Every vector in a space is orthogonal to the zero vector of that space. Every orthonormal basis is the standard basis.
Every vector in a space is orthogonal to the zero vector of that space. Every orthonormal basis is the standard basis.
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter5: Orthogonality
Section5.1: Orthogonality In Rn
Problem 34EQ
Related questions
Question
![Which of the following is/are true?
DAn orthogonal basis is always an orthonormal basis.
]Every vector in a space is orthogonal to the zero vector of that space.
Every orthonormal basis is the standard basis.
]Every vector of an orthonormal basis is a unit vector.
Submit
You have used 0 of 1 attempt
Save](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F2fbe9672-4cbd-41c7-af75-505a865b4d4d%2F9b369b34-b9d4-4f45-b5ce-2907cf426188%2Fu7bem9g_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following is/are true?
DAn orthogonal basis is always an orthonormal basis.
]Every vector in a space is orthogonal to the zero vector of that space.
Every orthonormal basis is the standard basis.
]Every vector of an orthonormal basis is a unit vector.
Submit
You have used 0 of 1 attempt
Save
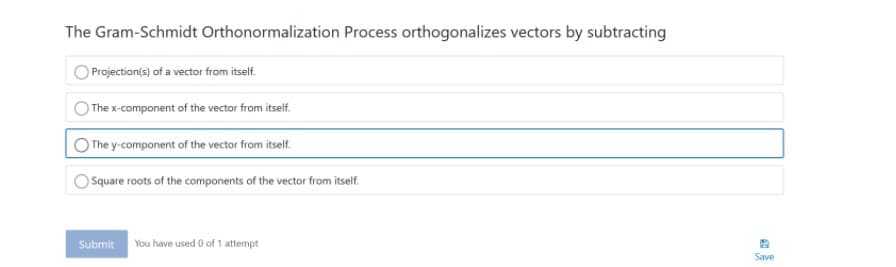
Transcribed Image Text:The Gram-Schmidt Orthonormalization Process orthogonalizes vectors by subtracting
Projection(s) of a vector from itself.
The x-component of the vector from itself.
The y-component of the vector from itself.
Square roots of the components of the vector from itself.
Submit
You have used 0 of 1 attempt
Save
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)
Algebra
ISBN:
9781305658004
Author:
Ron Larson
Publisher:
Cengage Learning