Consider the polar curves C₁ : r = 3 (in blue) and C₂: r = 2-2 sin (in red) and let R be the shaded region as shown in the figure below. 1. Find all point/s of intersection of C₁ and C₂. Write your answer as polar coordinates (r, 0), where r > 0, 0 [0, 2π). 2. Set up an integral for the perimeter of R. 3. Set up an integral for the area of R.
Consider the polar curves C₁ : r = 3 (in blue) and C₂: r = 2-2 sin (in red) and let R be the shaded region as shown in the figure below. 1. Find all point/s of intersection of C₁ and C₂. Write your answer as polar coordinates (r, 0), where r > 0, 0 [0, 2π). 2. Set up an integral for the perimeter of R. 3. Set up an integral for the area of R.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18T
Related questions
Question
100%
ANSWER EVERYTHING COMPLETELY, TYPEWRITTEN, AND CORRECT. NO SHORTCUTS. DO IT STEP BY STEP WITH BRIEF EXPLANATIONS. NO HANDWRITTEN PLEASE. I WANT TYPEWRITTEN. IF YOU DO ALL OF THIS. I WILL UPVOTE. SKIP THIS IF YOU ALREADY DID THIS.
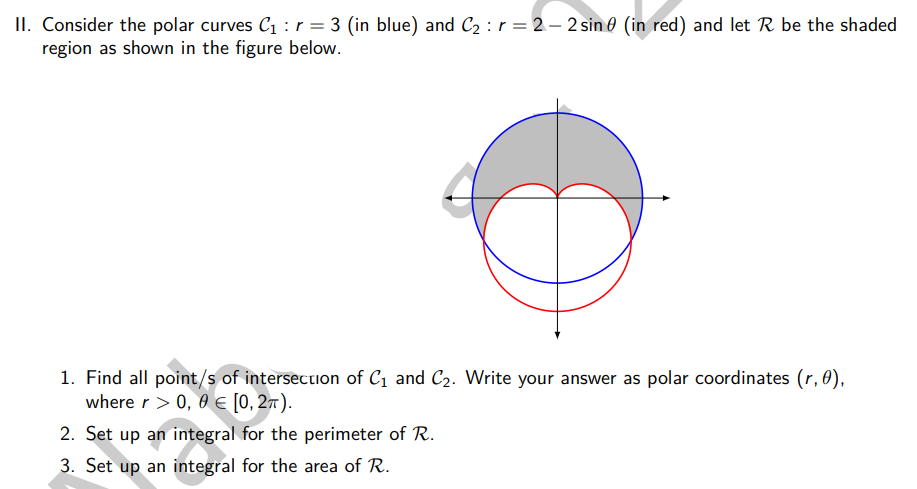
Transcribed Image Text:II. Consider the polar curves C₁ : r = 3 (in blue) and C₂ : r = 2-2 sin (in red) and let R be the shaded
region as shown in the figure below.
1. Find all point/s of intersection of C₁ and C₂. Write your answer as polar coordinates (r, 0),
where r > 0, 0 € [0, 2π).
2. Set up an integral for the perimeter of R.
3. Set up an integral for the area of R.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage