Expand the function f(x) in a Taylor series about ak. Retain linear only terms in a- ak and set r to rk+1. Obtain Newton's method for solving the problem f(x) = 0 by requiring f(rk+1) = 0. %3D
Expand the function f(x) in a Taylor series about ak. Retain linear only terms in a- ak and set r to rk+1. Obtain Newton's method for solving the problem f(x) = 0 by requiring f(rk+1) = 0. %3D
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:David Poole
Chapter2: Systems Of Linear Equations
Section2.5: Iterative Methods For Solving Linear Systems
Problem 20EQ
Related questions
Question
Please help with this step by showing every step. Thanks!
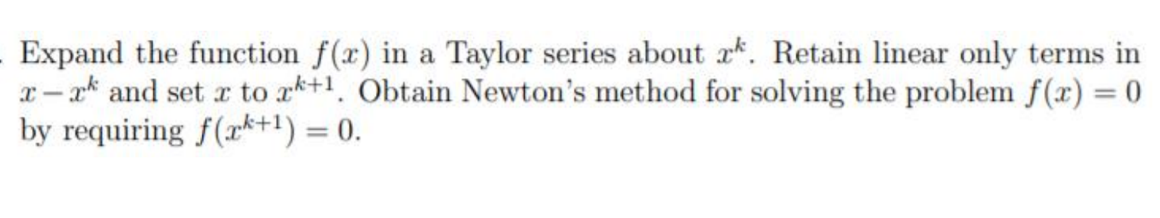
Transcribed Image Text:Expand the function f(x) in a Taylor series about ak. Retain linear only terms in
x – ak and set r to ak+1. Obtain Newton's method for solving the problem f(x) = 0
by requiring f(r*+1) = 0.
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 1 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:
9781285463247
Author:
David Poole
Publisher:
Cengage Learning