Evaluate Solution √25 Let x = 5 sin(8), where 플 플 √25 - x² = √√√25 - 25 sin²(0) = √√25 cos² (8) = 5|cos(0)| = 5 cos(0). (Note that cos(0) ≥ 0 because sos ..) Thus, the inverse substitution rule gives √25-x² dx. dx = sos 5 cos(0) 25 sin²(0) cos² (8) Then dx = = [cot²(8) de = √ (csc²(8) − 1) de de + C. de de and
Evaluate Solution √25 Let x = 5 sin(8), where 플 플 √25 - x² = √√√25 - 25 sin²(0) = √√25 cos² (8) = 5|cos(0)| = 5 cos(0). (Note that cos(0) ≥ 0 because sos ..) Thus, the inverse substitution rule gives √25-x² dx. dx = sos 5 cos(0) 25 sin²(0) cos² (8) Then dx = = [cot²(8) de = √ (csc²(8) − 1) de de + C. de de and
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter6: Vector Spaces
Section6.6: The Matrix Of A Linear Transformation
Problem 30EQ
Related questions
Question
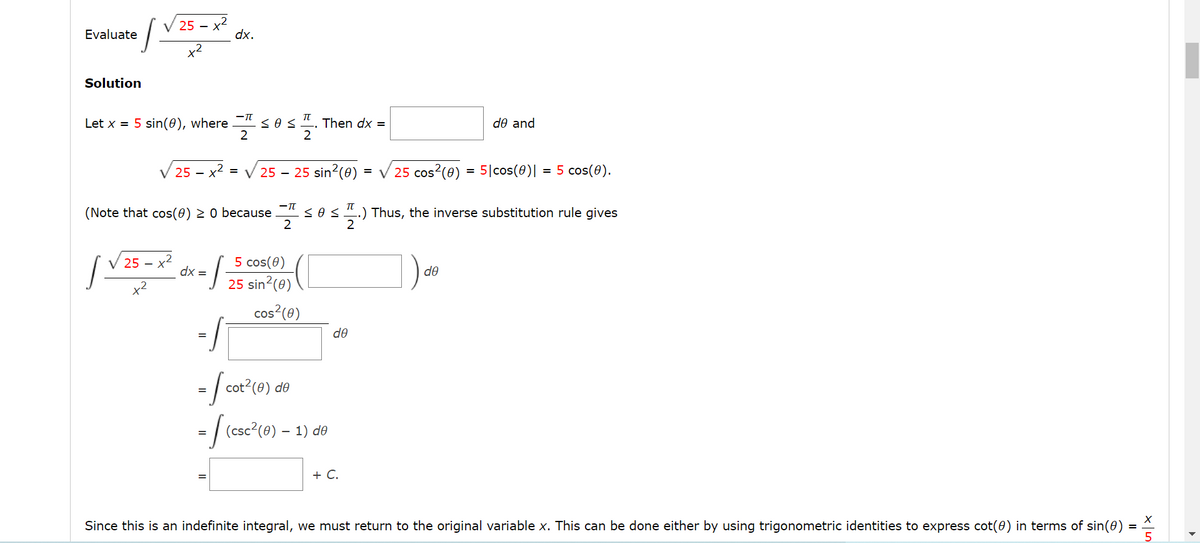
Transcribed Image Text:Evaluate
[v
Solution
J
25 - x²
+²
TT
Let x = 5 sin(0), where < # <
2
√25-x²
25x²
+²
(Note that cos(0) ≥ 0 because
dx.
dx =
-TT
2
=
= 1₂
=
=
✓ 25 - 25 sin²(0) = √ 25 cos² (0) = 5|cos(0)| = 5 cos(0).
5 cos(0)
Then dx =
≤0 ≤.) Thus, the inverse substitution rule gives
2
2
25 sin²(0)
cos²(0)
cot² (0) de
= [(csc²(0) — 1) de
de
de and
+ C.
de
Since this is an indefinite integral, we must return to the original variable x. This can be done either by using trigonometric identities to express cot(0) in terms of sin(0)
=
U|X
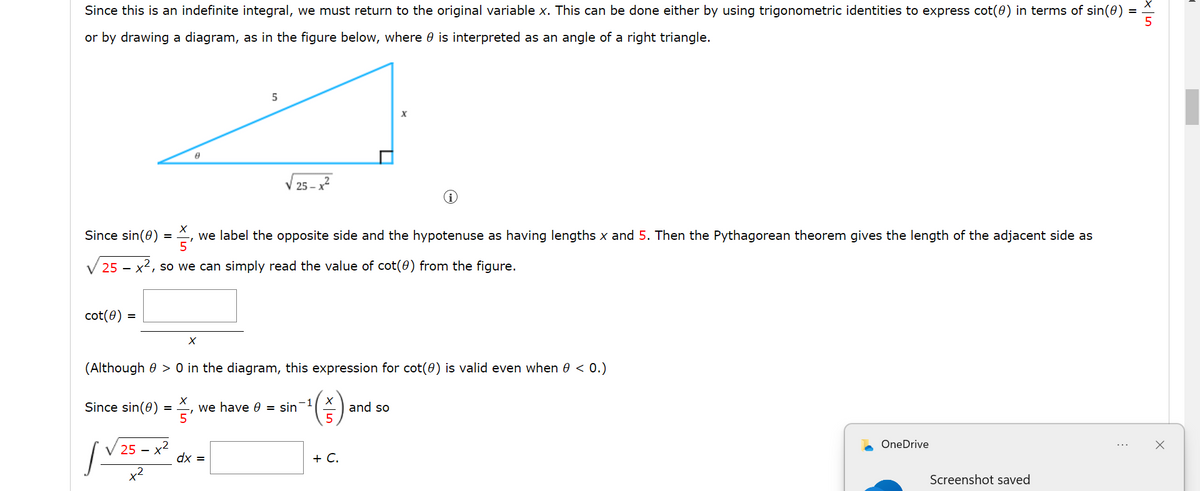
Transcribed Image Text:Since this is an indefinite integral, we must return to the original variable x. This can be done either by using trigonometric identities to express cot(0) in terms of sin(0)
or by drawing a diagram, as in the figure below, where is interpreted as an angle of a right triangle.
cot (8)
X
Since sin(0) = ¹
we label the opposite side and the hypotenuse as having lengths x and 5. Then the Pythagorean theorem gives the length of the adjacent side as
25 x2, so we can simply read the value of cot(0) from the figure.
A
Since sin(8) = ₁
25-
+²
X
+2
(Although > 0 in the diagram, this expression for cot(0) is valid even when 0 <0.)
5
25
dx =
we have 0 = sin¯¹
X
+ C.
and so
OneDrive
Screenshot saved
X5
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage