et l2 be the same region as in part (2). Write this region in the form 12 = {(z, y) : e
et l2 be the same region as in part (2). Write this region in the form 12 = {(z, y) : e
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter9: Systems Of Equations And Inequalities
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 21RE
Related questions
Question
100%
Plz solve correctly part 3 only plz correctly and take a thumb up plz
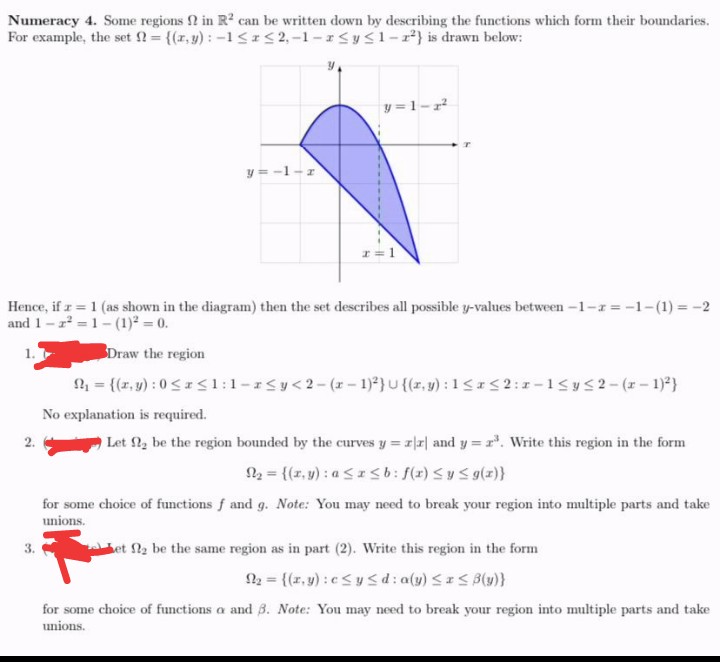
Transcribed Image Text:Numeracy 4. Some regions 2 in R2 can be written down by describing the functions which form their boundaries.
For example, the set = {(r,y) : -1<I<2,-1-rSy s1-r²} is drawn below:
y = 1-r
y = -1-r
I=1
Hence, if z = 1 (as shown in the diagram) then the set describes all possible y-values between -1-r = -1-(1) = -2
and 1- z = 1- (1)² = 0.
1.
Draw the region
= {(r, y) : 0 <*<1:1-rSy<2-(*- 1)²} u {(z, y) : 1<*< 2:1-1<y52-(*-1)*}
No explanation is required.
2.
Let 2, be the region bounded by the curves y = r|r| and y = r. Write this region in the form
N2 = {(r, y) : a <Isb: f(r) <y Sg(z)}
for some choice of functions f and g. Note: You may need to break your region into multiple parts and take
unions.
3.
et 2 be the same region as in part (2). Write this region in the form
N = {(r, y) : c<y <d: a(y) << B(u)}
for some choice of functions a and 8. Note: You may need to break your region into multiple parts and take
unions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage