dx dt dy = −y − x(x² + y²)¹/2, = x − y(x² + y²)¹/2 dt (a) Show that the system is almost linear in the neighborhood of the origin. (b) Determine the type and stability of (0,0) for the corresponding linear system. (c) Now consider the original nonlinear equation. Let r² = x² + y², show that r → 0 as t → ∞o.
dx dt dy = −y − x(x² + y²)¹/2, = x − y(x² + y²)¹/2 dt (a) Show that the system is almost linear in the neighborhood of the origin. (b) Determine the type and stability of (0,0) for the corresponding linear system. (c) Now consider the original nonlinear equation. Let r² = x² + y², show that r → 0 as t → ∞o.
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN:9781305658004
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Ron Larson
Chapter1: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section1.1: Introduction To Systems Of Linear Equations
Problem 90E: Consider the system of linear equations in x and y. ax+by=ecx+dy=f Under what conditions will the...
Related questions
Question
Please show all work!!
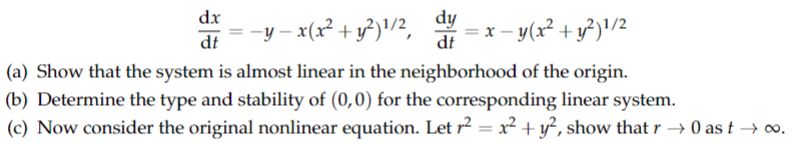
Transcribed Image Text:dx
dt
dy
= −y − x(x² + y²)¹/2, = x − y(x² + y²)¹/2
dt
(a) Show that the system is almost linear in the neighborhood of the origin.
(b) Determine the type and stability of (0,0) for the corresponding linear system.
(c) Now consider the original nonlinear equation. Let r² = x² + y², show that r → 0 as t → ∞o.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning