Consider an object that sinks to the bottom of a beaker of liquid. The object is a block with a weight of 20 N, when weighed in air. The beaker it is to be placed in contains some water, as well as a waterproof scale that rests on the bottom of the beaker. This scale is tared to read zero, and let's assume the scale is unaffected by any changes in the level of the water above it. The beaker itself rests on a second scale that reads 50 N, the combined weight of the beaker, the water, and the scale inside the beaker. When the 20-N block is placed in the beaker, it sinks to the bottom and comes to rest on the scale in the beaker, which now reads 5.0 N. This is known as the apparent weight of the block. Let's assume g = 10 m/s2 to simplify the calculations. What is the block's density? Select one: O a. 1200 kg/m3 O b. 1320 kg/m3 O c. 1330 kg/m3 d. 1400 kg/m3
Consider an object that sinks to the bottom of a beaker of liquid. The object is a block with a weight of 20 N, when weighed in air. The beaker it is to be placed in contains some water, as well as a waterproof scale that rests on the bottom of the beaker. This scale is tared to read zero, and let's assume the scale is unaffected by any changes in the level of the water above it. The beaker itself rests on a second scale that reads 50 N, the combined weight of the beaker, the water, and the scale inside the beaker. When the 20-N block is placed in the beaker, it sinks to the bottom and comes to rest on the scale in the beaker, which now reads 5.0 N. This is known as the apparent weight of the block. Let's assume g = 10 m/s2 to simplify the calculations. What is the block's density? Select one: O a. 1200 kg/m3 O b. 1320 kg/m3 O c. 1330 kg/m3 d. 1400 kg/m3
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter8: Centroids And Distributed Loads
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8.121P: One side of the container has a 03-m square door that is hinged at its top edge. If the container is...
Related questions
Topic Video
Question
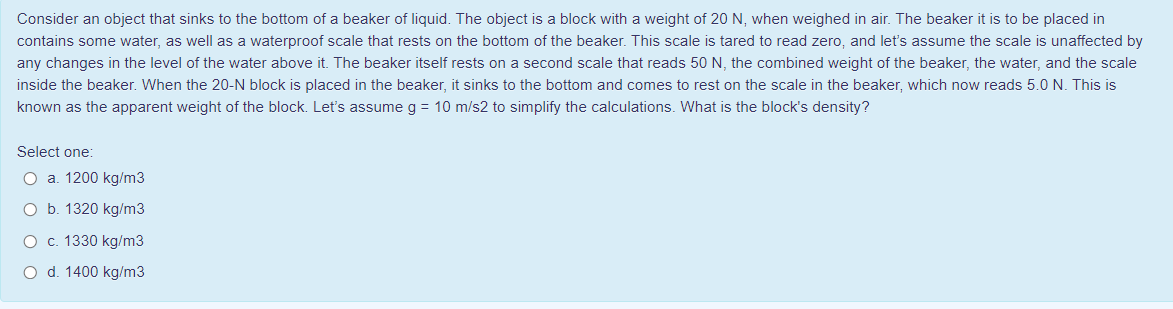
Transcribed Image Text:Consider an object that sinks to the bottom of a beaker of liquid. The object is a block with a weight of 20 N, when weighed in air. The beaker it is to be placed in
contains some water, as well as a waterproof scale that rests on the bottom of the beaker. This scale is tared to read zero, and let's assume the scale is unaffected by
any changes in the level of the water above it. The beaker itself rests on a second scale that reads 50 N, the combined weight of the beaker, the water, and the scale
inside the beaker. When the 20-N block is placed in the beaker, it sinks to the bottom and comes to rest on the scale in the beaker, which now reads 5.0 N. This is
known as the apparent weight of the block. Let's assume g = 10 m/s2 to simplify the calculations. What is the block's density?
Select one:
O a. 1200 kg/m3
O b. 1320 kg/m3
O c. 1330 kg/m3
O d. 1400 kg/m3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L