EXAMPLE 2 Differentiate (a) y = sin(x³) and (b) sin3(x). SOLUTION (a) If y = sin(x³), then the outer function is the sine function and the inner function is the power function, so the Chain Rule gives dy dx d sin (x³) (x³) Cos = dx evaluated at inner function derivative evaluated derivative of inner function outer of outer function function at inner function (b) Note that sin3(x) = (sin(x))' Here the outer function is the power function and the inner function is the sine function. So dy dx d (sin(x)) 3 3· (sin(x))2 dx inner function derivative of outer function evaluated derivative of inner function at inner function
EXAMPLE 2 Differentiate (a) y = sin(x³) and (b) sin3(x). SOLUTION (a) If y = sin(x³), then the outer function is the sine function and the inner function is the power function, so the Chain Rule gives dy dx d sin (x³) (x³) Cos = dx evaluated at inner function derivative evaluated derivative of inner function outer of outer function function at inner function (b) Note that sin3(x) = (sin(x))' Here the outer function is the power function and the inner function is the sine function. So dy dx d (sin(x)) 3 3· (sin(x))2 dx inner function derivative of outer function evaluated derivative of inner function at inner function
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:James Stewart
Chapter1: Functions And Models
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RCC: (a) What is a function? What are its domain and range? (b) What is the graph of a function? (c) How...
Related questions
Question
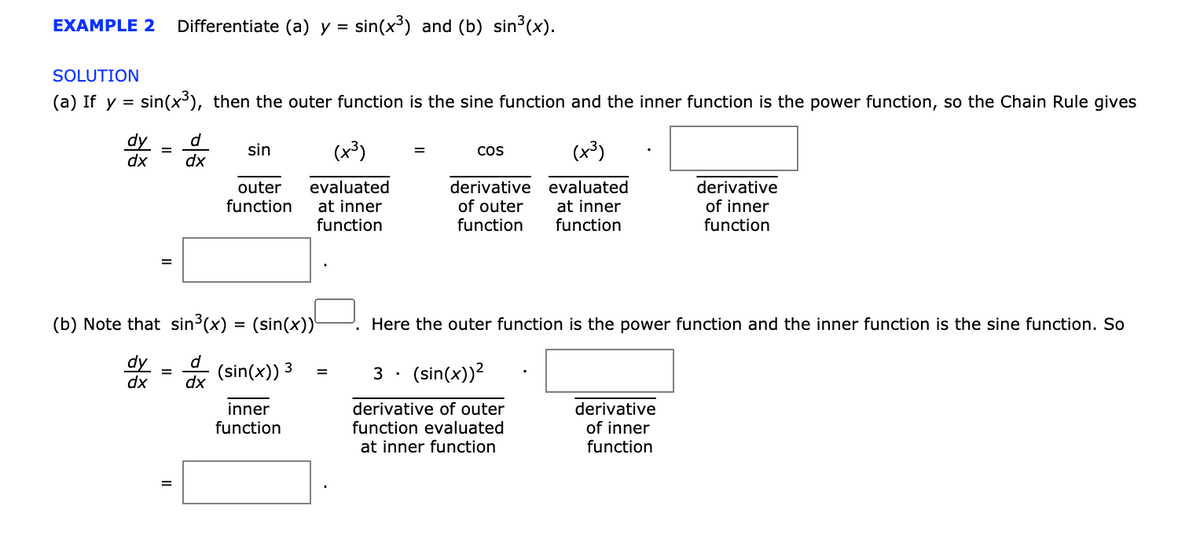
Transcribed Image Text:EXAMPLE 2
Differentiate (a) y = sin(x³) and (b) sin (x).
%3D
SOLUTION
(a) If y = sin(x), then the outer function is the sine function and the inner function is the power function, so the Chain Rule gives
%3D
dy
dx
d
sin
(x³)
(x³)
CoS
=
dx
evaluated
at inner
function
derivative evaluated
of outer
function
derivative
of inner
outer
function
at inner
function
function
(b) Note that sin3(x) = (sin(x))'
Here the outer function is the power function and the inner function is the sine function. So
d
(sin(x)) 3
dx
(sin(x))2
3 ·
%3D
dx
inner
function
derivative of outer
function evaluated
at inner function
derivative
of inner
function
II
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781285741550
Author:
James Stewart
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134438986
Author:
Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:
9780134763644
Author:
William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:
PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:
9781319050740
Author:
Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:
9781337552516
Author:
Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:
Cengage Learning