) Compute the Fourier transform of the function. (a) f(x) = h(x + 1) – 2h(x) + h(x - 1), where 1, if a> 1, 0, otherwise. h(r) = (b) g(r) = e-rlri, %3D
) Compute the Fourier transform of the function. (a) f(x) = h(x + 1) – 2h(x) + h(x - 1), where 1, if a> 1, 0, otherwise. h(r) = (b) g(r) = e-rlri, %3D
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter4: Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors
Section4.6: Applications And The Perron-frobenius Theorem
Problem 70EQ
Related questions
Question
5
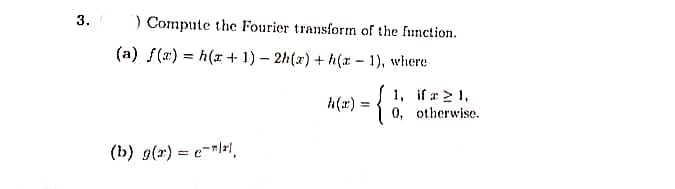
Transcribed Image Text:3.
) Compute the Fourier transform of the function.
(a) f(r) = h(x + 1) – 2h(x) + h(x - 1), where
{
1, if a> 1,
0, otherwise.
h(r) :
(b) g(r) = e-rli,
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps with 5 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning