Chemical rate equations The reaction of certain chemical com- pounds can be modeled using a differential equation of the form y' (t) = -ky" (t), where y(t) is the concentration of the com- pound, for t = 0, k > 0 is a constant that determines the speed of the reaction, and n is a positive integer called the order of the reaction. Assume the initial concentration of the compound is y(0) = yo > 0. a. Consider a first-order reaction (n = 1) and show that the solu- tion of the initial value problem is y(t) = y,e¬. b. Consider a second-order reaction (n = 2) and show that the Yo Yokt + 1° solution of the initial value problem is y(t) c. Let yo = 1 and k = 0.1. Graph the first-order and second- order solutions found in parts (a) and (b). Compare the two reactions.
Chemical rate equations The reaction of certain chemical com- pounds can be modeled using a differential equation of the form y' (t) = -ky" (t), where y(t) is the concentration of the com- pound, for t = 0, k > 0 is a constant that determines the speed of the reaction, and n is a positive integer called the order of the reaction. Assume the initial concentration of the compound is y(0) = yo > 0. a. Consider a first-order reaction (n = 1) and show that the solu- tion of the initial value problem is y(t) = y,e¬. b. Consider a second-order reaction (n = 2) and show that the Yo Yokt + 1° solution of the initial value problem is y(t) c. Let yo = 1 and k = 0.1. Graph the first-order and second- order solutions found in parts (a) and (b). Compare the two reactions.
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to College Algebra (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Chapter2: Graphical And Tabular Analysis
Section2.4: Solving Nonlinear Equations
Problem 17E: Van der Waals Equation In Exercise 18 at the end of Section 2.3, we discussed the ideal gas law,...
Related questions
Question
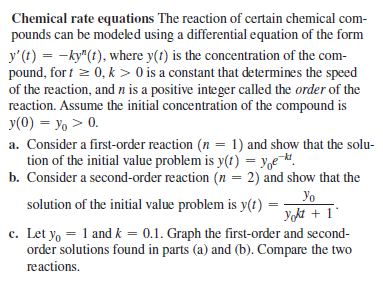
Transcribed Image Text:Chemical rate equations The reaction of certain chemical com-
pounds can be modeled using a differential equation of the form
y' (t) = -ky" (t), where y(t) is the concentration of the com-
pound, for t = 0, k > 0 is a constant that determines the speed
of the reaction, and n is a positive integer called the order of the
reaction. Assume the initial concentration of the compound is
y(0) = yo > 0.
a. Consider a first-order reaction (n = 1) and show that the solu-
tion of the initial value problem is y(t) = y,e¬.
b. Consider a second-order reaction (n = 2) and show that the
Yo
Yokt + 1°
solution of the initial value problem is y(t)
c. Let yo = 1 and k = 0.1. Graph the first-order and second-
order solutions found in parts (a) and (b). Compare the two
reactions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 21 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll…
Algebra
ISBN:
9781337111348
Author:
Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:
Cengage Learning