Consider the following Tarski world (same world as the previous question, but different questions): AO d. e h Predicates exist as follows: Blue(x) means "x is blue" (and similarly for the other two colors) Triangle(x) means "x is a triangle" (and similarly for the other two shapes) RightOf(x.y) means "x is to the right of y" although possibly in a different row. ShapeSame(x.y) means x is the same shape as y" ColorSame(x,y) means "x is the same color as y RowSame(x.y) means "x is in the same row as y For each of the following statements, say whether the statement is T or F, and then say why. When saying why, you may use the letter c to refer to shape c on the Tarski world, and so on. a) 3 x, Vy, Square(x) ^ (Blue(y) v ~ RightOf(x,y)) Tor F: If False, give a value for y for which no such x exists. If True, give a value for x for which the statement is True: b) Vx, Vy, (x*y a RowSame(x,y) →(~ ShapeSame(x,y) ^ ~ColorSame(x,y)) Tor F: If False, give values for x, y for which the statement is false. If True, describe the meaning of the statement in words (one sentence): c) 3w, Vv, (w- v) → RightOf(v, w) Tor F: If True, give a value of w for which it is true; if False, give a value for v for which there is no such w:
Consider the following Tarski world (same world as the previous question, but different questions): AO d. e h Predicates exist as follows: Blue(x) means "x is blue" (and similarly for the other two colors) Triangle(x) means "x is a triangle" (and similarly for the other two shapes) RightOf(x.y) means "x is to the right of y" although possibly in a different row. ShapeSame(x.y) means x is the same shape as y" ColorSame(x,y) means "x is the same color as y RowSame(x.y) means "x is in the same row as y For each of the following statements, say whether the statement is T or F, and then say why. When saying why, you may use the letter c to refer to shape c on the Tarski world, and so on. a) 3 x, Vy, Square(x) ^ (Blue(y) v ~ RightOf(x,y)) Tor F: If False, give a value for y for which no such x exists. If True, give a value for x for which the statement is True: b) Vx, Vy, (x*y a RowSame(x,y) →(~ ShapeSame(x,y) ^ ~ColorSame(x,y)) Tor F: If False, give values for x, y for which the statement is false. If True, describe the meaning of the statement in words (one sentence): c) 3w, Vv, (w- v) → RightOf(v, w) Tor F: If True, give a value of w for which it is true; if False, give a value for v for which there is no such w:
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.4: Applications
Problem 33EQ
Related questions
Question
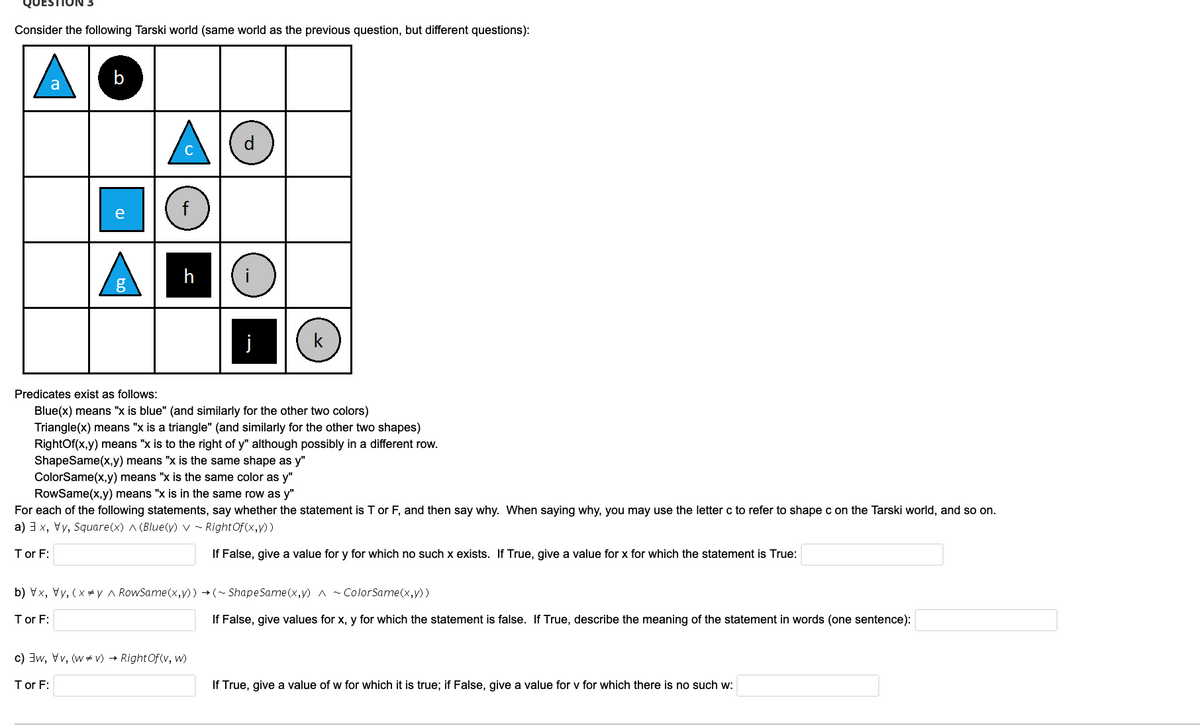
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the following Tarski world (same world as the previous question, but different questions):
A
b
a
h
j
k
Predicates exist as follows:
Blue(x) means "x is blue" (and similarly for the other two colors)
Triangle(x) means "x is a triangle" (and similarly for the other two shapes)
RightOf(x,y) means "x is to the right of y" although possibly in a different row.
ShapeSame(x,y) means "x is the same shape as y"
ColorSame(x,y) means "x is the same color as y"
RowSame(x,y) means "x is in the same row as y"
For each of the following statements, say whether the statement is T or F, and then say why. When saying why, you may use the letter c to refer to shape c on the Tarski world, and so on.
a) 3 x, Vy, Square(x) ^ (Blue(y) v ~ RightOf(x,y))
Tor F:
If False, give a value for y for which no such x exists. If True, give a value for x for which the statement is True:
b) Vx, Vy, (xy ^ RowSame(x,y)) → (~ Shape Same(x,y) A ~ ColorSame(x,y))
T or F:
If False, give values for x, y for which the statement is false. If True, describe the meaning of the statement in words (one sentence):
c) 3w, Vv, (w # v) → RightOf (v, w)
Tor F:
If True, give a value of w for which it is true; if False, give a value for v for which there is no such w:
Expert Solution
Step 1

Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Elementary Geometry for College Students
Geometry
ISBN:
9781285195698
Author:
Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. Koeberlein
Publisher:
Cengage Learning