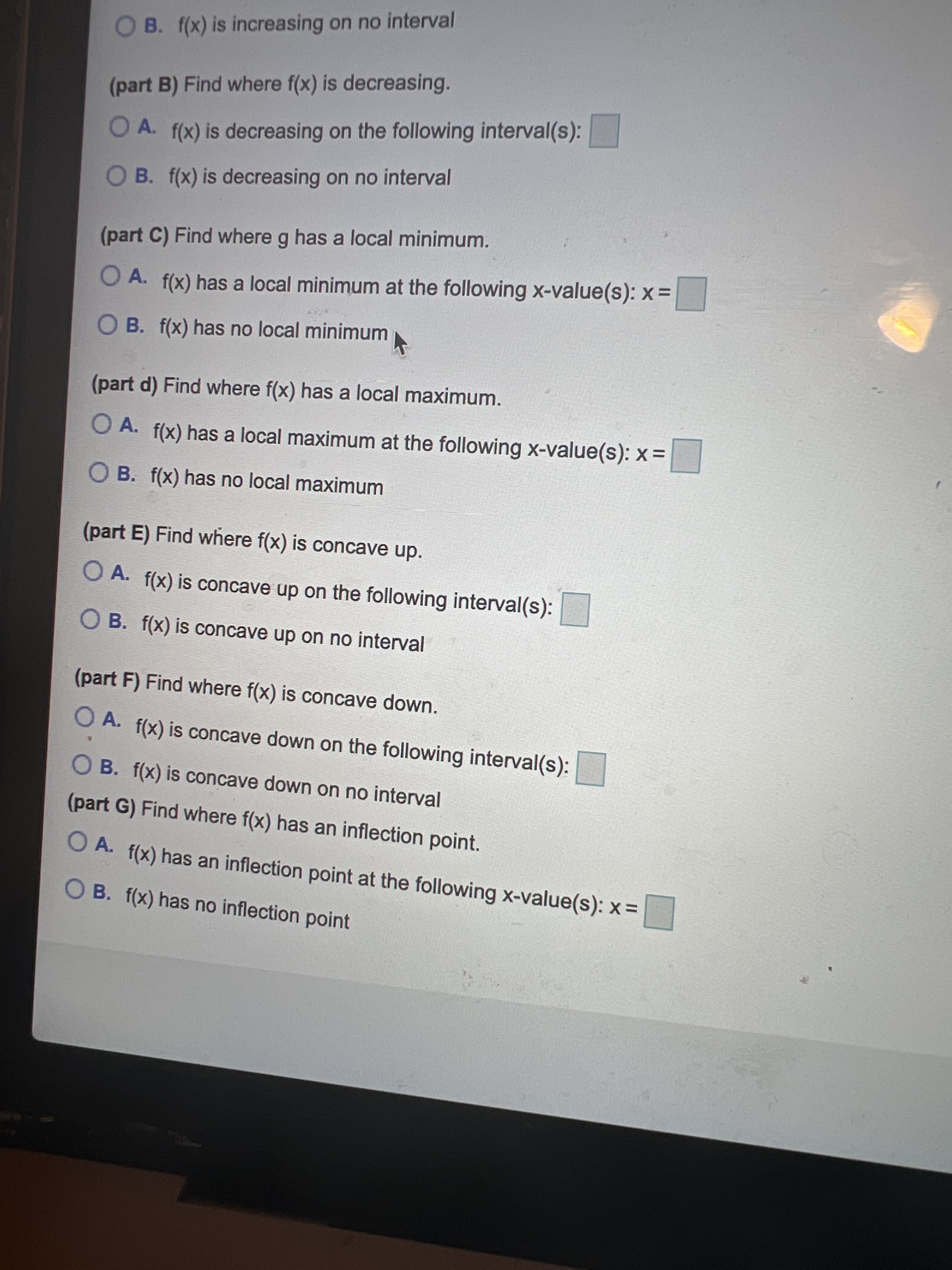
Transcribed Image Text:OB. f(x) is increasing on no interval
(part B) Find where f(x) is decreasing.
O A. f(x) is decreasing on the following interval(s):
O B. f(x) is decreasing on no interval
(part C) Find where g has a local minimum.
O A. f(x) has a local minimum at the following x-value(s): x =
O B. f(x) has no local minimum
(part d) Find where f(x) has a local maximum.
O A. f(x) has a local maximum at the following x-value(s): x =
O B. f(x) has no local maximum
(part E) Find where f(x) is concave up.
O A. f(x) is concave up on the following interval(s):
O B. f(x) is concave up on no interval
(part F) Find where f(x) is concave down.
O A. f(x) is concave down on the following interval(s):
O B. f(x) is concave down on no interval
(part G) Find where f(x) has an inflection point.
O A. f(x) has an inflection point at the following x-value(s): x =
O B. f(x) has no inflection point
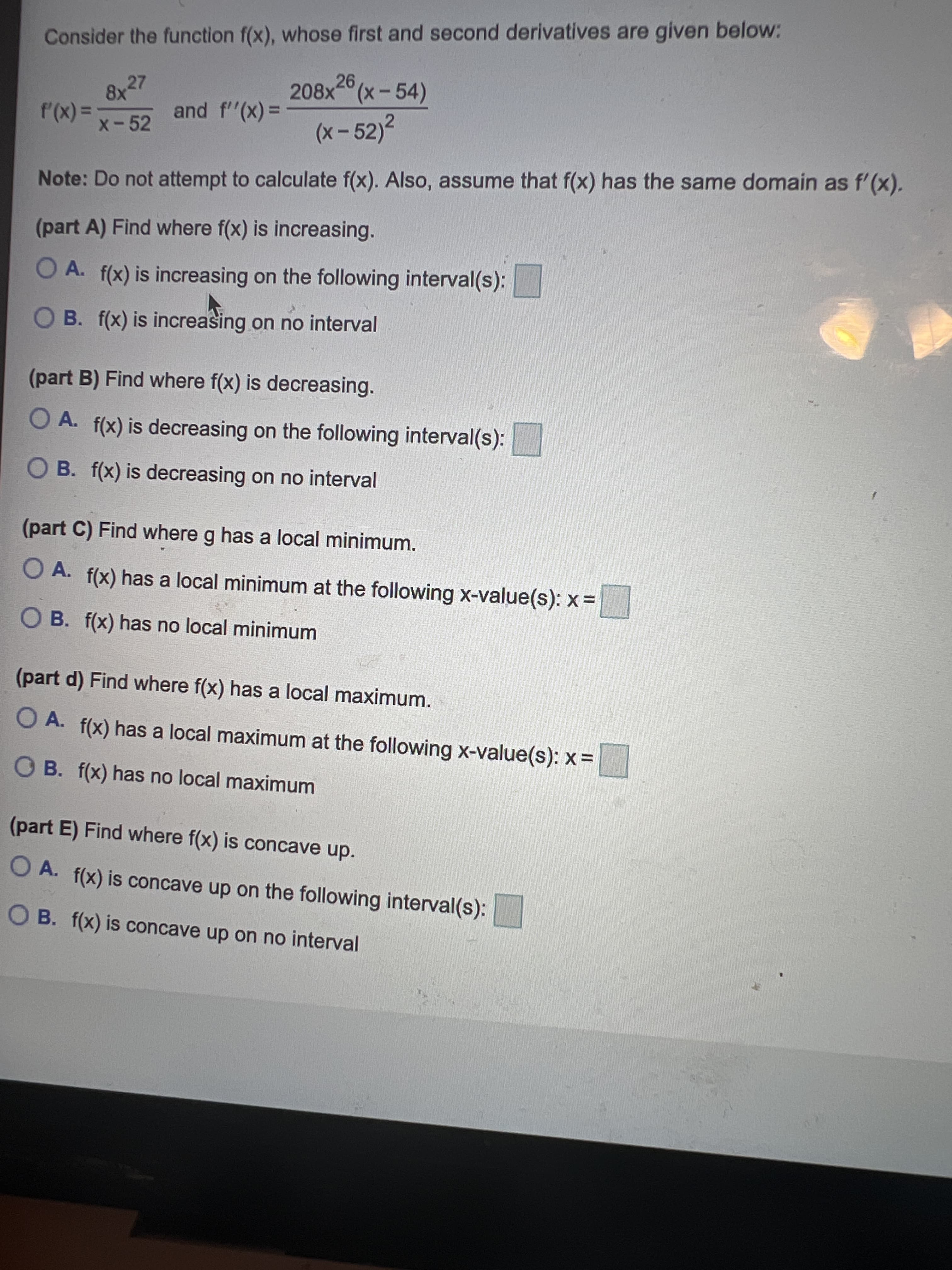
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the function f(x), whose first and second derivatives are given below:
26
8x27
208x(x-54)
= (x),
(x-52)2
%3D
%3D
x-52
Note: Do not attempt to calculate f(x). Also, assume that f(x) has the same domain as f'(x).
(part A) Find where f(x) is increasing.
O A. f(x) is increasing on the following interval(s):
O B. f(x) is increasing on no interval
(part B) Find where f(x) is decreasing.
O A. f(x) is decreasing on the following interval(s):
O B. f(x) is decreasing on no interval
(part C) Find where g has a local minimum.
O A. f(x) has a local minimum at the following x-value(s): x=
O B. f(x) has no local minimum
(part d) Find where f(x) has a local maximum.
O A. f(x) has a local maximum at the following x-value(s): x =
O B. f(x) has no local maximum
(part E) Find where f(x) is concave up.
O A. f(x) is concave up on the following interval(s):
O B. f(x) is concave up on no interval
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning