Consider the three sets: {D} (a) For each set above, determine if it is an orthogonal set and if it is a basis for R. (b) A normal basis consists of vectors length one and an orthonormal basis consists of vectors that are orthogonal to one another and length one. Convert an orthogonal basis from above into an orthonormal basis {ủ1, ū2, ūz} (without changing the direction of the vectors).
Consider the three sets: {D} (a) For each set above, determine if it is an orthogonal set and if it is a basis for R. (b) A normal basis consists of vectors length one and an orthonormal basis consists of vectors that are orthogonal to one another and length one. Convert an orthogonal basis from above into an orthonormal basis {ủ1, ū2, ūz} (without changing the direction of the vectors).
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305658004
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
Chapter5: Inner Product Spaces
Section5.3: Orthonormal Bases:gram-schmidt Process
Problem 17E: Complete Example 2 by verifying that {1,x,x2,x3} is an orthonormal basis for P3 with the inner...
Related questions
Question
100%
Do both parts ASAP
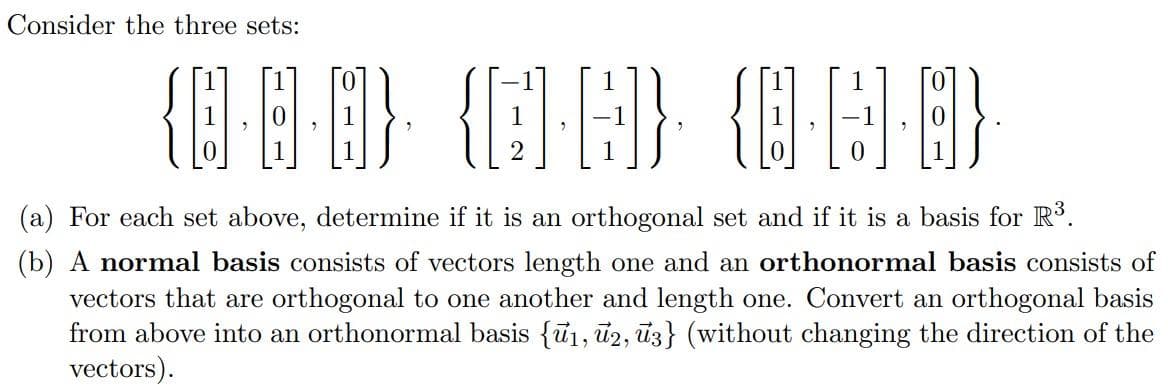
Transcribed Image Text:Consider the three sets:
(a) For each set above, determine if it is an orthogonal set and if it is a basis for R³.
(b) A normal basis consists of vectors length one and an orthonormal basis consists of
vectors that are orthogonal to one another and length one. Convert an orthogonal basis
from above into an orthonormal basis {u1, ủ2, ū3} (without changing the direction of the
vectors).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning