Considering that it rotates with a constant angular speed, which one of the following statements is false for the link shown below? L2 a. Normal component of the acceleration vector at Point A is always directed towards Point C. IfL1 and L2 were equal in length, the magnitude of the normal component of acceleration at Points Band C both would be b. equal. IfLy and L2 were equal in length, the magnitude of the tangential component of acceleration at Points Band Cwould not be equal to each other. d. Normal component of the acceleration vector at Point Bis always directed towards Point C. QUESTION 3 Given that the link in Question 2 is rotating clockwise with 4.3 radis and accelerating with 5.7 radis?, and L 2.86 in, L2n 4.29 in, V(gamma) - 12.3 deg, and p(beta) - 26.9 deg What is the magnitude of acceleration at Point B in in/s? QUESTION 4 Given that the link in Question #2 is rotating clockwise with 2.8 rad/s and accelerating with 45.1 rad/s, and L1 - 2.23 in, L2n 4.61 in, y (gamma) - 2.6 deg and p(beta) - 30.1 deg What is the angle between the acceleration vector at Point A and the horizontal? Please note that you must enter the angle that is less than 90 deg.
Considering that it rotates with a constant angular speed, which one of the following statements is false for the link shown below? L2 a. Normal component of the acceleration vector at Point A is always directed towards Point C. IfL1 and L2 were equal in length, the magnitude of the normal component of acceleration at Points Band C both would be b. equal. IfLy and L2 were equal in length, the magnitude of the tangential component of acceleration at Points Band Cwould not be equal to each other. d. Normal component of the acceleration vector at Point Bis always directed towards Point C. QUESTION 3 Given that the link in Question 2 is rotating clockwise with 4.3 radis and accelerating with 5.7 radis?, and L 2.86 in, L2n 4.29 in, V(gamma) - 12.3 deg, and p(beta) - 26.9 deg What is the magnitude of acceleration at Point B in in/s? QUESTION 4 Given that the link in Question #2 is rotating clockwise with 2.8 rad/s and accelerating with 45.1 rad/s, and L1 - 2.23 in, L2n 4.61 in, y (gamma) - 2.6 deg and p(beta) - 30.1 deg What is the angle between the acceleration vector at Point A and the horizontal? Please note that you must enter the angle that is less than 90 deg.
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Chapter1: Introduction To Statics
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1.19P: Plot the earths gravitational acceleration g(m/s2) against the height h (km) above the surface of...
Related questions
Question
Do question 3 Please
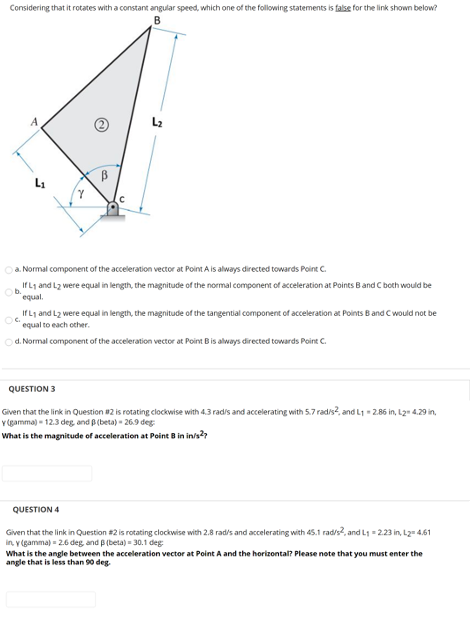
Transcribed Image Text:Considering that it rotates with a constant angular speed, which one of the following statements is false for the link shown below?
B
A
L2
a. Normal component of the acceleration vector at Point A is always directed towards Point C.
IfL1 and Lz were equal in length, the magnitude of the normal component of acceleration at Points Band C both would be
b.
equal.
If L1 and Lz were equal in length, the magnitude of the tangential component of acceleration at Points B and Cwould not be
equal to each other.
d. Normal component of the acceleration vector at Point Bis always directed towards Point C.
QUESTION 3
Given that the link in Question #2 is rotating clockwise with 4.3 radis and accelerating with 5.7 radis?, and L1 - 2.86 in, L2" 4.29 in,
Y(gamma) - 12.3 deg, and B(beta) - 26.9 deg
What is the magnitude of acceleration at Point B in in/s2?
QUESTION 4
Given that the link in Question #2 is rotating clockwise with 2.8 rad's and accelerating with 45.1 rad/s?, and L1 = 223 in, L2= 4.61
in, y (gamma) = 2.6 deg and p (beta) = 30.1 deg
What is the angle between the acceleration vector at Point A and the horizontal? Please note that you must enter the
angle that is less than 90 deg.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Question (3)
Given:
- The angular velocity of the link is ,
- The angular acceleration of the link is ,
- ,
- .
The resultant of tangential and radial acceleration will give the total acceleration at point B.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St…
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:
9781305501607
Author:
Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:
CENGAGE L