(d) Show that the logical connectives ¬, A, and V can each be expressed entirely in terms of ↓, without using any other logical connectives. Specifically, prove the following: i. ¬P = (P↓ P). ii. PAQ (P↓ P) ↓ (Q ↓ Q). = iii. PV Q = (P↓ Q) ↓ (P ↓ Q). (e) Prove that the logical connective ⇒ can be expressed entirely in terms of ↓. That is, show that the sentence P⇒ Q is logically equivalent to a sentence involving ↓ and no other logical connectives.
(d) Show that the logical connectives ¬, A, and V can each be expressed entirely in terms of ↓, without using any other logical connectives. Specifically, prove the following: i. ¬P = (P↓ P). ii. PAQ (P↓ P) ↓ (Q ↓ Q). = iii. PV Q = (P↓ Q) ↓ (P ↓ Q). (e) Prove that the logical connective ⇒ can be expressed entirely in terms of ↓. That is, show that the sentence P⇒ Q is logically equivalent to a sentence involving ↓ and no other logical connectives.
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
(REV)00th Edition
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Chapter10: Inequalities
Section10.3: Solving Problems Involving Inequalities
Problem 28E
Related questions
Question
I have gotten the first three done but need help with the last two please show work.

Transcribed Image Text:Step 1
Disclaimer: Since you have posted a question with multiple sub-parts, we will solve first three sub-parts
for you. To get remaining sub-parts solved please repost the complete question and mention the sub-
parts to be solved.
The logical symbol "v" is used to denote "OR". The logical symbol "-" is used to denote "NOT".
Any two propositions are said to be logically equivalent if the truth value in each row of the truth table is
the same for both propositions.
(a)
It is provided that P↓Q is true if both P, Q are false and false in all other scenarios. Use this data to make
the truth table of P↓Q as follows.
P
Q
T
T
T
F
F
T
F
F
F
T
Make the truth table of ¬PvQ as follows.
P
Q
PVQ
T
P
T
T
T
T
F
T
F
T
וד
F
F
F
F
F
T
Comparing the last columns of both truth tables, it can be concluded that the expressions: P+Q and
PvQ are logically equivalent.
Q
(b)
Make the truth table of QvP as follows.
P
Q
T
T
T
F
F
F
Comparing the last columns of both truth tables, it can be concluded that the expressions: P Q and QvP
are logically equivalent. Hence, is commutative.
T
T
F
T
FL
F
T
T
T
F
(c)
Make the truth table of P Q R and P Q R as follows.
P↓↓
R
T
F
R
T
F
T
F
T
F
T
P+Q
F
F
F
LL
P↓Q
F
F
F
F
T
F
T
T
Q+P
F
F
F
T
F
T
F
T
-PVQ
F
T
F
Q&R
F
F
F
T
F
F
F
F
F
F
P↓Q
R
F
F
F
F
T
T
T
F
F
F
T
F
T
F
Comparing the columns of P Q R and P Q R, it can be concluded that the expressions: P+Q+R and
P Q R are logically not equivalent. Hence, it is proved that is not associative.
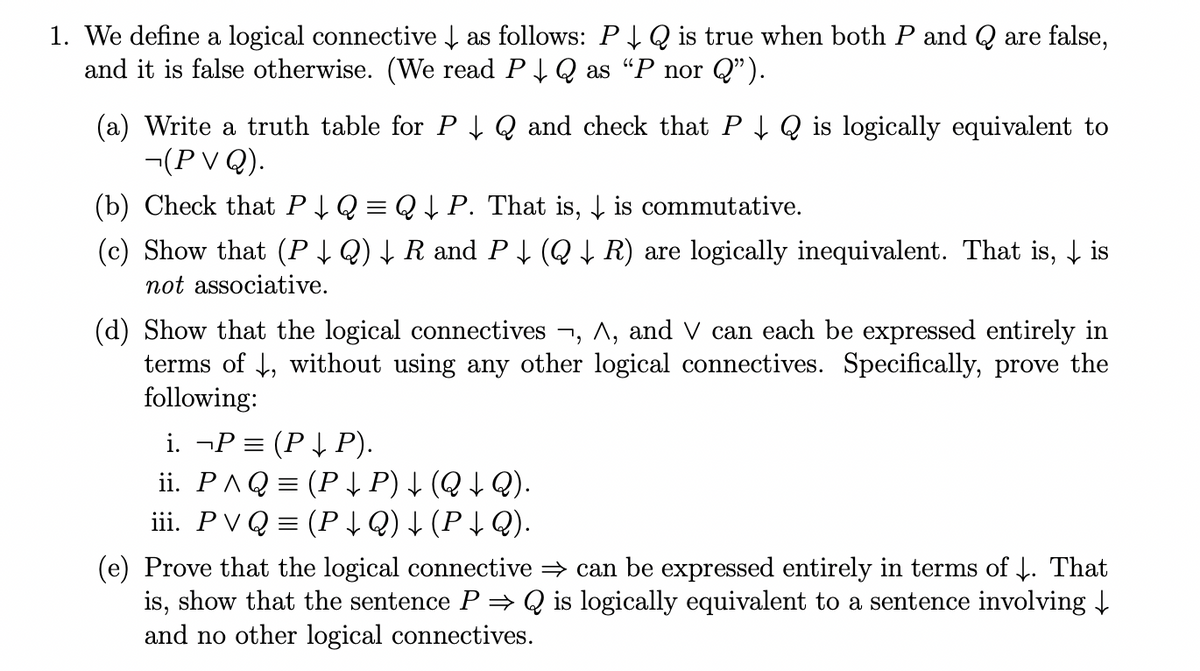
Transcribed Image Text:1. We define a logical connective ↓ as follows: P↓ Q is true when both P and Q are false,
and it is false otherwise. (We read P↓ Q as "P nor Q”).
(a) Write a truth table for P↓ Q and check that P↓ Q is logically equivalent to
¬(P V Q).
(b) Check that P↓ Q = Q ↓ P. That is, is commutative.
(c) Show that (P ↓ Q) ↓ R and P ↓ (Q ↓ R) are logically inequivalent. That is, ↓ is
not associative.
(d) Show that the logical connectives ¬, A, and V can each be expressed entirely in
terms of ↓, without using any other logical connectives. Specifically, prove the
following:
i. ¬P = (P ↓ P).
ii. P^Q = (P ↓ P) ↓ (Q ↓ Q).
iii. PVQ (P ↓Q) ↓ (P↓ Q).
(e) Prove that the logical connective ⇒ can be expressed entirely in terms of ↓. That
is, show that the sentence P⇒ Q is logically equivalent to a sentence involving ↓
and no other logical connectives.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 26 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:
9780395977224
Author:
Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:
McDougal Littell