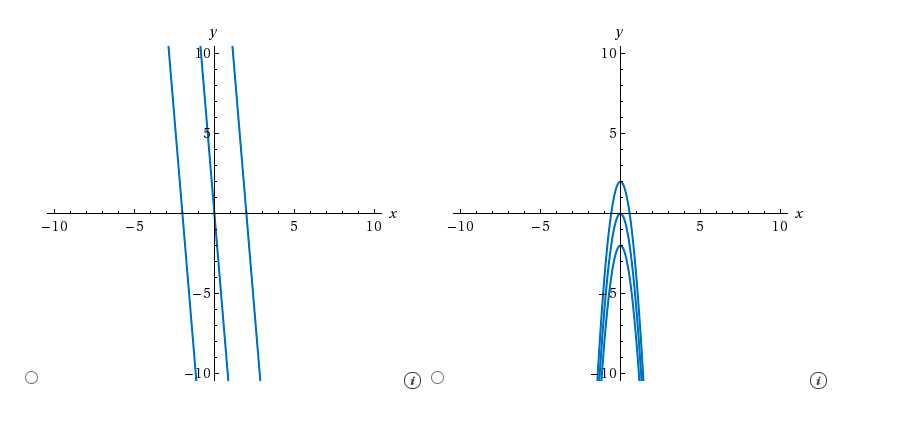
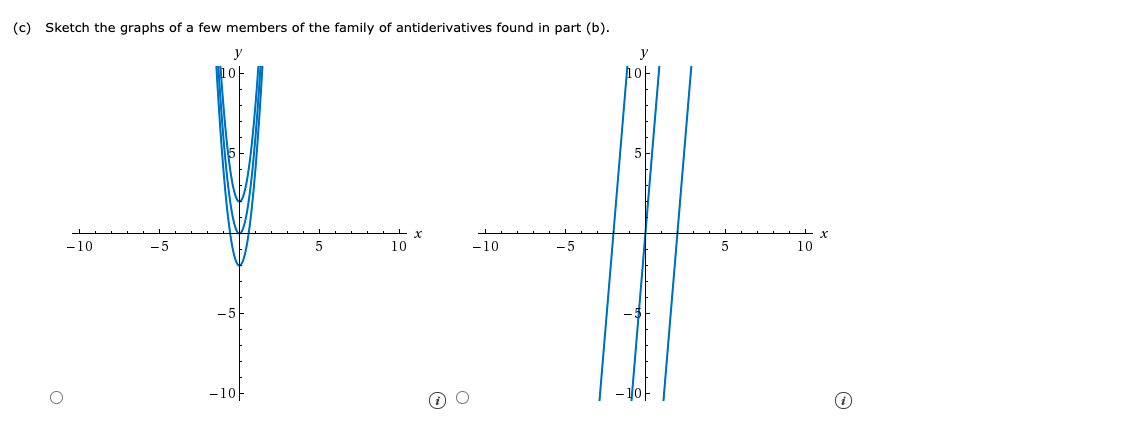
Consider the following functions. G(x) = 6x2; f(x) = 12x (a) Verify that G is an antiderivative of f. (1) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because f '(x) = G(x) for all x. (2) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because G(x) = f(x) + C for all x. (3) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because f(x) = G(x) + C for all x. (4) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because G(x) = f(x) for all x. (5)G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because G'(x) = f(x) for all x. (b) Find all antiderivatives of f. (Use C for the constant of integration.) (c) in photo
Consider the following functions. G(x) = 6x2; f(x) = 12x (a) Verify that G is an antiderivative of f. (1) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because f '(x) = G(x) for all x. (2) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because G(x) = f(x) + C for all x. (3) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because f(x) = G(x) + C for all x. (4) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because G(x) = f(x) for all x. (5)G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because G'(x) = f(x) for all x. (b) Find all antiderivatives of f. (Use C for the constant of integration.) (c) in photo
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
10th Edition
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
ChapterP: Prerequisites
SectionP.6: Analyzing Graphs Of Functions
Problem 6ECP: Find the average rates of change of f(x)=x2+2x (a) from x1=3 to x2=2 and (b) from x1=2 to x2=0.
Related questions
Question
Consider the following functions.
G(x) = 6x2; f(x) = 12x
(a) Verify that G is an antiderivative of f.
(1) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because f '(x) = G(x) for all x.
(2) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because G(x) = f(x) + C for all x.
(3) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because f(x) = G(x) + C for all x.
(4) G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because G(x) = f(x) for all x.
(5)G(x) is an antiderivative of f(x) because G'(x) = f(x) for all x.
(b) Find all antiderivatives of f. (Use C for the constant of integration .)
(c) in photo
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:
9781337278461
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning