Consider the depicted state for relation R in the table below: C y 2. Which of the following statements regarding functional dependencies in R is correct? Functional dependency B>C may hold, but C B cannot hold. Functional dependency C B may hold, but B C cannot hold. Functional dependency A→C may hold, but C A cannot hold. Functional dependency C-A may hold, but A→C cannot hold.
Consider the depicted state for relation R in the table below: C y 2. Which of the following statements regarding functional dependencies in R is correct? Functional dependency B>C may hold, but C B cannot hold. Functional dependency C B may hold, but B C cannot hold. Functional dependency A→C may hold, but C A cannot hold. Functional dependency C-A may hold, but A→C cannot hold.
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Management
11th Edition
ISBN:9781285196145
Author:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos Coronel
Publisher:Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos Coronel
Chapter5: Advanced Data Modeling
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 8RQ: According to the data model, is it required that every entity instance in the PRODUCT table be...
Related questions
Question
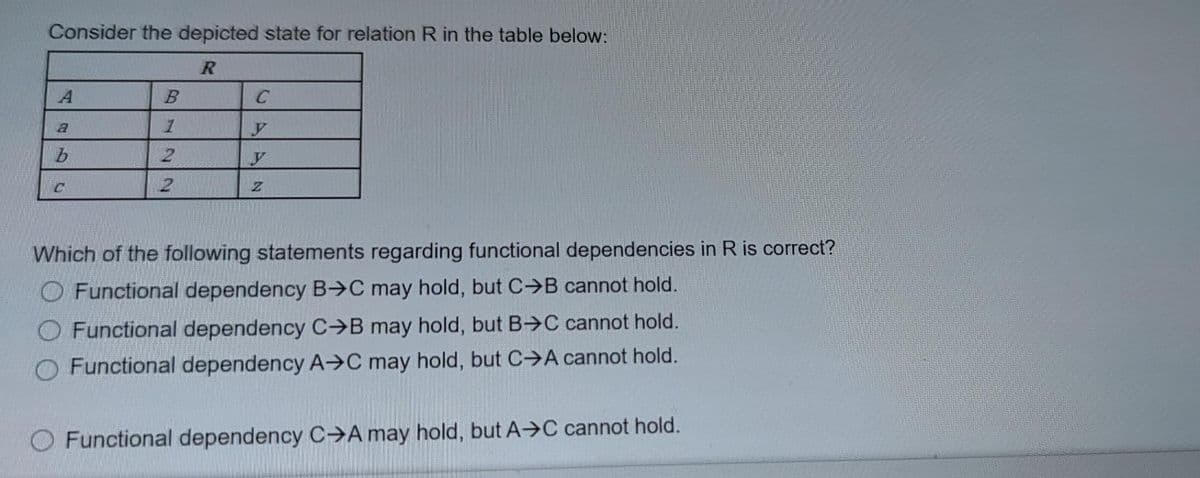
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the depicted state for relation R in the table below:
C
Which of the following statements regarding functional dependencies in R is correct?
O Functional dependency B C may hold, but C B cannot hold.
O Functional dependency C>B may hold, but B→C cannot hold.
O Functional dependency A→C may hold, but C>A cannot hold.
O Functional dependency C→A may hold, but A→C cannot hold.

Transcribed Image Text:QUESTION 8
The principal difference between a weak and strong entity in the Entity-Relationship model is best characterized by which of the following?
Strong entities cannot have attributes.
A weak entity exists in the model regardless of its affiliation with other entities, while a strong entity exists solely due to its relationship to one
or more weak entities in the model.
O Weak entities cannot have attributes.
A strong entity exists in the model regardless of its affiliation with other entities, while a weak entity exists solely due to its relationship to one
or more strong entities in the model.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285196145
Author:
Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos Coronel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305627482
Author:
Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781285196145
Author:
Steven, Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel, Carlos, Coronel, Carlos; Morris, Carlos Coronel and Steven Morris, Carlos Coronel; Steven Morris, Steven Morris; Carlos Coronel
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag…
Computer Science
ISBN:
9781305627482
Author:
Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:
Cengage Learning