CHAPTER 9. MULTIVARIABLE AND VECTOR FUNCTIONS Activity 9.4.4 Suppose u = (3, 5, -1) and v= (2, -2, 1). a. Find two unit vectors orthogonal to both u and v. b. Find the volume of the parallelepiped formed by the vectors u, v, and w = (3,3, 1). 25 c. Find a vector orthogonal to the plane containing the points (0, 1, 2), (4, 1,0), and (-2, 2, 2). d. Given the vectors u and v shown below in Figure 9.4.4, sketch the cross products u x v and v x u. y Y u Figure 9.4.4 Vectors u and v e. Do the vectors a = (1,3,-2),b= (2, 1,-4), and c = (0, 1, 0) in standard position lie in the same plane? Use the concepts from this section to explain.
CHAPTER 9. MULTIVARIABLE AND VECTOR FUNCTIONS Activity 9.4.4 Suppose u = (3, 5, -1) and v= (2, -2, 1). a. Find two unit vectors orthogonal to both u and v. b. Find the volume of the parallelepiped formed by the vectors u, v, and w = (3,3, 1). 25 c. Find a vector orthogonal to the plane containing the points (0, 1, 2), (4, 1,0), and (-2, 2, 2). d. Given the vectors u and v shown below in Figure 9.4.4, sketch the cross products u x v and v x u. y Y u Figure 9.4.4 Vectors u and v e. Do the vectors a = (1,3,-2),b= (2, 1,-4), and c = (0, 1, 0) in standard position lie in the same plane? Use the concepts from this section to explain.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter8: Applications Of Trigonometry
Section8.3: Vectors
Problem 60E
Related questions
Question
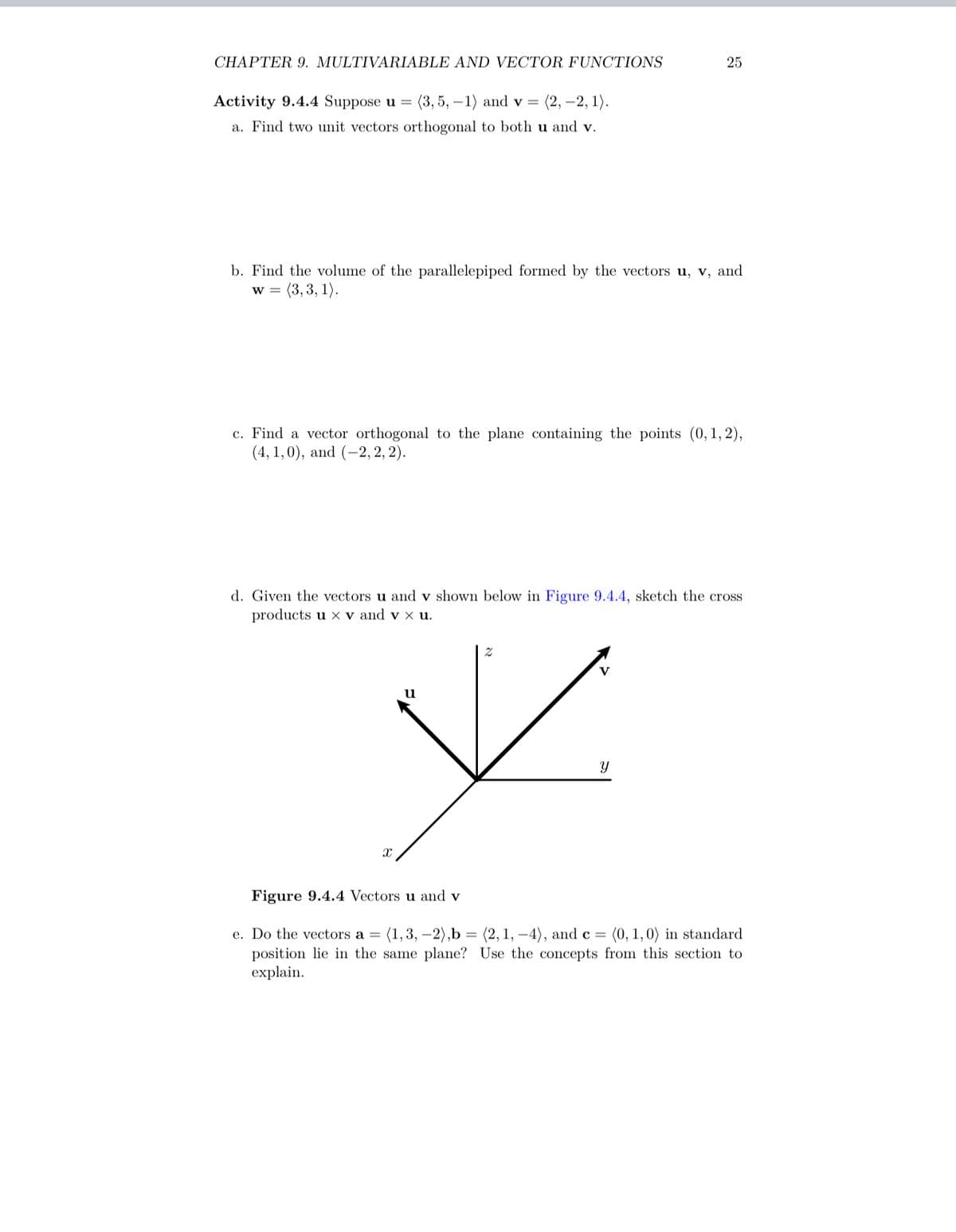
Transcribed Image Text:CHAPTER 9. MULTIVARIABLE AND VECTOR FUNCTIONS
Activity 9.4.4 Suppose u = (3, 5, -1) and v = (2, -2, 1).
a. Find two unit vectors orthogonal to both u and v.
25
b. Find the volume of the parallelepiped formed by the vectors u, v, and
W = (3, 3, 1).
c. Find a vector orthogonal to the plane containing the points (0,1,2),
(4, 1,0), and (-2, 2, 2).
d. Given the vectors u and v shown below in Figure 9.4.4, sketch the cross
products u xv and v x u.
y
Y
Figure 9.4.4 Vectors u and v
e. Do the vectors a = (1, 3, -2),b= (2, 1,-4), and c = (0, 1, 0) in standard
position lie in the same plane? Use the concepts from this section to
explain.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning