Clairaut's Theorem Let DCR? be a disk containing the origin and assume that g: DR is a function given by g(x,y) = " (cos y+ a sin y). Prove that g(r, y) satisfies the Clairaut Theorem at point (0, 0).
Clairaut's Theorem Let DCR? be a disk containing the origin and assume that g: DR is a function given by g(x,y) = " (cos y+ a sin y). Prove that g(r, y) satisfies the Clairaut Theorem at point (0, 0).
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 17T
Related questions
Question
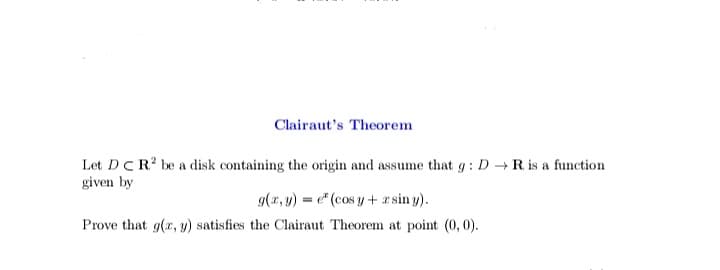
Transcribed Image Text:Clairaut's Theorem
Let DCR? be a disk containing the origin and assume that g : D R is a function
given by
g(x, y) = e" (cos y +r sin y).
Prove that g(x, y) satisfies the Clairaut Theorem at point (0, 0).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305071742
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning