EXAMPLE 4 The region R enclosed by the curves y = 3x and y = x2 is rotated about the x-axis. Find the volume of the resulting solid. SOLUTION The curves y = 3x and y = x intersect at the points 0, and The region between them, the solid of rotation, and a cross section perpendicular to the x-axis are shown in the figures. A cross-section in the plane P, has the shape of a washer (an annular ring) with inner radius and an outer radius , so we find the y- 3x cross-sectional area by subtracting the area of the inner circle from the area of the outer circle: A(x) = 9Tx? - T(x?)2 = y =x Therefore, we have V = A(x) dx = - -[ A(X)
EXAMPLE 4 The region R enclosed by the curves y = 3x and y = x2 is rotated about the x-axis. Find the volume of the resulting solid. SOLUTION The curves y = 3x and y = x intersect at the points 0, and The region between them, the solid of rotation, and a cross section perpendicular to the x-axis are shown in the figures. A cross-section in the plane P, has the shape of a washer (an annular ring) with inner radius and an outer radius , so we find the y- 3x cross-sectional area by subtracting the area of the inner circle from the area of the outer circle: A(x) = 9Tx? - T(x?)2 = y =x Therefore, we have V = A(x) dx = - -[ A(X)
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter4: Polynomial And Rational Functions
Section4.2: Properties Of Division
Problem 53E
Related questions
Question
100%
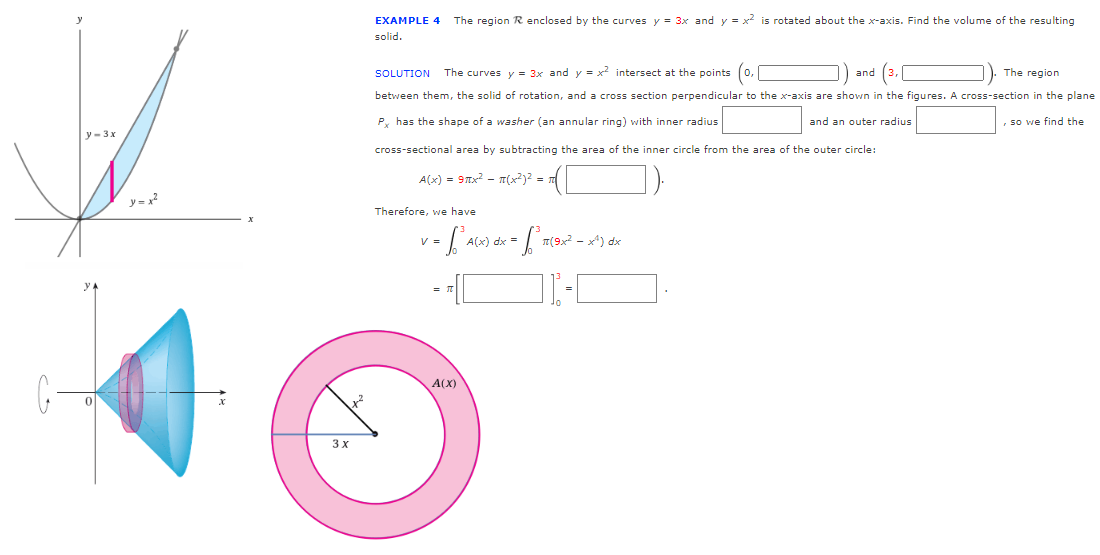
Transcribed Image Text:EXAMPLE 4
The region R enclosed by the curves y = 3x and y = x? is rotated about the x-axis. Find the volume of the resulting
solid.
SOLUTION
The curves y = 3x and y = x intersect at the points
and
The region
between them, the solid of rotation, and a cross section perpendicular to the x-axis are shown in the figures. A cross-section in the plane
P, has the shape of a washer (an annular ring) with inner radius
and an outer radius
so we find the
y- 3x
cross-sectional area by subtracting the area of the inner circle from the area of the outer circle:
A(x) = 9Tx? - T(x?)2 =
Therefore, we have
V =
A(x) dx =
T(9x2 - x*) dx
A(X)
3 x
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition…
Algebra
ISBN:
9780547587776
Author:
HOLT MCDOUGAL
Publisher:
HOLT MCDOUGAL

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:
9781337614085
Author:
Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:
Cengage,