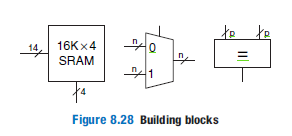
Consider a cache with the following parameters: N (associativity) = 2, b (block size) = 2 words, W (word size) = 32 bits, C (cache size) = 32 K words, A (address size) = 32 bits. You need consider only word addresses. (a) Show the tag, set, block offset, and byte offset bits of the address. State how many bits are needed for each field. (b) What is the size of all the cache tags in bits? (c) Suppose each cache block also has a valid bit (V) and a dirty bit (D). What is the size of each cache set, including data, tag, and status bits? (d) Design the cache using the building blocks in Figure 8.28 and a small number of two-input logic gates. The cache design must include tag storage, data storage, address comparison, data output selection, and any other parts you feel are relevant. Note that the multiplexer and comparator blocks may be any size (n or p bits wide, respectively), but the SRAM blocks must be 16K × 4 bits. Be sure to include a neatly labeled block diagram. You need only design the cache for reads.
Consider a cache with the following parameters: N (associativity) = 2, b (block size) = 2 words, W (word size) = 32 bits,
C (cache size) = 32 K words, A (address size) = 32 bits. You need consider only word addresses.
(a) Show the tag, set, block offset, and byte offset bits of the address. State how many bits are needed for each field.
(b) What is the size of all the cache tags in bits?
(c) Suppose each cache block also has a valid bit (V) and a dirty bit (D). What is the size of each cache set, including data, tag, and status bits?
(d) Design the cache using the building blocks in Figure 8.28 and a small number of two-input logic gates. The cache design must include tag storage, data storage, address comparison, data output selection, and any other parts you feel are relevant. Note that the multiplexer and comparator blocks may be any size (n or p bits wide, respectively), but the SRAM blocks must be 16K × 4 bits. Be sure to include a neatly labeled block diagram. You need only design the cache for reads.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps









