Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
13th Edition
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Swokowski
Chapter5: Inverse, Exponential, And Logarithmic Functions
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 18T
Related questions
Question
100%
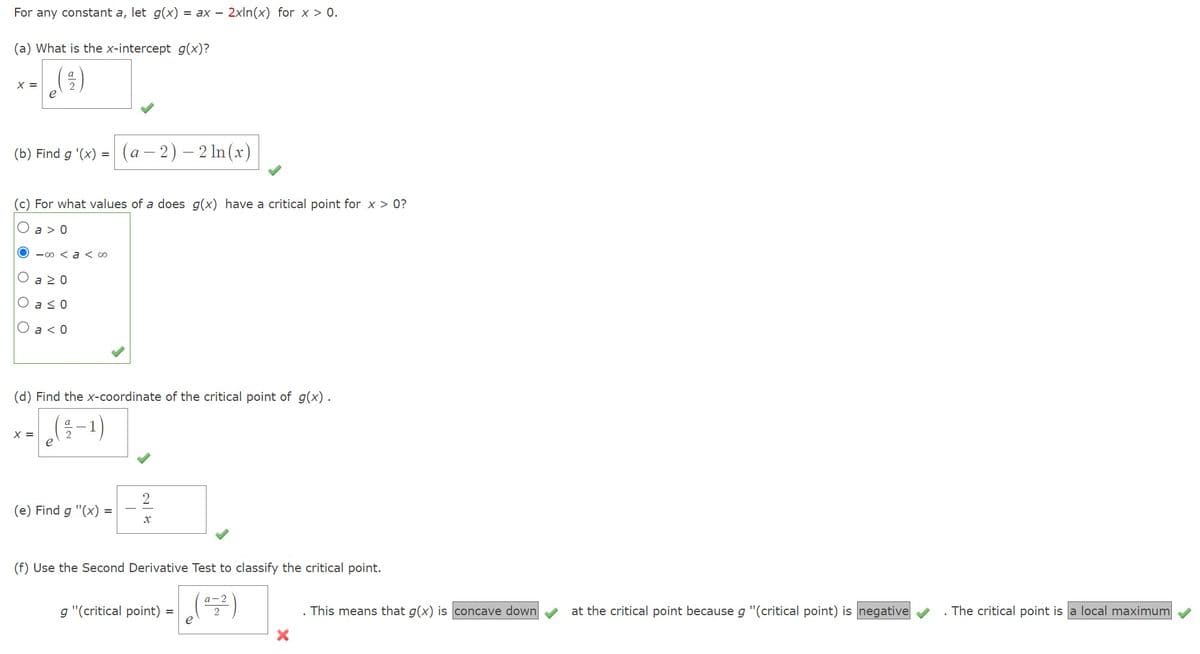
Transcribed Image Text:For any constant a, let g(x) = ax - 2xln(x) for x > 0.
(a) What is the x-intercept g(x)?
X =
(b) Find g '(x) = (a − 2) - 2 ln(x)
(c) For what values of a does g(x) have a critical point for x > 0?
O a > 0
O
O a ≥ 0
O a ≤0
O
-∞ < a < 00
X =
a < 0
(d) Find the x-coordinate of the critical point of g(x).
(²-1)
e
(e) Find g "(x)
=
2
X
(f) Use the Second Derivative Test to classify the critical point.
0-2²)
g "(critical point)
=
e
. This means that g(x) is concave down
at the critical point because g "(critical point) is negative
The critical point is a local maximum
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 3 images

Recommended textbooks for you

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:
9781133382119
Author:
Swokowski
Publisher:
Cengage