Clark Industries has a defined benefit pension plan that specifies annual, year-end retirement benefits equal to: 1.3% x Service years x Final year's salary Stanley Mills was hired by Clark at the beginning of 2005. • Mills is expected to retire at the end of 2049 after 45 years of service. • His retirement is expected to span 15 years. At the end of 2024, 20 years after being hired, his salary is $81,000. • The company's actuary projects Mills's salary to be $280,000 at retirement. The actuary's discount rate is 8%. For all requirements, round final answers to the nearest whole dollars. Do not round intermediate calculations. Use tables, Excel, or a financial calculator. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) Required: 1. Estimate the amount of Stanley Mills's annual retirement payments for the 15 retirement years earned as of the end of 2024. 2. Suppose Clark's pension plan permits a lump-sum payment at retirement in lieu of annuity payments. Determine the lump-sum equivalent as the present value as of the earned retirement annuity at the expected date of retirement (the end of 2049). 3. What is the company's projected benefit obligation at the end of 2024 with respect to Stanley Mills? 4. Even though pension accounting centers on the PBO calculation, the ABO still must be disclosed in the pension disclosure note. What is the company's accumulated benefit obligation at the end of 2024 with respect to Stanley Mills? 5. If we assume no estimates change in the meantime, what is the company's projected benefit obligation at the end of 2025 with respect to Stanley Mills? 6. What portion of the 2025 increase in the PBO is attributable to 2025 service (the service cost component of pension expense) and to accrued interest (the interest cost component of pension expense)?
Clark Industries has a defined benefit pension plan that specifies annual, year-end retirement benefits equal to: 1.3% x Service years x Final year's salary Stanley Mills was hired by Clark at the beginning of 2005. • Mills is expected to retire at the end of 2049 after 45 years of service. • His retirement is expected to span 15 years. At the end of 2024, 20 years after being hired, his salary is $81,000. • The company's actuary projects Mills's salary to be $280,000 at retirement. The actuary's discount rate is 8%. For all requirements, round final answers to the nearest whole dollars. Do not round intermediate calculations. Use tables, Excel, or a financial calculator. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1) Required: 1. Estimate the amount of Stanley Mills's annual retirement payments for the 15 retirement years earned as of the end of 2024. 2. Suppose Clark's pension plan permits a lump-sum payment at retirement in lieu of annuity payments. Determine the lump-sum equivalent as the present value as of the earned retirement annuity at the expected date of retirement (the end of 2049). 3. What is the company's projected benefit obligation at the end of 2024 with respect to Stanley Mills? 4. Even though pension accounting centers on the PBO calculation, the ABO still must be disclosed in the pension disclosure note. What is the company's accumulated benefit obligation at the end of 2024 with respect to Stanley Mills? 5. If we assume no estimates change in the meantime, what is the company's projected benefit obligation at the end of 2025 with respect to Stanley Mills? 6. What portion of the 2025 increase in the PBO is attributable to 2025 service (the service cost component of pension expense) and to accrued interest (the interest cost component of pension expense)?
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
3rd Edition
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Chapter19: Accounting For Post Retirement Benefits
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1E
Related questions
Question
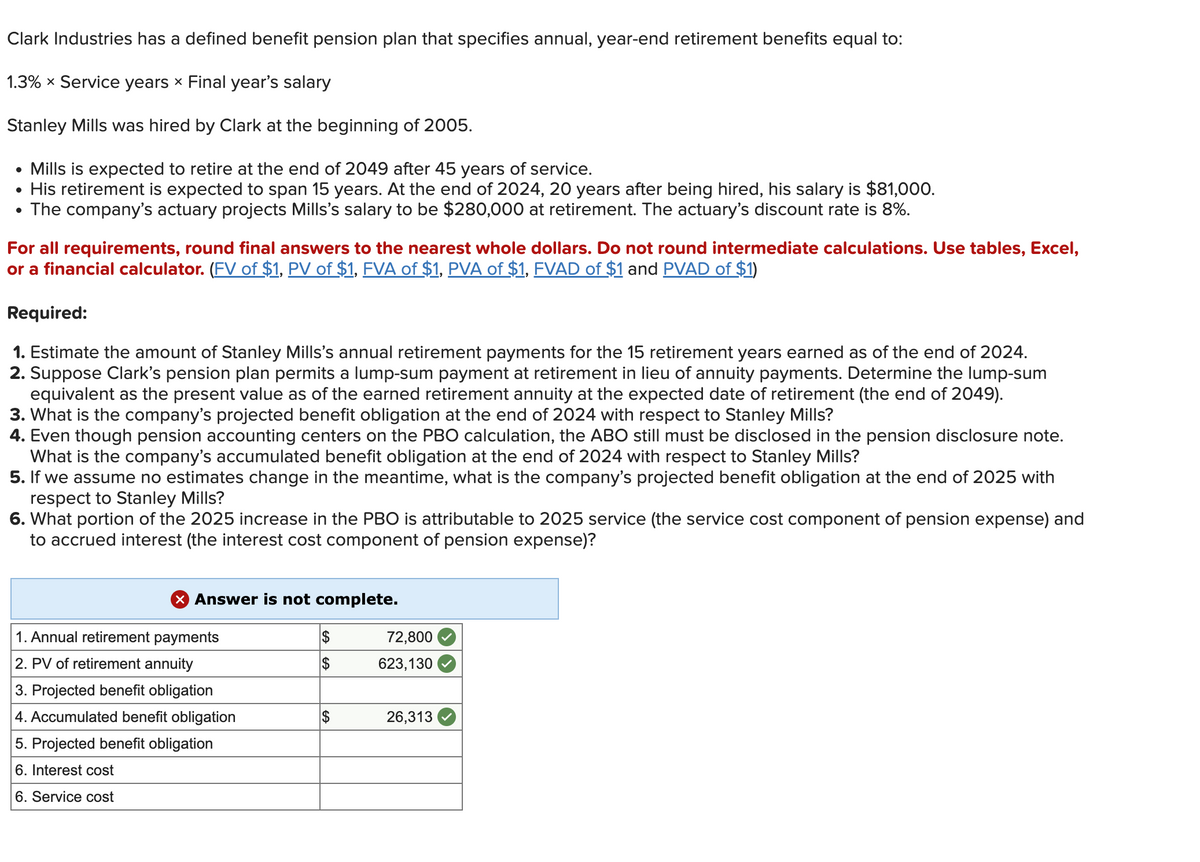
Transcribed Image Text:Clark Industries has a defined benefit pension plan that specifies annual, year-end retirement benefits equal to:
1.3% x Service years × Final year's salary
Stanley Mills was hired by Clark at the beginning of 2005.
• Mills is expected to retire at the end of 2049 after 45 years of service.
His retirement is expected to span 15 years. At the end of 2024, 20 years after being hired, his salary is $81,000.
• The company's actuary projects Mills's salary to be $280,000 at retirement. The actuary's discount rate is 8%.
For all requirements, round final answers to the nearest whole dollars. Do not round intermediate calculations. Use tables, Excel,
or a financial calculator. (FV of $1, PV of $1, FVA of $1, PVA of $1, FVAD of $1 and PVAD of $1)
Required:
1. Estimate the amount of Stanley Mills's annual retirement payments for the 15 retirement years earned as of the end of 2024.
2. Suppose Clark's pension plan permits a lump-sum payment at retirement in lieu of annuity payments. Determine the lump-sum
equivalent as the present value as of the earned retirement annuity at the expected date of retirement (the end of 2049).
3. What is the company's projected benefit obligation at the end of 2024 with respect to Stanley Mills?
4. Even though pension accounting centers on the PBO calculation, the ABO still must be disclosed in the pension disclosure note.
What is the company's accumulated benefit obligation at the end of 2024 with respect to Stanley Mills?
5. If we assume no estimates change in the meantime, what is the company's projected benefit obligation at the end of 2025 with
respect to Stanley Mills?
6. What portion of the 2025 increase in the PBO is attributable to 2025 service (the service cost component of pension expense) and
to accrued interest (the interest cost component of pension expense)?
X Answer is not complete.
1. Annual retirement payments
2. PV of retirement annuity
3. Projected benefit obligation
4. Accumulated benefit obligation
5. Projected benefit obligation
6. Interest cost
6. Service cost
$
$
72,800
623,130
26,313
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Individual Income Taxes
Accounting
ISBN:
9780357109731
Author:
Hoffman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:
9781337788281
Author:
James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Individual Income Taxes
Accounting
ISBN:
9780357109731
Author:
Hoffman
Publisher:
CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


