Consider the polar curves r = 2 sin 0 + cos 0 and r = sin 0 + 2 cos 0 as shown in the figure below. r= 2 sin 0 + cos 0 r= sin 0 + 2 cos 0 (a) Find the value of 0 where the curves intersect in the first quadrant. (b) Set up, but DO NOT EVALUATE, an integral or integrals for the area of the shaded region.
Consider the polar curves r = 2 sin 0 + cos 0 and r = sin 0 + 2 cos 0 as shown in the figure below. r= 2 sin 0 + cos 0 r= sin 0 + 2 cos 0 (a) Find the value of 0 where the curves intersect in the first quadrant. (b) Set up, but DO NOT EVALUATE, an integral or integrals for the area of the shaded region.
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter11: Topics From Analytic Geometry
Section11.4: Plane Curves And Parametric Equations
Problem 53E
Related questions
Question
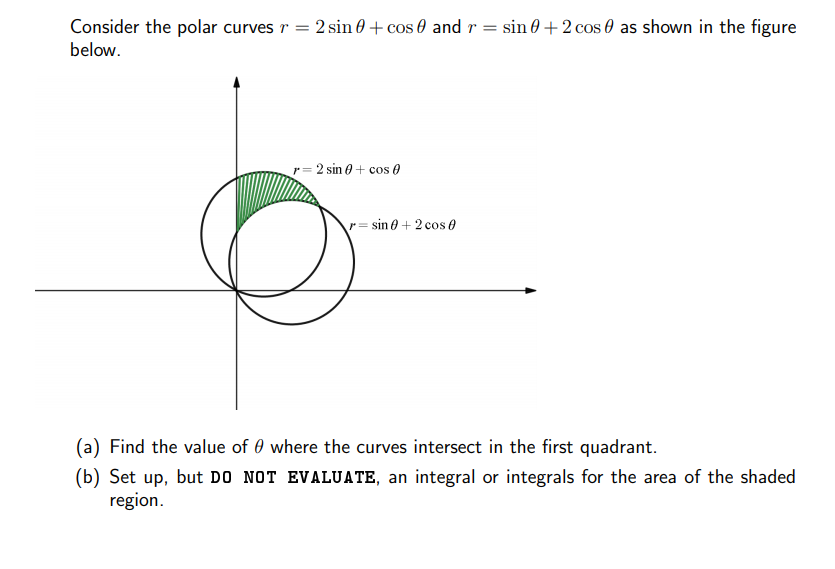
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the polar curves r = 2 sin 0 + cos 0 and r = sin 0 + 2 cos 0 as shown in the figure
below.
r= 2 sin 0 + cos 0
r= sin 0 + 2 cos 0
(a) Find the value of 0 where the curves intersect in the first quadrant.
(b) Set up, but DO NOT EVALUATE, an integral or integrals for the area of the shaded
region.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage