Determine whether the set, together with the indicated operations, is a vector space. If it is not, then identify one of the vector space axioms that fails. The set of all 4 x 4 matrices of the form oba bo b a C COb а а с 1 with the standard operations O The set is a vector space. O The set is not a vector space because it is not closed under addition. O The set is not a vector space because it does not satisfy the associative property of addition. O The set is not a vector space because a scalar identity does not exist. O The set is not a vector space because it does not satisfy the distributive property. Need Help? Watch It Read It 6. DETAILS LARLINALG8 4.2.020. Determine whether the set, together with the indicated operations, is a vector space. If it is not, then identify one of the vector space axioms that fails. The set of all quadratic functions whose graphs pass through the point (0, 5) with the standard operations The set is a vector space. O The set is not a vector space because it is not closed under addition. O The set is not a vector space because the commutative property of addition is not satisfied. O The set is not a vector space because the associative property of addition is not satisfied. O The set is not a vector space because a scalar identity does not exist. Need Help? Read It Watch It
Determine whether the set, together with the indicated operations, is a vector space. If it is not, then identify one of the vector space axioms that fails. The set of all 4 x 4 matrices of the form oba bo b a C COb а а с 1 with the standard operations O The set is a vector space. O The set is not a vector space because it is not closed under addition. O The set is not a vector space because it does not satisfy the associative property of addition. O The set is not a vector space because a scalar identity does not exist. O The set is not a vector space because it does not satisfy the distributive property. Need Help? Watch It Read It 6. DETAILS LARLINALG8 4.2.020. Determine whether the set, together with the indicated operations, is a vector space. If it is not, then identify one of the vector space axioms that fails. The set of all quadratic functions whose graphs pass through the point (0, 5) with the standard operations The set is a vector space. O The set is not a vector space because it is not closed under addition. O The set is not a vector space because the commutative property of addition is not satisfied. O The set is not a vector space because the associative property of addition is not satisfied. O The set is not a vector space because a scalar identity does not exist. Need Help? Read It Watch It
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter7: Distance And Approximation
Section7.1: Inner Product Spaces
Problem 44EQ
Related questions
Question
Pls answer this 2
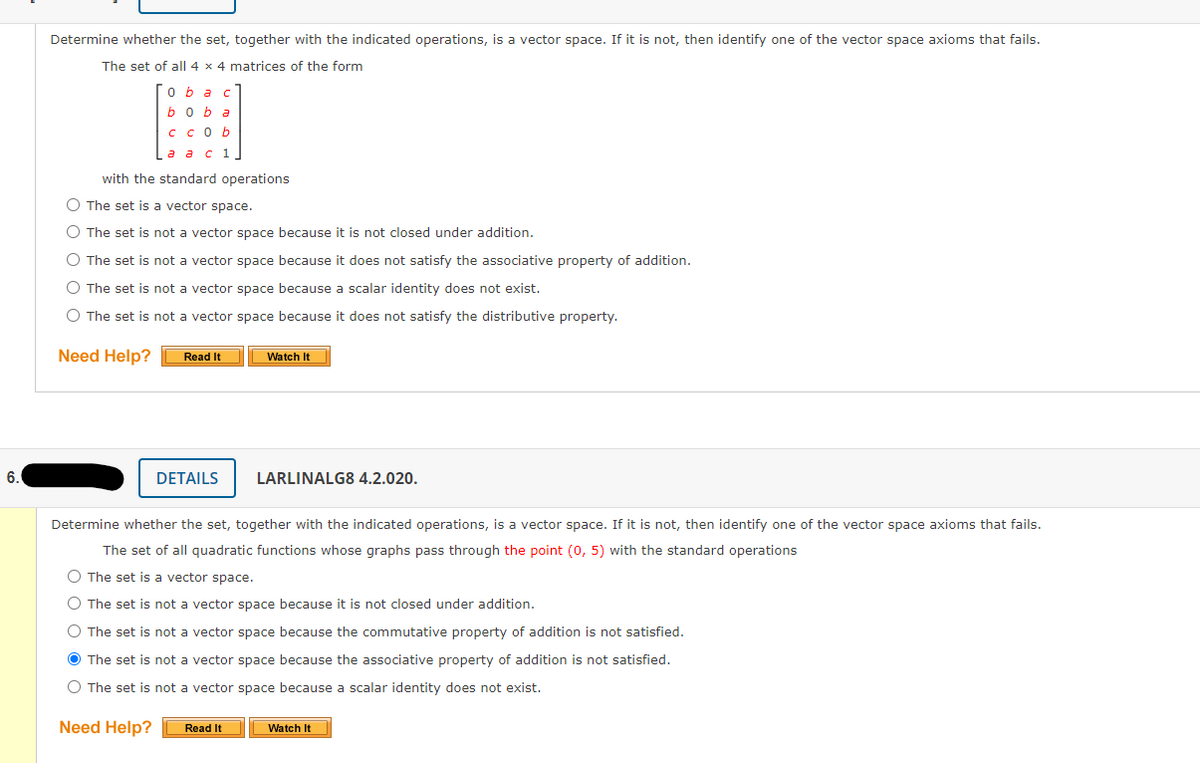
Transcribed Image Text:Determine whether the set, together with the indicated operations, is a vector space. If it is not, then identify one of the vector space axioms that fails.
The set of al| 4 x 4 matrices of the form
O b ac
b 0
a
C COb
а ас
1
with the standard operations
O The set is a vector space.
O The set is not a vector space because it is not closed under addition.
O The set is not a vector space because it does not satisfy the associative property of addition.
O The set is not a vector space because a scalar identity does not exist.
O The set is not a vector space because it does not satisfy the distributive property.
Need Help?
Read It
Watch It
6.
DETAILS
LARLINALG8 4.2.020.
Determine whether the set, together with the indicated operations, is a vector space. If it is not, then identify one of the vector space axioms that fails.
The set of all quadratic functions whose graphs pass through the point (0, 5) with the standard operations
O The set is a vector space.
O The set is not a vector space because it is not closed under addition.
O The set is not a vector space because the commutative property of addition is not satisfied.
O The set is not a vector space because the associative property of addition is not satisfied.
O The set is not a vector space because a scalar identity does not exist.
Need Help?
Read It
Watch It
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning