Consider the function f (x) = x-3 x+3 (a) Find the domain of f(x). Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter oo, type infinity. Domain: (b) Give the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of f(x), if any. Enter the equations for the asymptotes. If there is no horizontal or vertical asymptote, enter NA in the associated response area. horizontal asymptote: vertical asymptote:
Consider the function f (x) = x-3 x+3 (a) Find the domain of f(x). Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter oo, type infinity. Domain: (b) Give the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of f(x), if any. Enter the equations for the asymptotes. If there is no horizontal or vertical asymptote, enter NA in the associated response area. horizontal asymptote: vertical asymptote:
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter4: Polynomial And Rational Functions
Section4.5: Rational Functions
Problem 54E
Related questions
Question
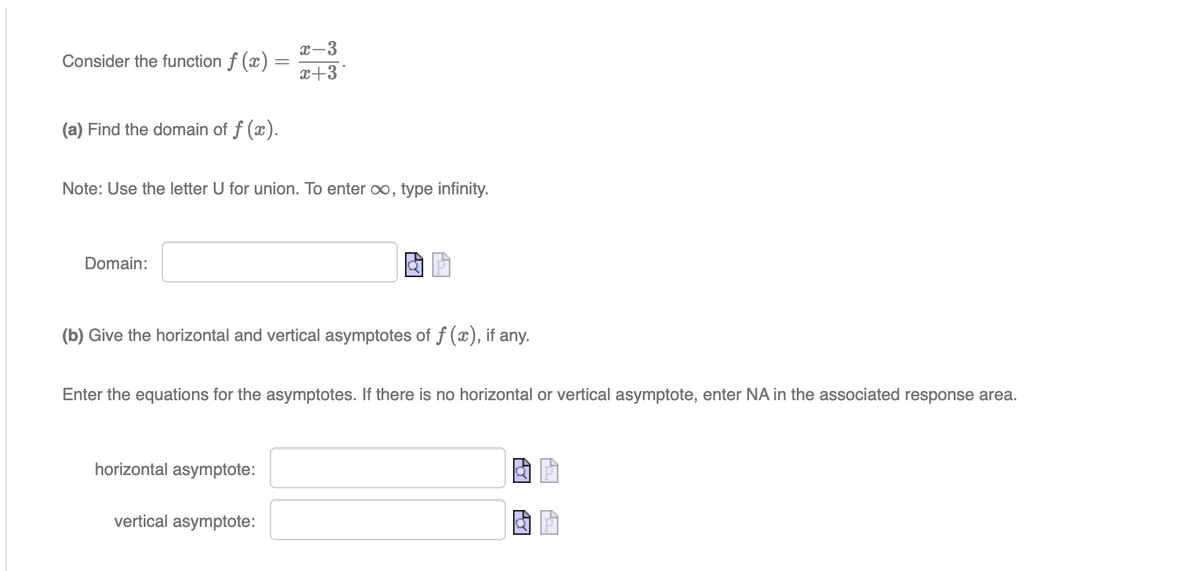
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the function ƒ (x) =
X- -3
x+3*
(a) Find the domain of f(x).
Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter ∞, type infinity.
Domain:
(b) Give the horizontal and vertical asymptotes of f (x), if any.
Enter the equations for the asymptotes. If there is no horizontal or vertical asymptote, enter NA in the associated response area.
horizontal asymptote:
vertical asymptote:
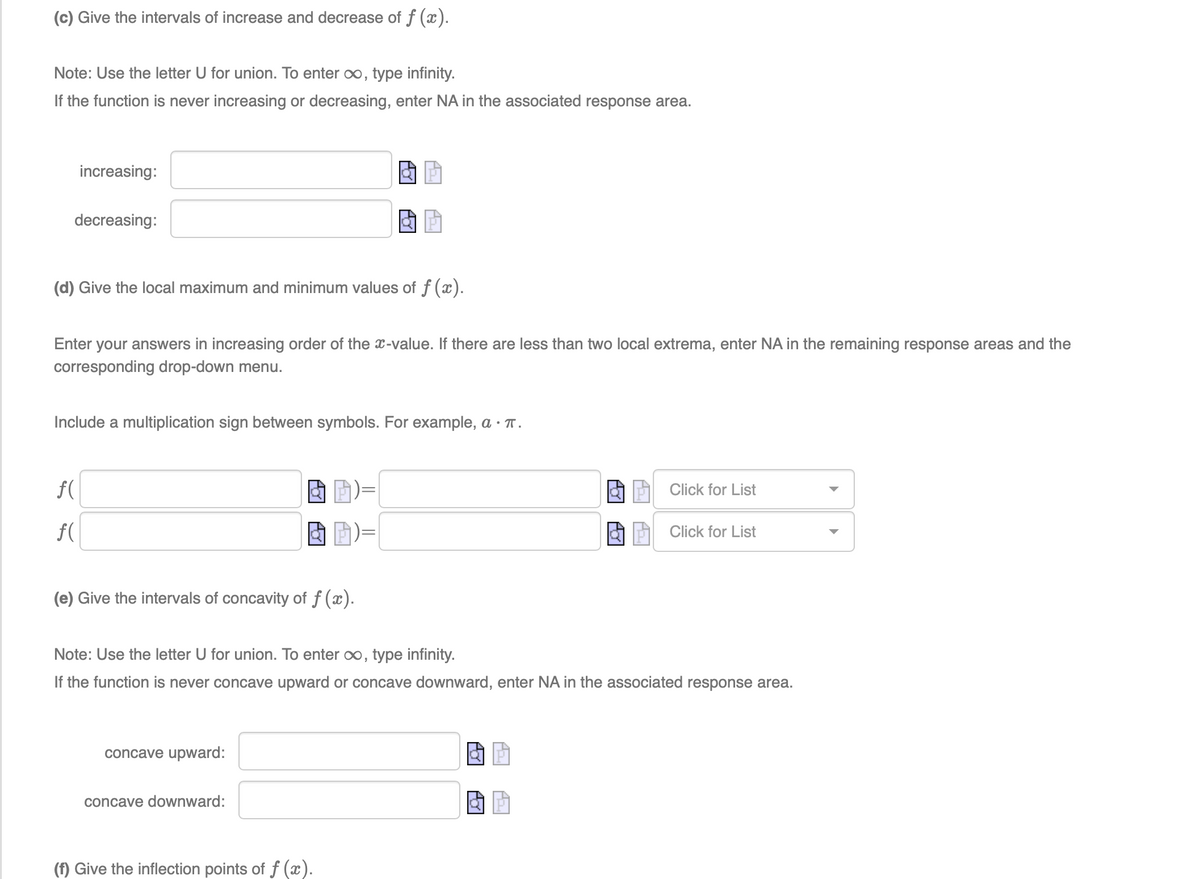
Transcribed Image Text:(c) Give the intervals of increase and decrease of f(x).
Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter ∞, type infinity.
If the function is never increasing or decreasing, enter NA in the associated response area.
increasing:
decreasing:
(d) Give the local maximum and minimum values of f(x).
Enter your answers in increasing order of the x-value. If there are less than two local extrema, enter NA in the remaining response areas and the
corresponding drop-down menu
Include a multiplication sign between symbols. For example, a . π.
Click for List
f(
f(
Click for List
(e) Give the intervals of concavity of f(x).
Note: Use the letter U for union. To enter ∞, type infinity.
If the function is never concave upward or concave downward, enter NA in the associated response area.
concave upward:
concave downward:
(f) Give the inflection points of f (x).
Po
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning


Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305115545
Author:
James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning
