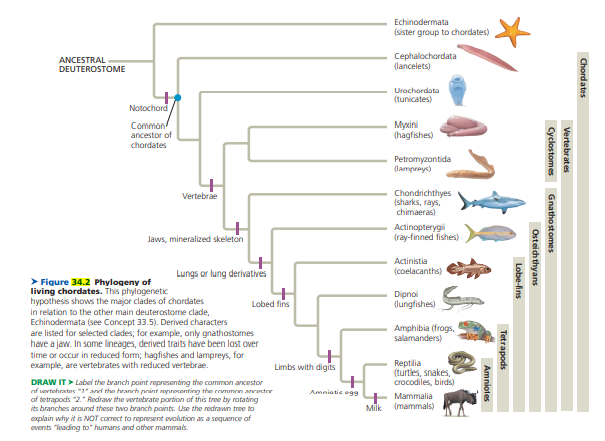
Echinodermata (sister group to chordates) ANCESTRAL DEUTEROSTOME Cephalochordata (lancelets) Urochordata (tunicates) Notochord Common Myxini (hagfishes) ancestor of chordates Petromyzontida (lampreys) Chondrichthyes (sharks, rays, chimaeras) Vertebrae Actinopterygi (ray-finned fishes) Jaws, mineralized skeleton Actinistia Lungs or lung derivathves (coelacanths) > Figure 34.2 Phylogeny of living chordates. This phylogenetic hypothesis shows the major clades of chordates in relation to the other main deuterostome clade, Dipnoi Jungfishes) Lobed fins Echinodermata (see Concept 33.5). Derived characters are listed for selected clades; for example, only gnathostomes have a jaw. In some lineages, derived traits have been lost over time or occur in reduced form; hagfishes and lampreys, for example, are vertebrates with reduced vertebrae. Amphibia (frogs, salamanders) Reptilia (turtles, snakes, crocodiles, birds) Limbs with digits DRAW IT > Label the branch point representing the common ancestor af vortohratos "1" and the hranch pnint mprosenting the commen ancoctor af tetrapods "2." Roedraw the vertebrate portion of this tree by rotating its branches around these two branch points. Use the redrawn tree to explain why it is NOT correct to represent evolution as a seqence of events "leading to" humans and other mammmals. Amniatie e99 Mammalia Milk (mammals) Chordates Vertebrates Cyclostomes Gnathostomes Osteichthyans Lobe-fins Tetrapods Amniotes
Evolution
The history and science of origin and evolution comprise two events, the beginning of life and expansion of life. Our earth originated about 4.5 billion years ago. The term evolution is derived from two Latin words and means the act of unfolding or unrolling. English philosopher Herbert Spencer first used it. Evolution is defined as the change in heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. These traits are the manifestations of genes that are passed down from parent to offspring during reproduction.
Cladistics
Cladistics is a technique in the classification of organisms, where they are grouped into different clades. The proof for the relationships that are hypothesized is based on the shared derived characteristics known as synapomorphies. These characteristics do not exist in many of the distant ancestors and groups. The common ancestor along with its descendants is considered to be a part of the clade. The rate of closeness is directly proportional to the cladistic grouping and is useful in analyzing the evolutionary mechanism.
Outgroups
Outgroups are significant in studying cladistics or phylogenetics (that describe the evolutionary relationship between different organisms). Further, it is also important to understand the differences and similarities between different organisms.
Taxonomy
It is the branch of biology that works with the identification of organisms at first, then naming, and classification of them into phenetic or phylogenetic groups (a classification system). In other words, it is the scientific study of biological diversity and a part of systematic biology.
Phylogenetics
Phylogenetics is the scientific study of how various groups of organisms are related at the evolutionary level. It finds the relationship between various organisms based on their evolutionary similarities and differences. It is a part of the taxonomy. Although the taxonomic study is not only concerned about phylogeny but taxonomic studies are also concerned about the classification and nomenclature of the different individuals from different taxon.
Based on the phylogenetic tree diagram in Figure 34.2, predict which vertebrate groups should have lungs or lung derivatives. Explain.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps






